Total laryngectomy is one of the most mutilating oncological operations. There are no specific studies evaluating return to work after this surgery.
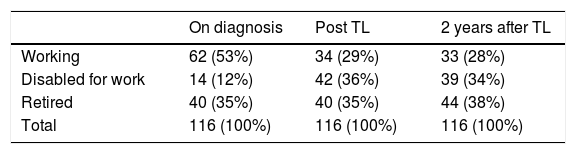
Patients and methodsA cross-sectional study was performed on a sample of 116 laryngectomized patients who were disease-free and had a minimum follow-up of 2 years from total laryngectomy. A survey was conducted to find out their employment situation before and after surgery. At the time of surgery, 62 (53%) were working, 40 (35%) were retired and 14 (12%) were in a disability situation.
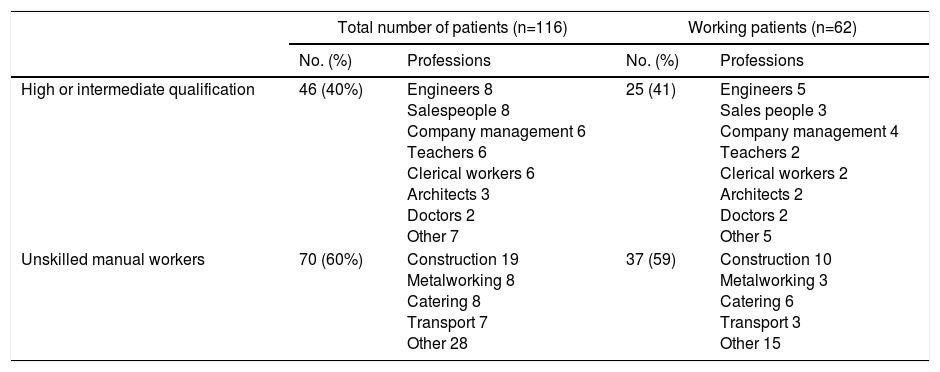
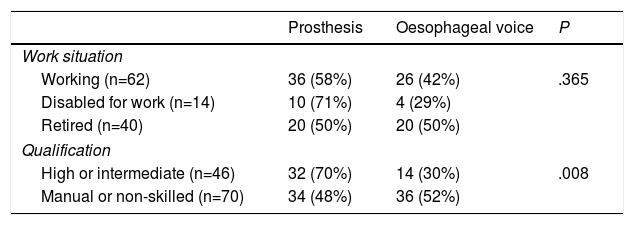
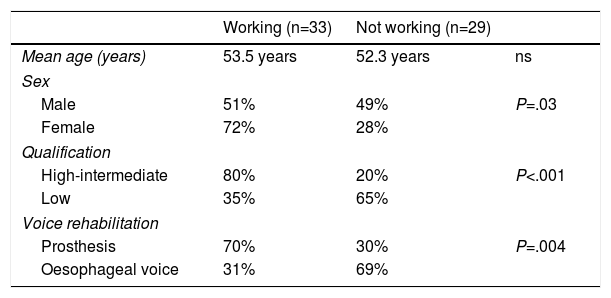
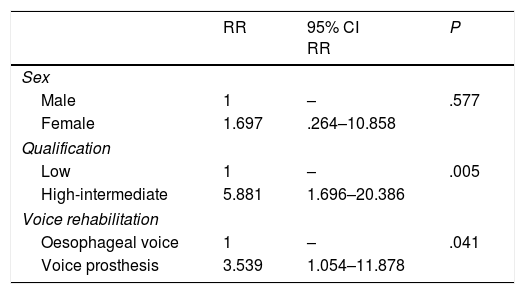
Results60% had professions with low qualification requirements, the largest group being construction workers. Of the 62 patients active at the time of total laryngectomy, 29 became inactive and 33 (53%) maintained their work activity. The most important factors in maintaining work activity were the level of professional qualification and the method of vocal rehabilitation. Eighty percent of the patients with high-intermediate qualification maintained their jobs, compared to 35% of those with low professional qualifications (P<.001). Seventy percent of the patients with voice prostheses maintained their work activity, compared to 31% of the patients rehabilitated with oesophageal voice (P=.004). Logistic regression confirmed these as independent variables for continuing to work.
ConclusionsThis is the first study that analyzes the impact of total laryngectomy on the work situation. The most important factors for a return to work were having a high-intermediate skilled job and the use of voice prosthesis as a method of vocal rehabilitation.
La laringectomía total es una de las cirugías oncológicas más mutilantes. No existen estudios específicos que evalúen el retorno laboral después de la misma.
Pacientes y métodosSe realizó un estudio transversal de una muestra de 116 pacientes laringectomizados que se hallaban libres de enfermedad y con un seguimiento mínimo de 2 años desde la laringectomía total. Se les realizó una encuesta dirigida a conocer la situación laboral, tanto previa como posterior. En el momento de la cirugía 62 (53%) estaban activos laboralmente, 40 (35%) estaban jubilados y 14 (12%) tenían una situación de invalidez.
ResultadosEl 60% tenía profesiones con bajo grado de cualificación, siendo el grupo más numeroso los trabajadores de la construcción. De los 62 pacientes laboralmente activos en el momento de la laringectomía total 29 pasaron a inactivos y 33 (53%) mantuvieron la actividad laboral. Los factores más importantes para mantener la actividad laboral fueron el nivel de cualificación profesional y el método de rehabilitación vocal. El 80% de los pacientes con cualificación alta-intermedia mantuvieron su trabajo, frente al 35% en los de cualificación profesional baja (p < 0,001). El 70% de los pacientes con prótesis fonatoria mantuvo la actividad laboral, frente a un 31% de los pacientes rehabilitados con erigmofonía (p = 0,004). La regresión logística confirmó estas variables como independientes para seguir trabajando.
ConclusionesEste es el primer estudio que analiza el impacto de la laringectomía total en la situación laboral. Los factores más importantes para volver a trabajar fueron tener un trabajo cualificado alto-intermedio y la utilización de prótesis fonatoria como método de rehabilitación vocal.