To evaluate the success rate of primary stapedotomy and to investigate the influence of prosthesis diameter on hearing outcome.
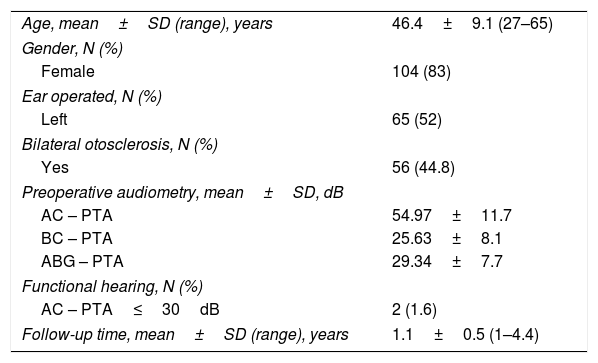
Material and methodsRetrospective medical chart review of 125 cases who underwent primary small fenestra stapedotomy, from January 2001 to December 2018. The study population was divided in two groups based on Teflon prosthesis diameter – .6mm (60%, N=75) and .4mm (40%, N=50). Pre- and postoperative (≥12 months) air-conduction (AC), bone conduction (BC) and air-bone gap (ABG) thresholds were compared.
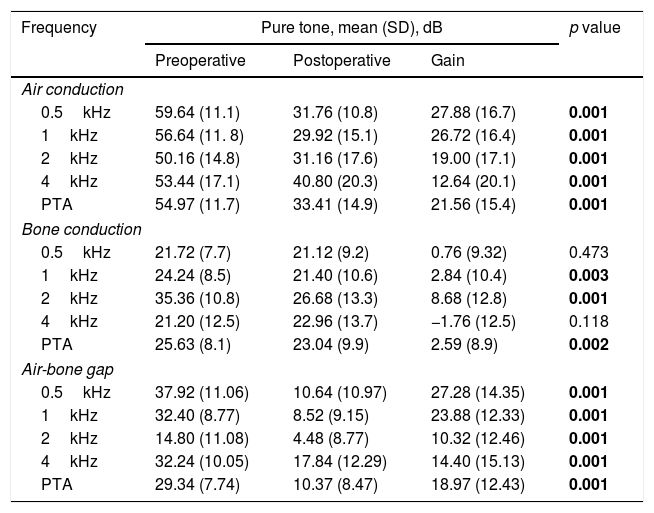
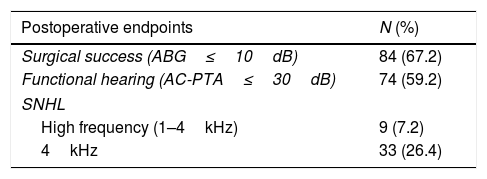
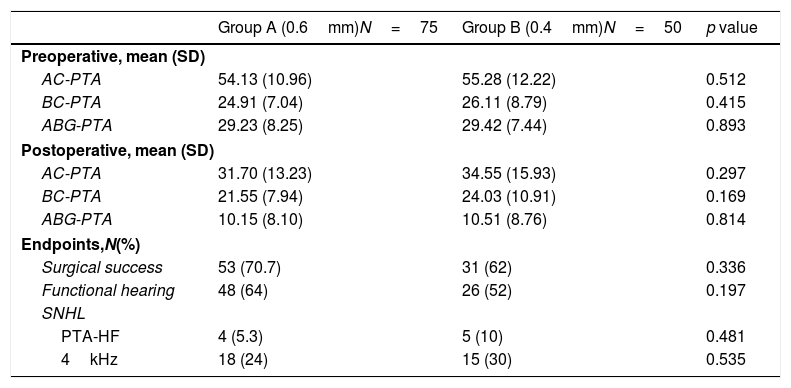
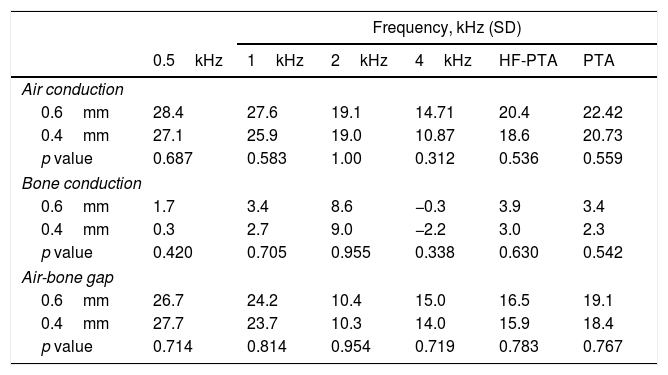
ResultsPostoperative ABG≤10dB and ≤20dB was achieved by 65.7% and 90% of the patients. A functional hearing (PTA-AC≤30dB) was achieved by 59.2% of patients. Sensorineural hearing loss (SNHL, worsening in BC-PTA>10dB) was identified in 7.2% of patients. Comparison of the .6mm- and .4mm-groups, revealed no differences regarding improvements in AC-PTA (22.4 vs. 20.7dB, p=.56), BC-PTA (3.4 vs. 2.3dB, p=.54) and ABG-PTA (19.1 vs. 18.4dB, p=.77). Hearing outcome evaluation identified similar postoperative success rate (.6mm, 79.7% vs. .4mm, 62%, p=.336) and comparable functional hearing (.6mm, 64% vs. .4mm, 52%; p=.197). The incidence of postoperative SNHL was similar between the two pistons (.6m, 5.3% vs. .4mm, 10%, p=.481).
ConclusionPrimary small fenestra stapedotomy is an effective and safe procedure. A postoperative ABG within 10dB was achieved in 67.2% of patients and there was a reduced incidence of sensorineural hearing loss. Hearing outcome was not influenced by diameter of the selected prosthesis. Postoperative bone conduction hearing thresholds did not differ between the groups, which revealed no significant inner ear trauma caused by the larger piston. Although we did not find evidence to suggest one piston over the other, our results showed a trend toward better results with the larger prosthesis.
Evaluar la tasa de éxito de la estapedotomía primaria, y estudiar la influencia del diámetro de la prótesis en el resultado auditivo.
Material y métodosRevisión retrospectiva de historias médicas de 125 casos sometidos a estapedotomía primaria de la ventana oval, de julio de 2001 a diciembre de 2018. La población de estudio se dividió en 2 grupos, sobre la base del diámetro de la prótesis de teflón de 0,6mm (60%, N=75) y 0,4mm (40%, N=50). Se compararon los valores preoperatorios y postoperatorios (≥12 meses) de los umbrales de conducción aérea (AC), conducción ósea (OC) y desviación aérea-ósea (ABG).
ResultadosEl 65,7 y el 90% de los pacientes lograron valores postoperatorios de ABG≤10dB y ≤20dB. Se logró audición funcional (PTA-AC≤30dB) en el 59,2% de los pacientes. La hipoacusia neurosensorial (SNHL, con empeoramiento en BC-PTA>10dB) se identificó en el 7,2% de los pacientes. La comparación entre los grupos de 0,6 y 0,4mm, no reveló diferencias en cuanto a las mejoras de AC-PTA (22,4 vs. 20,7dB; p=0,56), BC-PTA (3,4 vs. 2,3dB; p=0,54) y ABG-PTA (19,1 vs. 18,4dB; p=0,77). La evaluación del resultado auditivo identificó una tasa de éxito postoperatorio similar (0,6/79,7 vs. 0,4mm/62%; p=0,336) y una audición funcional comparable (0,6/64 vs. 0,4mm/52%; p=0,197). La incidencia de SNHL postoperatorio fue similar entre los 2 pistones (0,6/5,3% vs. 0,4mm/10%; p=0,481).
ConclusiónLa estapedotomía primaria de ventana oval es un procedimiento efectivo y seguro. Se logró ABG postoperatoria dentro del rango de 10dB en el 67,2% de los pacientes, y se redujo la incidencia de hipoacusia neurosensorial. El resultado auditivo no se vio influido por el diámetro de la prótesis seleccionada. Los umbrales postoperatorios de conducción ósea no difirieron entre los grupos, lo cual reveló la ausencia de daño significativo en el oído interno causado por el pistón de mayor diámetro. Aunque no hallamos evidencia que sugiera la elección de un pistón u otro, nuestros resultados reflejaron una tendencia a la obtención de mejores resultados con la prótesis de mayor tamaño.