Submandibular gland excision is the treatment of choice in chronic pathology resistant to medical treatments or in oncological cases. The aim of this study was to analyse its current postoperative complications.
Materials and methodsRetrospective study on submandibular gland excisions performed at our University Hospital between 2004 and 2010.
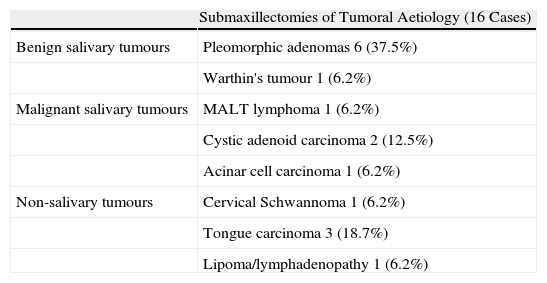
ResultsA total of 29 submandibular gland excisions were performed: 44.8% (13) for chronic sialadenitis, 37.9% (11) for salivary gland neoplasm and 17.2% (5) for adjacent tumours. Median length of hospital stay was 2 days. Complications were more common after gland excision due to inflammatory causes. There were only 2 cases of paralysis of the marginal facial nerve branch (6.8%); 1 was due to neoplastic pathology and 1 from inflammatory pathology.
ConclusionDespite marginal facial nerve paresis being one of the most relevant issues after submandibular gland excision, this type of surgery is a safe technique in our experience.
La submaxilectomía es el tratamiento de elección en afección crónica resistente a tratamiento médico o en sospechas tumorales. El objetivo de este estudio es evaluar la morbilidad actual de la submaxilectomía.
Material y métodoEstudio retrospectivo sobre las submaxilectomías realizadas en un hospital universitario entre 2004 y 2010.
ResultadosSe realizaron 29 submaxilectomías, 44,8% (13) por sialoadenitis crónica, 37,9% (11) por tumores submaxilares y en 17,2% (5) casos por tumores adyacentes a la glándula. El tiempo medio de ingreso posquirúrgico fue de dos días. Las complicaciones fueron más numerosas en los casos de submaxilectomía por etiología inflamatoria. Se evidenciaron dos casos (6,8%) de paresia marginal leve, una por etiología tumoral y otra por etiología inflamatoria.
ConclusiónA pesar de que la parálisis marginal es una de las complicaciones más relevantes de esta cirugía, en nuestra experiencia la submaxilectomía es una técnica segura.