Vestibular schwannoma is the most frequent cerebellopontine angle tumour. The aim of our study is to reflect our experience in the surgical treatment of this tumour.
Material and methodsRetrospective study of 420 vestibular schwannomas operated in our hospital between 1994 and 2014. We include tumour size, preoperative hearing, surgical approaches, definitive facial and hearing functional results, and complications due to surgery.
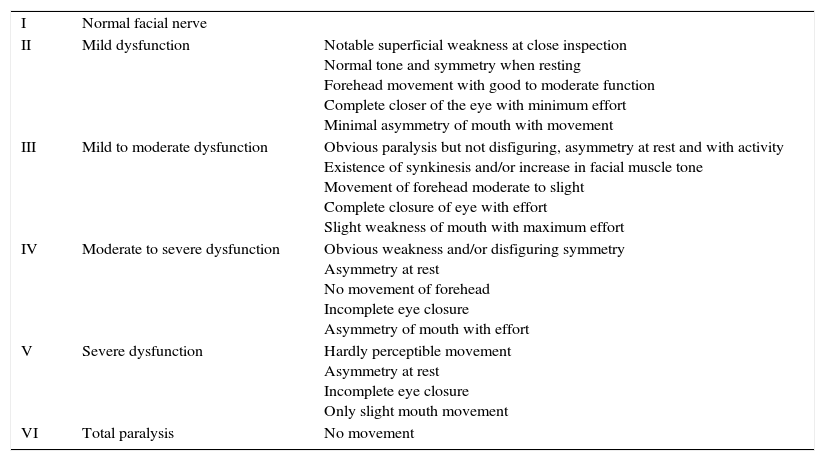
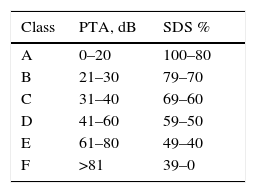
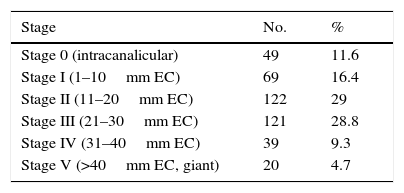
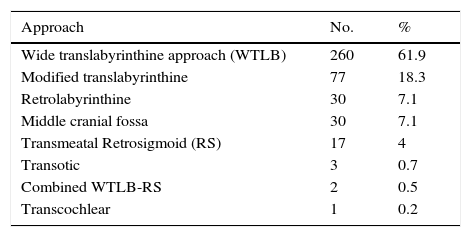
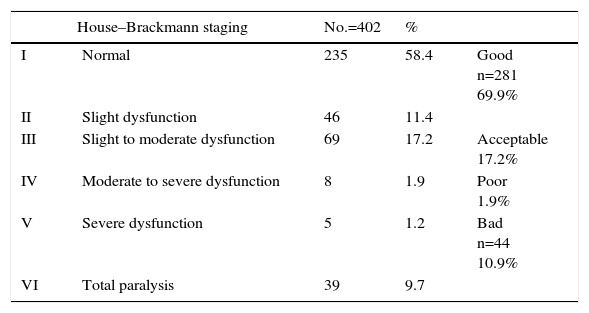
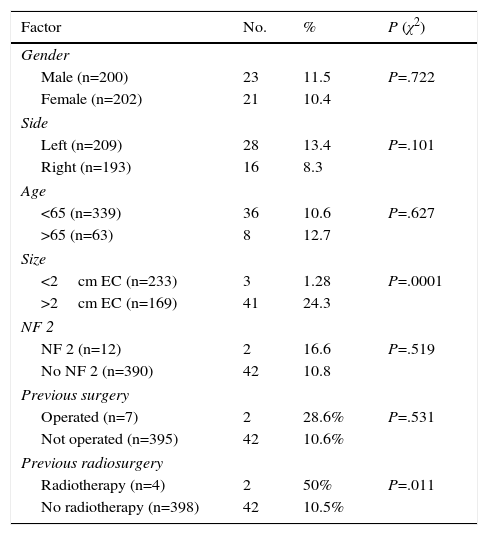
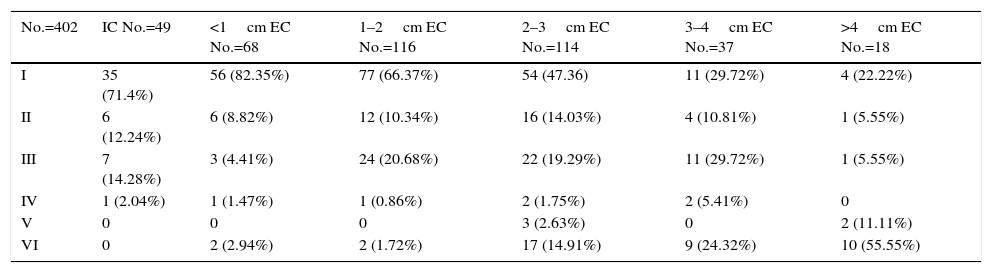
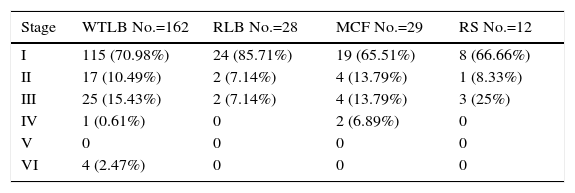
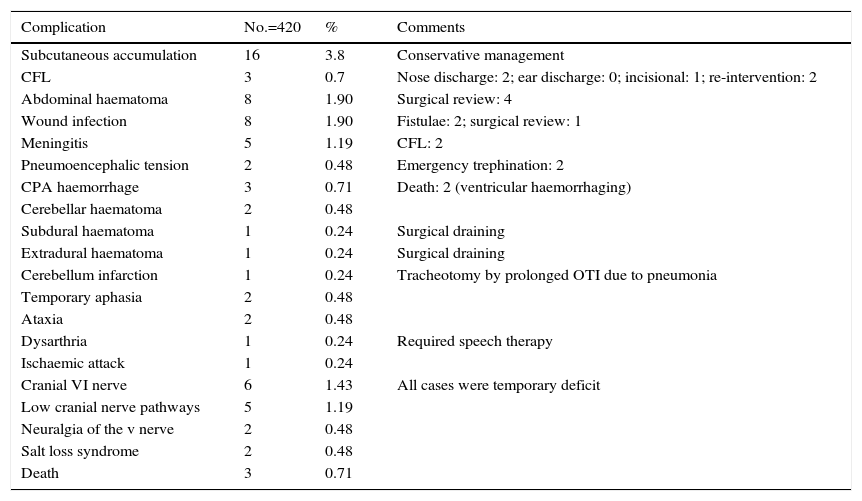
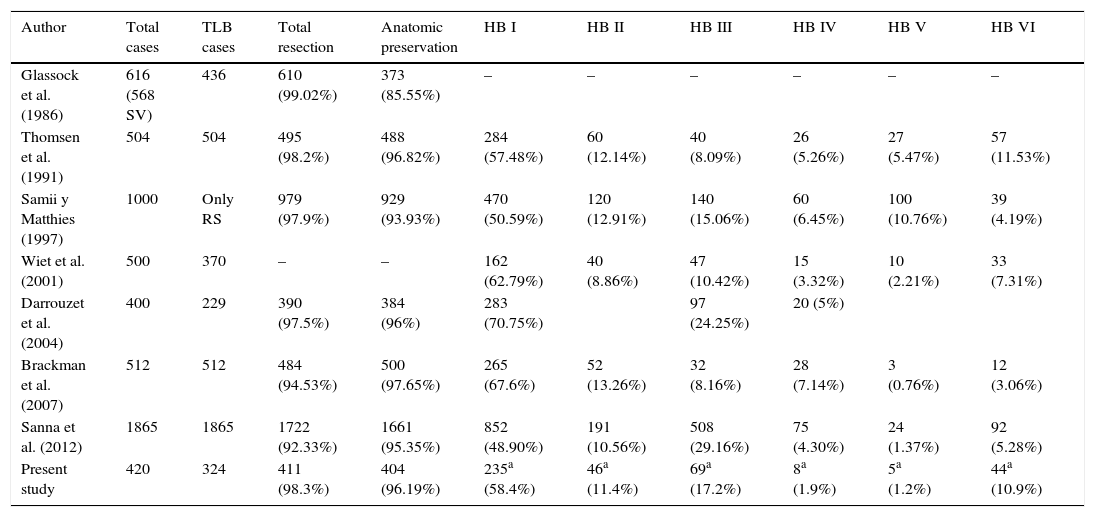
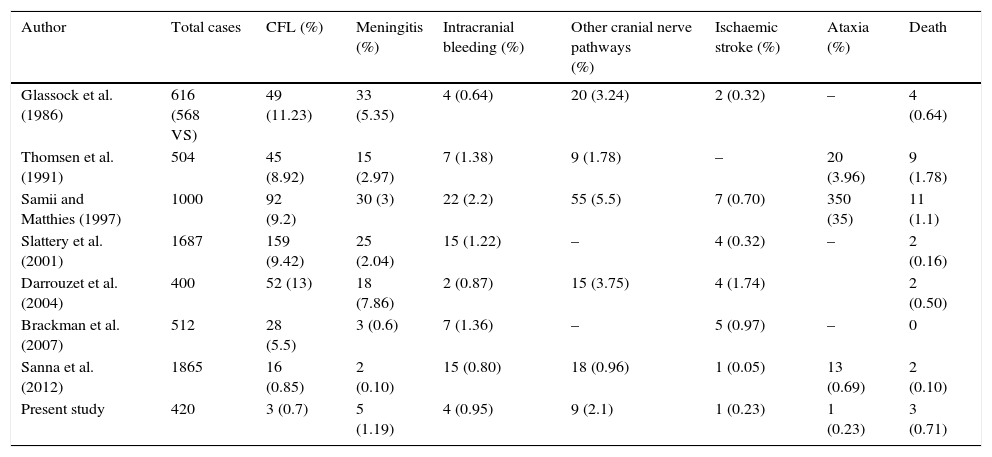
ResultsA total of 417 patients with 420 tumours were analysed, 209 female (50.1%) and 208 male (49.9%). Mean age at diagnosis was 49.8±13.2 years. The majority of the tumours were resected through a translabyrinthine approach (80.2%). Total tumour removal was achieved in 411 tumours (98.3%), and anatomic preservation of facial nerve in 404 (96.2%). Definitive facial nerve outcome was House–Brackmann grade I and II in 69.9%, and was significantly better in tumours under 20mm. Surgical complications included cerebrospinal fluid leakage in 3 patients (0.7%) and retroauricular subcutaneous collection in 16 (3.8%), 5 cases of meningitis (1.2%), 4 patients with intracraneal bleeding (0.9%), and death in 3 patients (0.7%).
ConclusionsSurgery is the treatment of choice for vestibular schwannoma in the majority of patients. In our experience, the complication rate is very low and tumour size is the main factor influencing postoperative facial nerve function.
El schwannoma vestibular es el tumour más frecuente en el ángulo ponto-cerebeloso. El objetivo de nuestro estudio es reflejar nuestra experiencia en el tratamiento quirúrgico de este tumour.
Material y métodosEstudio retrospectivo de 420 schwannomas vestibulares intervenidos en nuestro centro entre 1994-2014. Se incluyen el tamaño tumoral, la audición preoperatoria, los abordajes quirúrgicos utilizados, el resultado definitivo de la función facial y auditiva y las complicaciones derivadas de la cirugía.
ResultadosUn total de 417 pacientes con 420 tumores fueron analizados, siendo 209 mujeres (50,1%) y 208 varones (49,9%). La edad media fue de 49,8±13,2 años. La mayoría de los tumores se resecaron mediante abordaje translaberíntico (80,2%). La resección tumoral completa tuvo lugar en 411 tumores (98,3%), y la conservación de la integridad anatómica del nervio facial en 404 (96,2%). El resultado definitivo del facial fue grado i y ii de House-Brackmann en el 69,9%, siendo significativamente mejor en los tumores de menos de 20mm. Entre las complicaciones se incluyen 3 casos de fístula (0,7%) y 16 acúmulos retroauriculares de líquido cefalorraquídeo (3,8%), 5 de meningitis (1,2%), 4 sangrados intracraneales (0,9%) y exitus en 3 pacientes (0,7%).
ConclusionesEl tratamiento quirúrgico del schwannoma vestibular sigue siendo el de elección en la mayoría de los casos. En nuestra experiencia, la tasa de complicaciones es baja, siendo el tamaño tumoral el principal factor influyente en la función facial postoperatoria.