The aim of our study was to evaluate outcomes of a minimally invasive approach, using transoral surgery (TOS) as the primary treatment for oropharyngeal carcinoma.
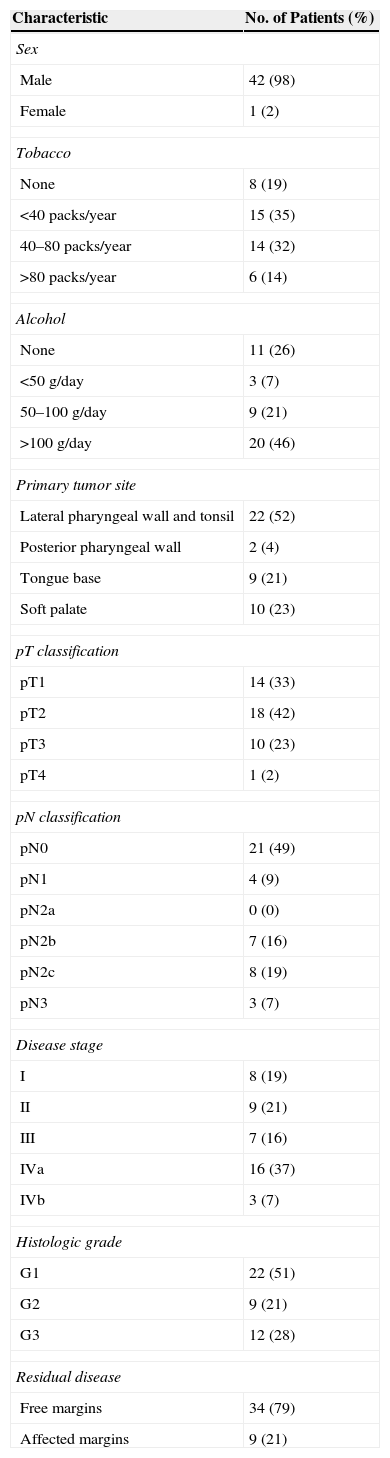
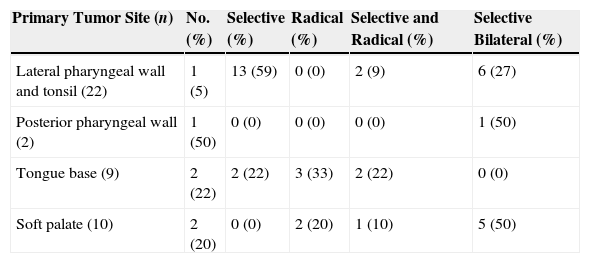
MethodsWe reviewed 43 previously untreated patients with oropharyngeal carcinoma, who were treated with TOS. Distribution of the primary tumor site was: tonsil (52%), soft palate (23%), base of the tongue (21%) and posterior wall (4%). Eight patients had a stage I disease, 9 had a stage II disease, 7 had a stage III disease, 16 had a stage IVA, and 3 had stage IVB disease. Eighteen patients underwent postoperative radiotherapy. Records of these patients were reviewed to obtain measures such as local and regional control, overall and disease-specific survival, and speech and swallowing function.
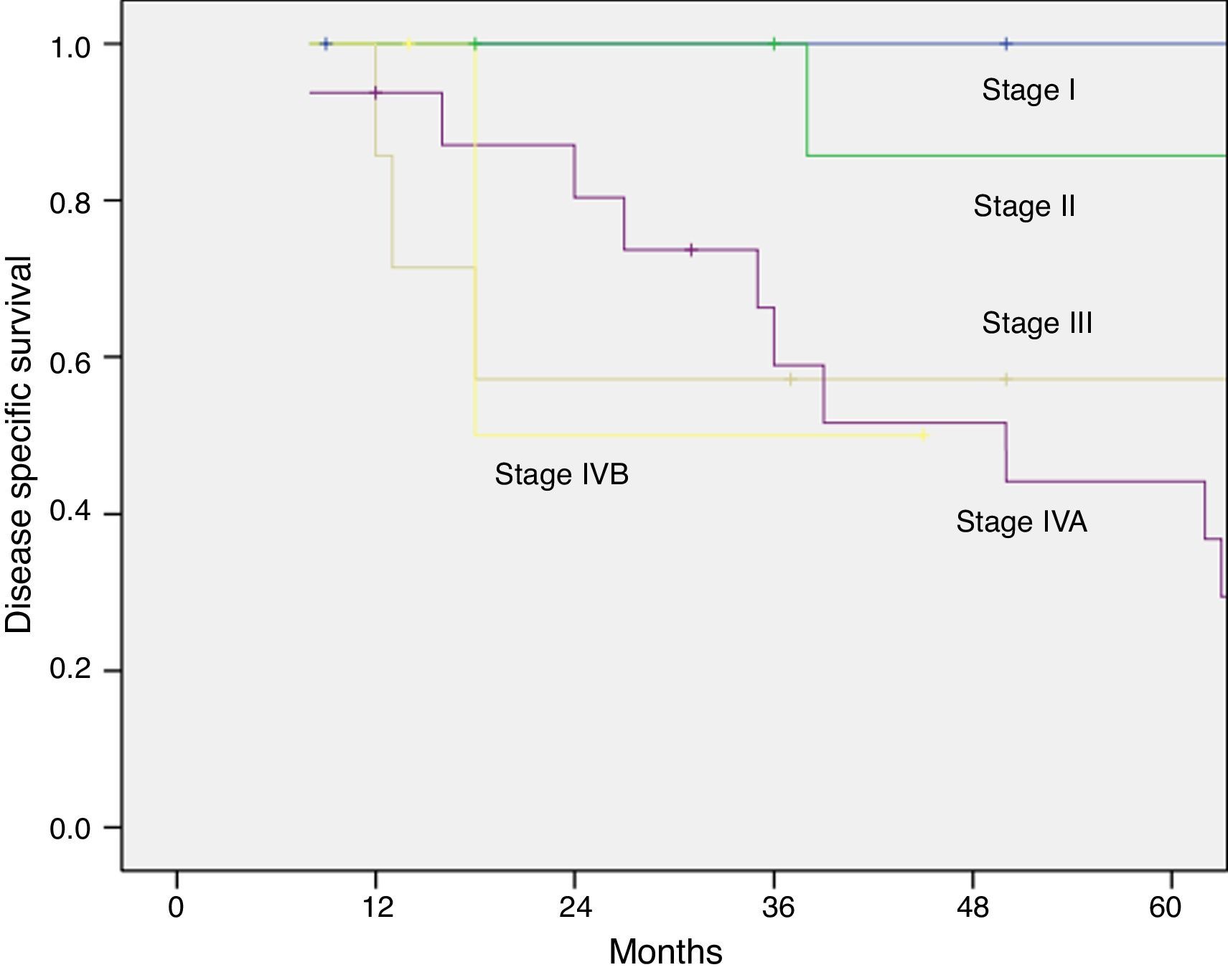
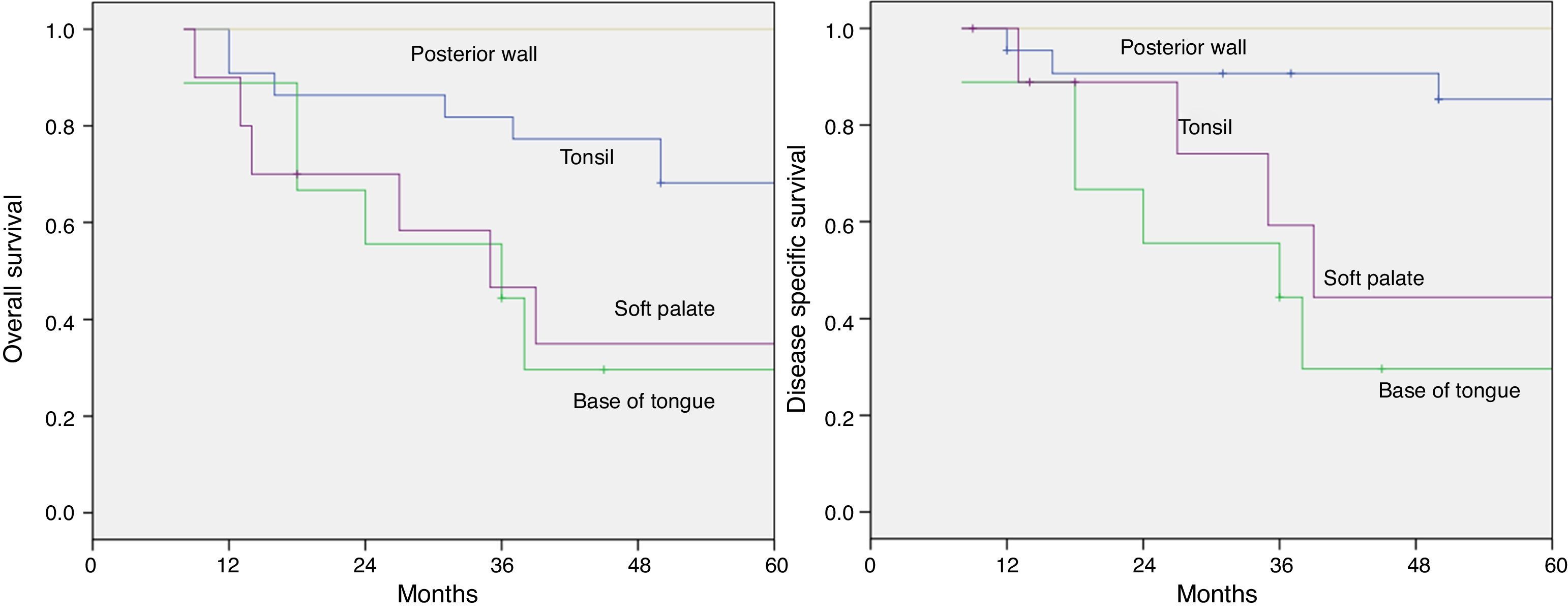
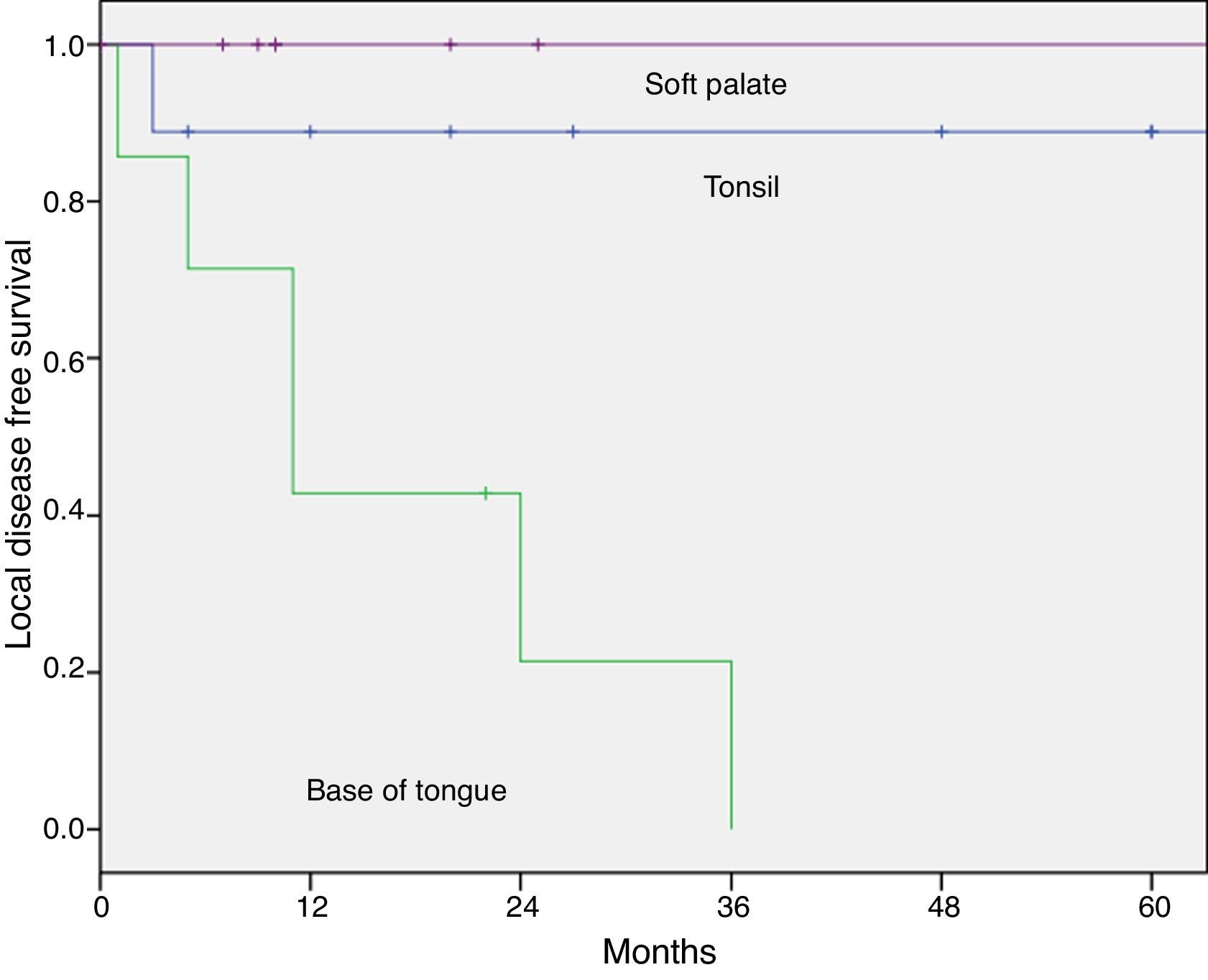
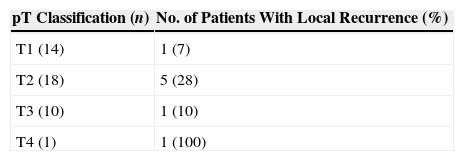
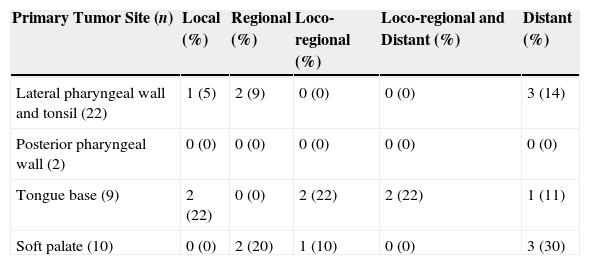
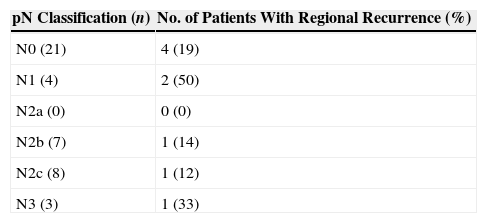
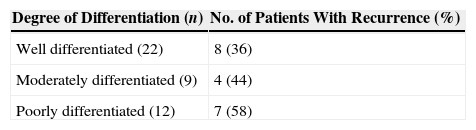
ResultsThe overall recurrence rate was 44%, and the local recurrence rate was 18%. The 5-year overall survival and disease-specific survival rates were 55% and 66%, respectively. Five-year disease-specific survival rates by site were as follows: 100%, 85%, 44%, and 30% for posterior wall, tonsil, soft palate and base of the tongue, respectively. Five-year estimates for local control were 100%, 90%, and 0% for palate, tonsil and for base of the tongue tumors, respectively. All of the patients preserved the larynx and life without tracheotomy and oral alimentation was successful without feeding tube.
ConclusionTOS as the primary treatment approach offers a surgical alternative for treatment of the primary oropharyngeal tumor, in the era of chemoradiation therapy. This approach confers a good local control and functional outcomes.
Los carcinomas de orofaringe son neoplasias agresivas habitualmente diagnosticadas en estadios avanzados. El objetivo de este estudio es exponer los resultados oncológicos y funcionales del tratamiento de estos tumores mediante resección quirúrgica transoral (RTO).
MétodosSe realizó un estudio retrospectivo en 43 pacientes con carcinoma epidermoide de orofaringe tratados mediante RTO. En el 52% de los casos el tumor se originaba en la región amigdalina, en el 23% en el paladar blando, en el 21% en la base de la lengua y en el 4% en la pared posterior. Ocho casos se clasificaron como estadio I, 9 como estadio II, 7 como estadio III, 16 como estadio IVA y 3 como estadio IVB. Dieciocho pacientes recibieron radioterapia postoperatoria. Se revisaron las historias de estos pacientes para obtener información en cuanto a control local y regional, supervivencia total y específica de la enfermedad, y función fonatoria y deglutoria.
ResultadosLa tasa global de recidivas fue del 44%, siendo la tasa de recidivas locales del 18%. La supervivencia global y específica a los 5 años fue del 55% y 66%, respectivamente. Las tasas de supervivencia específica a los 5 años según la localización tumoral fueron del 100%, 85%, 44%, y 30% para la pared posterior, amígdala, paladar blando y base de la lengua. El control local a los 5 años fue del 100%, 90%, y 0% para el paladar, amígdala y base de la lengua, respectivamente. En todos los casos se preservó la laringe, y los pacientes no requirieron traqueotomía definitiva y reanudaron la alimentación oral.
ConclusionesLa RTO es una alternativa terapéutica eficaz para el tratamiento primario de los carcinomas de orofaringe, obteniendo unos resultados oncológicos y funcionales favorables.