The aim of our study has been to investigate the perception of aspects related to nasal perforation among experts in Rhinology and ENT surgeons. Our aim was reporting the situations in different Countries to improve the knowledge of colleagues interested in this topic.
MethodsA panel of experts prepared a 20-question questionnaire regarding nasal perforations and their surgical repair, that were emailed to all the members of SIR (Società Italiana di Rnologia – Italian Society of Rhinology).
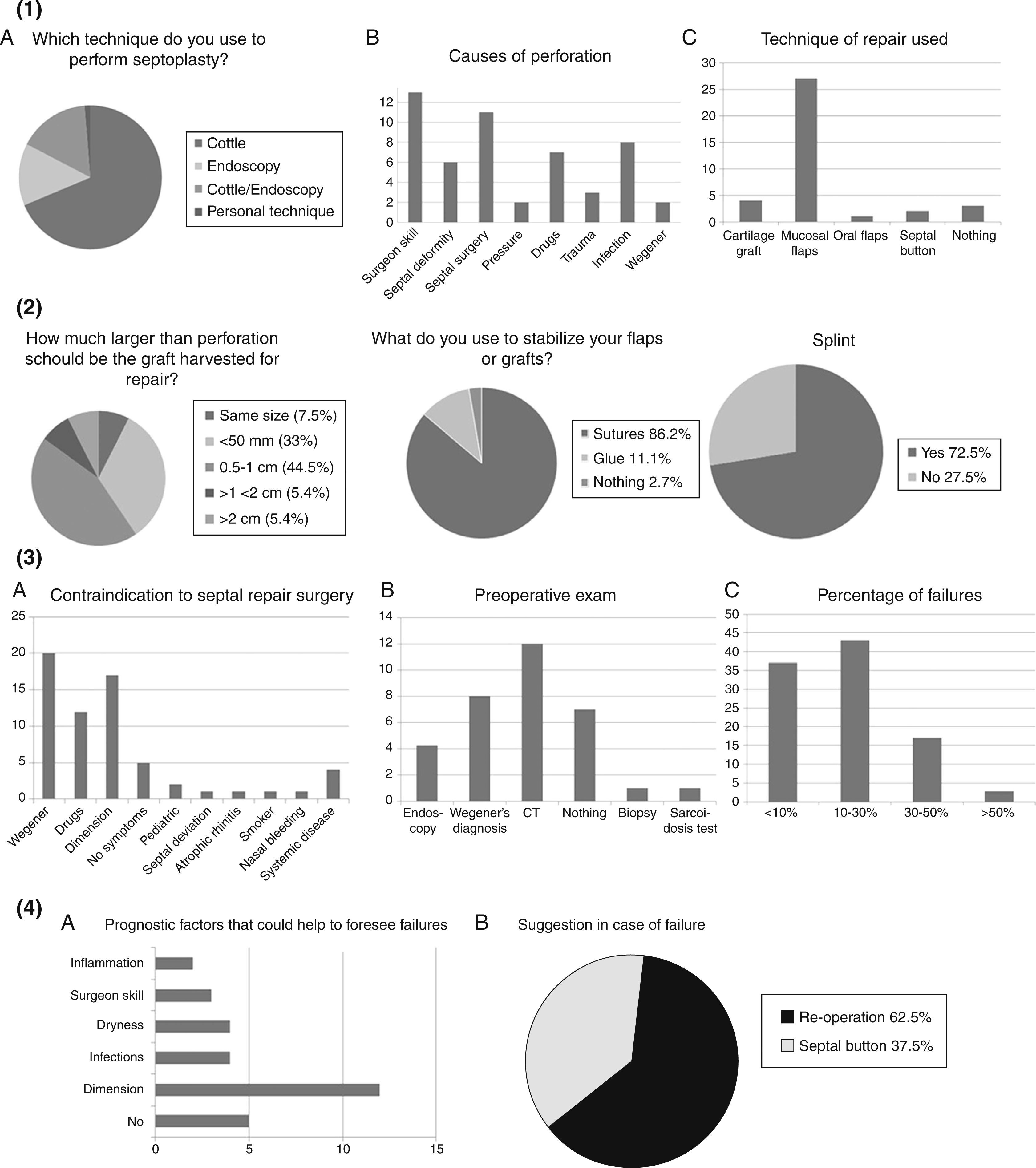
ResultsData obtained from their answers showed that Cottle technique (64%) is the most common technique to perform septoplasty worldwide. 37% of the sample reported an occurrence of nasal septal perforation in less than 1% of patients and 75% attributed this occurrence to the skill of the surgeon, to infections, to drug use and to septal deformity. Trauma, pressure and Wegener's granulomatosis were also mentioned. The most common closure technique is the mucosal flap (75%), followed by the cartilage grafts (11%). Much less common were oral flaps, septal buttons and others. The majority agreed not to suggest septal perforation surgery in minimal (less than 3–4mm) perforations (73.5%), or limiting it to symptomatic patients (43.5%). The contraindications to repair surgery were reported to be: Wegener's granulomatosis, drug abuse, non-symptomatic perforation, its dimension and age of the patient. Septal deviation, atrophic rhinitis, smoke epistaxis and systemic diseases were also claimed. Failure in repair surgery has been observed to occur in less than 30% of cases.
Discussion and conclusionsGiven the great difficulty to make random studies about controversial topics and obtain statistically significant data related to that, expert opinion shall be of great value (expert opinion, level of evidence 5)
El objetivo de nuestro estudio ha sido investigar la percepción de aspectos relacionados con la perforación nasal entre los expertos en cirugía nasal e informar sobre la situación en diferentes países para mejorar el conocimiento de los colegas interesados en este tema.
MétodosUn panel de expertos preparó un cuestionario de 20 preguntas sobre las perforaciones y su reparación quirúrgica, que fue enviado por correo electrónico a todos los miembros de la Sociedad Italiana de Rinología (SIR).
ResultadosLos datos obtenidos de sus respuestas mostraron que la técnica de Cottle (64%) es la técnica más común para realizar la septoplastia, el 37% de la muestra informó de una ocurrencia de perforación del tabique nasal en menos del 1% de los pacientes y el 75% atribuye este hecho a la habilidad del cirujano, a las infecciones, al consumo de drogas y a las deformidades del tabique. Los traumatismos y la granulomatosis de Wegener también se mencionaron. La técnica de cierre más común es el colgajo de la mucosa (75%), seguido por los injertos de cartílago (11%). La mayoría estuvo de acuerdo en no sugerir la cirugía del tabique en perforaciones de menos de 3-4mm o limitándola a los pacientes sintomáticos (43,5%). Las contraindicaciones de cirugía de reparación son: la granulomatosis de Wegener, la drogadicción, la perforación no sintomática y la edad del paciente.
Discusión y conclusionesEs muy difícil hacer estudios sobre este tema tan controvertido, la opinión de expertos será de gran valor (nivel de evidencia 5).