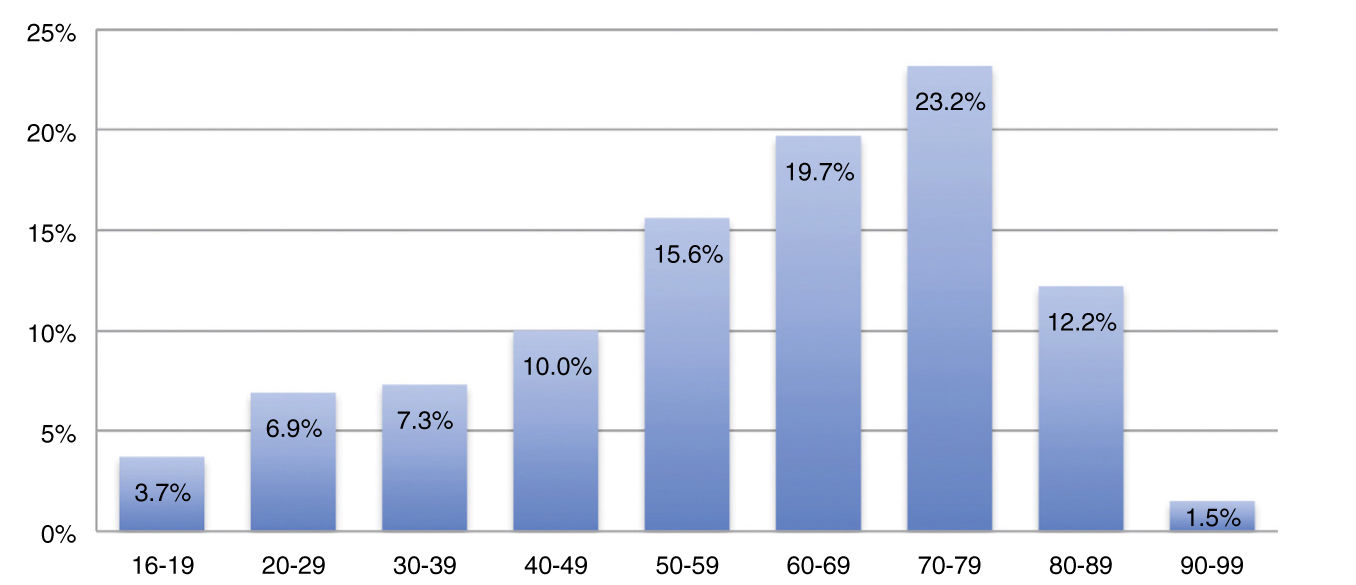
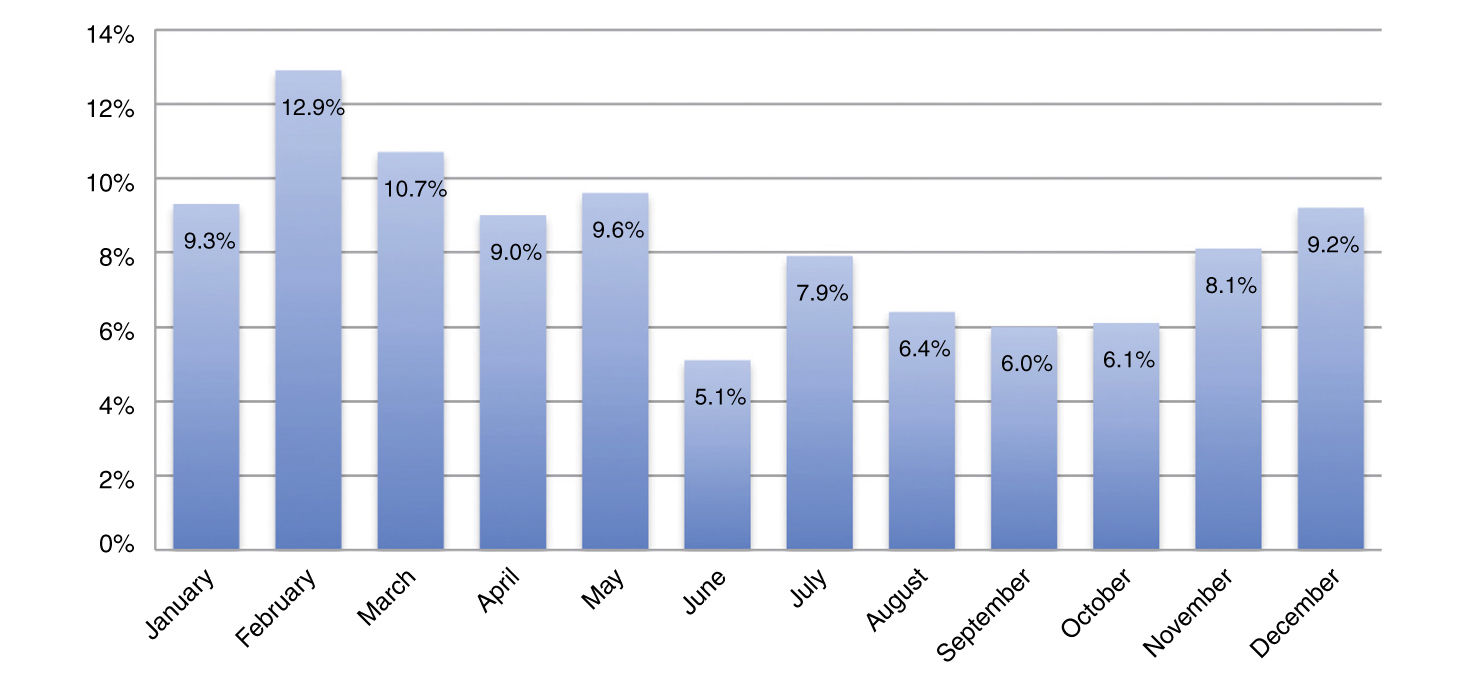
Epistaxis is one of the commonest causes of attendance of Otolaryngology emergency rooms. Given its incidence, potential severity and high recurrence rate, a systematic and careful management is mandatory. This work aims to define prognostic factors of epistaxis recurrence.
Material and methodsRetrospective review of medical records of patients with epistaxis admitted to our emergency department from January 2012 to December 2016. Data of 1005 patients with idiopathic epistaxis were analysed and independent risk factors for recurrence were determined by multiple logistic regression analysis.
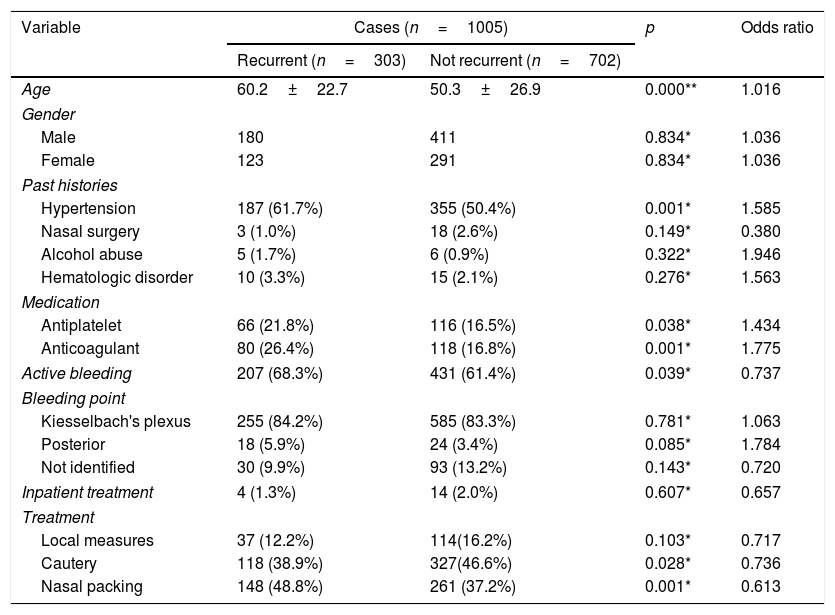
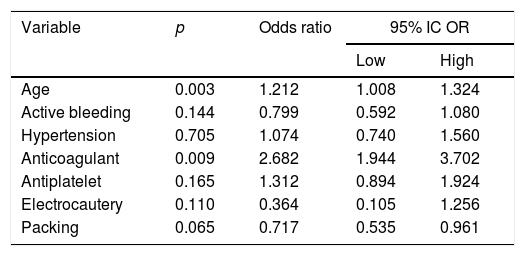
ResultsRecurrence of epistaxis was found in 303 (30.1%) patients. Patients with recurrent epistaxis were older (p<.001) and more commonly had a history of hypertension (p=.001) and antiplatelet (p=.048) and anticoagulant (p=.001) use than those with episodic epistaxis. Age (adjusted OR 1.21, 95%CI 1.08–1.32, p=.003) and anticoagulant use (adjusted OR 2.68, 95%CI 1.94–3.70, p=.009) were predictors of increased risk of recurrent epistaxis. Gender, alcohol abuse, medical history, active bleeding at admission, unidentified bleeding point or treatment modalities were not associated with recurrence.
ConclusionAge and use of anticoagulation drugs were risk factors for recurrence of epistaxis. None of the previously described risk factors for episodic epistaxis were found to increase the risk of recurrence. Knowledge of factors involved in recurrence might provide important information for assessment and management of increased risk patients.
La epistaxis es una causa frecuente de asistencia a los servicios de urgencias de otorrinolaringología. Dada su incidencia, posible gravedad y alta tasa de recurrencia, es obligatorio un manejo sistemático y cuidadoso. Este trabajo tiene como objetivo definir los factores pronósticos de recurrencia de la epistaxis.
Material y métodosRevisión retrospectiva de los registros médicos de pacientes con epistaxis admitidos en nuestro servicio de urgencias desde enero de 2012 a diciembre de 2016. Se analizaron los datos de 1.005 pacientes con epistaxis idiopática, y se determinaron los factores de riesgo independientes de recurrencia mediante análisis de regresión logística múltiple.
ResultadosLa recurrencia de la epistaxis se encontró en 303 (30,1%) pacientes. Los pacientes con epistaxis recurrente eran mayores (p<0,001), tenían con más frecuencia antecedentes de hipertensión (p=0,001) y de tratamiento con antiplaquetarios (p=0,048) y anticoagulantes (p=0,001) que aquellos con epistaxis episódica. La edad (OR ajustada: 1,21; IC 95%: 1,08-1,32; p=0,003) y el uso de anticoagulantes (OR ajustada: 2,68; IC 95%: 1,94-3,7; p=0,009) fueron factores predictivos de mayor riesgo de epistaxis recurrente. El sexo, el abuso del alcohol, el historial médico, el sangrado activo al ingreso, el punto de sangrado no identificado o las modalidades de tratamiento, no se asociaron a la recurrencia.
ConclusiónLa edad y el uso de medicamentos anticoagulantes fueron factores de riesgo para la recurrencia de la epistaxis. Ninguno de los factores de riesgo descritos anteriormente para la epistaxis episódica aumentó el riesgo de recurrencia. El conocimiento de los factores involucrados en la recurrencia podría proporcionar información importante para la evaluación y el manejo de los pacientes de mayor riesgo.