Gastro-oesophageal reflux disease (GERD) is one of the most common diseases, but is still a challenge to cure. Different medical treatments are used, first of all Proton pump inhibitors (PPIs), however these are sometimes ineffective and long-term intake can lead to underestimated complications. Recently, some studies investigated the role of inspiratory muscle training (IMT) in the medical treatment of GERD. It seems that IMT is able to increase the pressure generated by the lower oesophageal sphincter (LES), reduce spontaneous releases of LES, acid exposure, use of PPIs, and improve symptoms and quality of life for GERD patients.
ObjectiveThe aim of this study was to evaluate the effectiveness of IMT in association with myofunctional therapy exercises of swallowing set by Daniel Garliner (m-IMT) on the symptoms of patients with non-erosive gastro-oesophageal reflux disease (NERD).
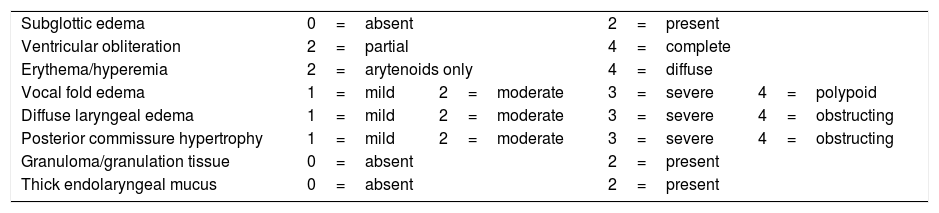
MethodsTwenty-one adult patients with NERD were enrolled from May to December 2017 and performed m-IMT over a period of 4 weeks. Before and after treatment, all the patients completed the following questionnaires: GERD oesophageal symptomatology (GERDQ), extra-oesophageal GERD symptomatology (RSI), quality of life (GERD-Health Related Quality of Life Questionnaire (GERD-HRQL), and underwent laryngeal endoscopy.
ResultsNineteen patients completed m-IMT. GERDQ (from 8.36±3.94 to 1.7±3.41; p<.05), RSI (from to 21.68±10.26 to 6.93±8.37; p<.05) and GERDHRQL (from 25.68±16.03 to 8.4±11.06; p<.05) the questionnaire scores significantly reduced after treatment. In addition, the laryngeal endoscopy score greatly improved (from 14.24±4.15 to 7.4±1.77; p<.05).
Conclusionsm-IMT is a low cost therapy without side effects. It could be useful in association with PPI or alone for selected GERD cases and for mild NERD forms, in association with diet. Further studies are required to prove the effects of m-IMT on GERD symptoms and decide the best treatment schedule.
La enfermedad por reflujo gastroesofágico (ERGE) es una de las enfermedades más comunes, pero sigue siendo un desafío para curar. Se utilizan diferentes tratamientos médicos, en primer lugar los inhibidores de la bomba de protones (IBP), sin embargo, en ocasiones son ineficaces y una ingesta a largo plazo puede llevar a complicaciones subestimadas. Recientemente, algunos estudios investigaron el papel del entrenamiento muscular inspiratorio (IMT) en el tratamiento médico de la ERGE. Parece que el IMT es capaz de aumentar la presión generada por el esfínter esofágico inferior (LES), reducir las liberaciones espontáneas del LES, la exposición al ácido, el uso de IBP, y mejorar los síntomas y la calidad de vida en pacientes con ERGE.
ObjetivoEl objetivo de este estudio es evaluar la efectividad de la IMT en asociación con los ejercicios de terapia miofuncional de tragar de Daniel Garliner (m-IMT) en los síntomas de los pacientes con ERGE no erosivo (NERGE).
MétodosVeintiún pacientes adultos con ERGE se inscribieron de mayo a diciembre de 2017 y realizaron un período de 4 semanas de m-IMT. Antes y después del tratamiento todos los pacientes completaron los siguientes cuestionarios: sintomatología esofágica de ERGE, sintomatología de ERGE extraesofágica (RSI), calidad de vida (cuestionario de calidad de vida relacionada con la salud [ERGE-HRQL]) y endoscopia laríngea.
ResultadosDiecinueve pacientes completaron m-IMT. GERDQ (desde 8,36±3,94 a 1,7±3,41; p<0,05), RSI (desde hasta 21,68±10,26 hasta 6,93±8,37; p<0,05) y ERGE-HRQL (desde 25,68±16,03 hasta 8,4±11,06; p<0,05), las puntuaciones se redujeron significativamente después del tratamiento. Además, la puntuación de la endoscopia laríngea mejoró enormemente (de 14,24±4,15 a 7,4±1,77; p<0,05).
Conclusionesm-IMT es una terapia de bajo costo sin efectos secundarios. Podría ser útil en asociación con IBP o solo en casos seleccionados de ERGE y en formas NERGE leves, en asociación con la dieta. Se requieren estudios adicionales para probar los efectos de m-IMT en los síntomas de ERGE y establecer el mejor programa de tratamiento.