The commonly used predictors for difficult airway management are not very accurate. We investigate the power of indirect laryngoscopy (IL) with the rigid 70-degree laryngoscope as a predictor of difficult visualisation of the larynx (DVL) with direct laryngoscopy (DL).
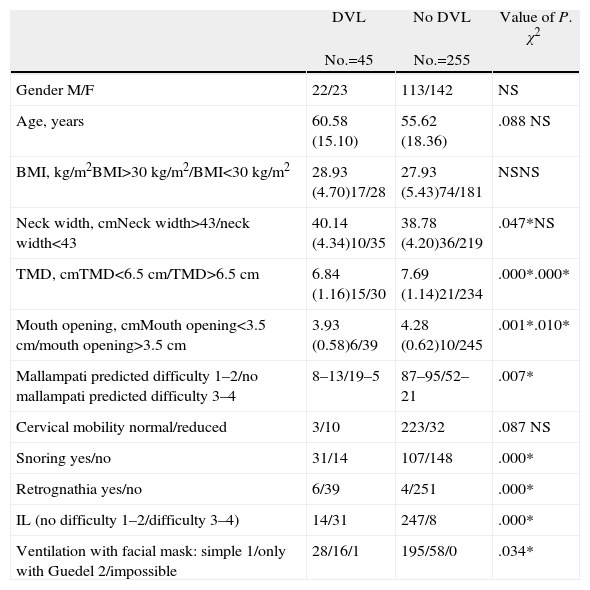
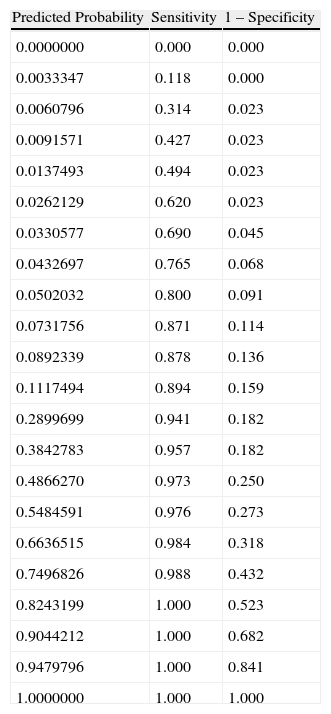
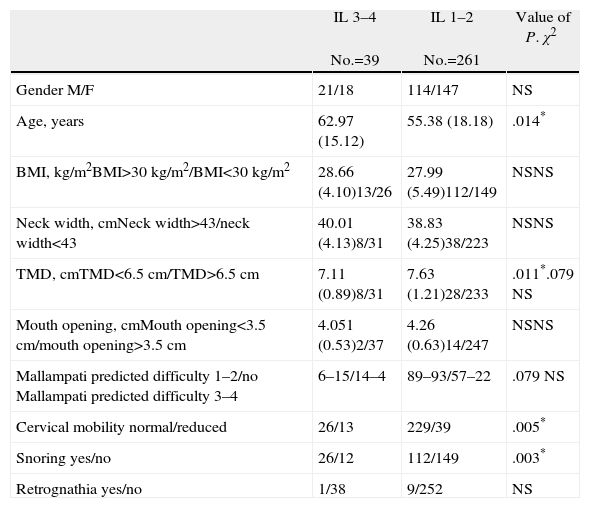
MethodsWe performed preoperative indirect laryngoscopy with the rigid laryngoscope on 300 patients. The vision obtained was classified into four grades: 1 (vocal cords visible), 2 (posterior commissure visible), 3 (epiglottis visible) and 4 (no glottic structure visible). Grades 3 and 4 were considered predictors of difficult larynx visualisation. Next, direct laryngoscopy with the Macintosh laryngoscope was carried out on the patients under general anaesthesia (GA). Positive value was defined as a Cormack and Lehane III and IV. Other common clinical predictors were also analysed. A logistic regression model using the relevant variables was elaborated. We also investigated predictors of difficult visualisation of the larynx with indirect laryngoscopy.
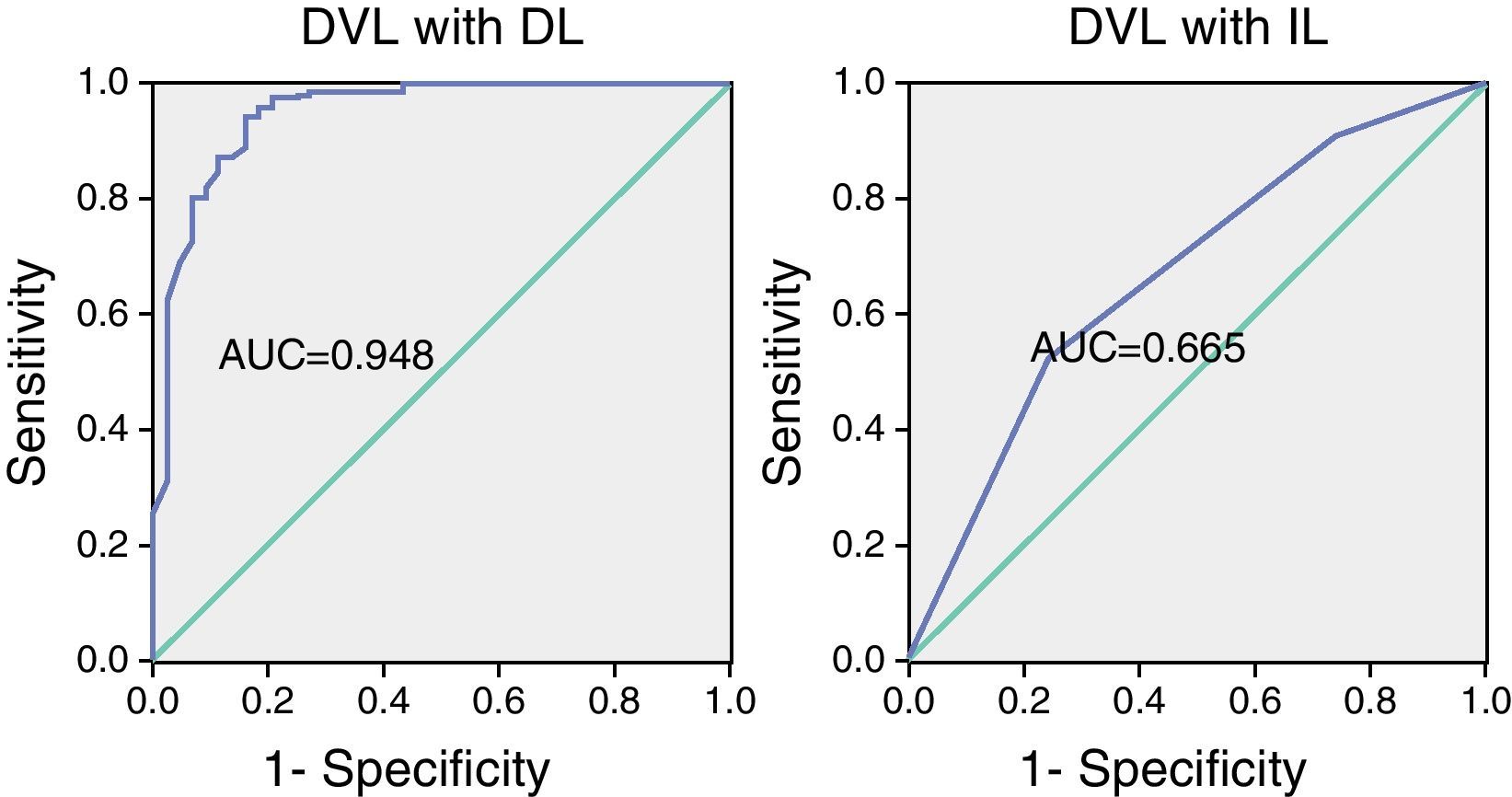
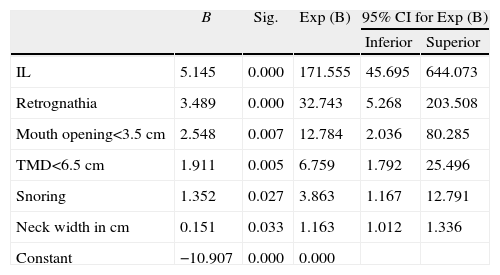
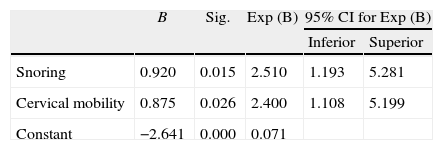
ResultsThe found model and the coefficients for preparing it were:f(x)=−10.097+5.145 indirect laryngoscopy (3–4)+3.489 retrognathia+2.548 mouth opening <3.5cm+1.911 thyromental distance (TMD) <6.5cm+1.352 snorer+(0.151cm neck thickness). This model provided a correct result in 94.3% of cases. In the case of indirect laryngoscopy, the model found was:f(x)=−2.641+0.920 snorer+0.875 cervical mobility.
ConclusionsIndirect laryngoscopy was the independent variable with the greatest predictive power. Snoring is a common predictor in both laryngoscopy models.
Los predictores comúnmente utilizados para prever la vía aérea difícil poseen poca capacidad para pronosticarla. Nuestro objetivo es investigar la potencia de la laringoscopia indirecta con el laringoscopio rígido de 70° como predictor de dificultad de visión de la laringe con la laringoscopia directa.
MétodosSe efectuó una laringoscopia indirecta con el laringoscopio rígido en el preoperatorio a 300 pacientes. Según la visión obtenida fueron clasificados en 4 grados: 1 (cuerdas vocales visibles), 2 (comisura posterior visible), 3 (visión solo de epiglotis) y 4 (ninguna estructura glótica visible). EL 3 y el 4 eran considerados predictores de dificultad de visión de la laringe. Después, bajo anestesia general, practicamos a los pacientes la laringoscopia directa con el laringoscopio de Macintosh. Valoramos como positivo el encontrar un Cormack–Lehane III–IV. Se registraron otros predictores clínicos comunes. Se elaboró un modelo de regresión logística con fines predictivos utilizando las variables relevantes. Investigamos también los predictores de la dificultad de visión de la laringe con la laringoscopia indirecta.
ResultadosEl modelo encontrado y sus coeficientes para confeccionarlo fueron: f(x)=−10,097+5,145 laringoscopia indirecta (3–4)+3,489 retrognatia+2,548 apertura boca<3,5cm+1,911 distancia tiromentoniana <6,5cm+1,352 roncopatía+(0,151*cm grosor cuello). Proporciona un resultado correcto en el 94,3% de los casos. En el caso de la laringoscopia indirecta el modelo hallado era: f(x)=−2,641+0,920 roncopatía+0,875 movilidad cervical.
ConclusionesLa laringoscopia indirecta fue la variable independiente con más poder predictivo (mayor coeficiente). La roncopatía es un predictor común entre los modelos de ambas laringoscopias.