Children up to 2 years old are at high risk of respiratory infections and nasal irrigation is often prescribed. Yet, to date there is no sufficient knowledge about its immediate effects on the nasopharynx and middle ear. Therefore, this study aimed to analyze the effect of a rhino-pharyngeal clearance intervention protocol on nasal obstruction and middle ear condition in children under 3 years of age with URTI.
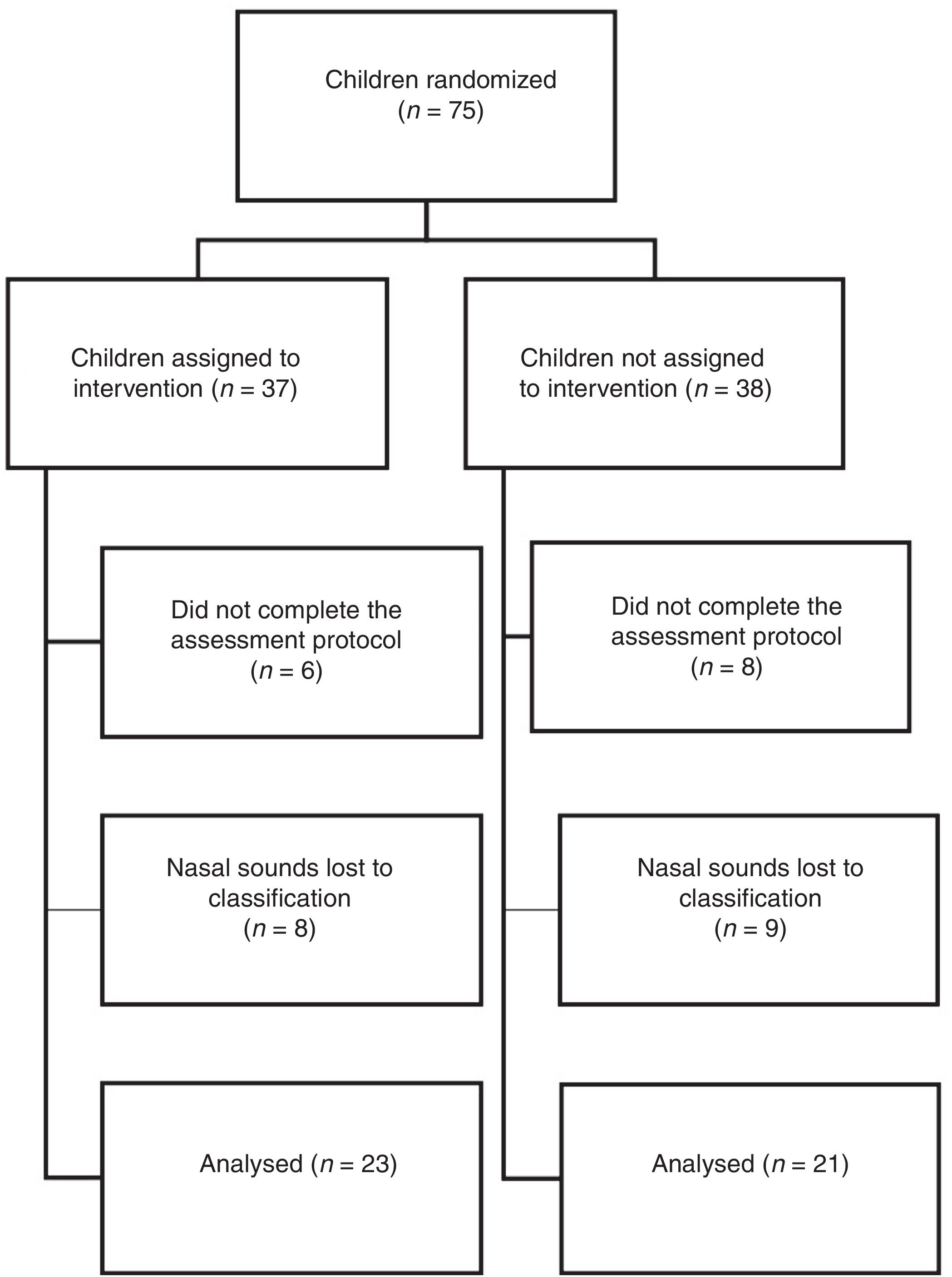
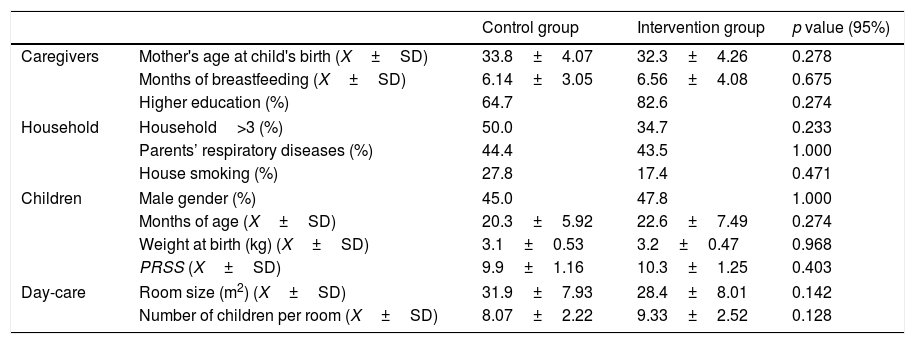
Materials and methodsRandomized controlled trial in a day-care centre of Porto, including 44 children randomized to Intervention Group (IG) and Control Group (CG). Nasal auscultation and tympanometry were performed at baseline (M0) as well as after the intervention (M1), which consisted of nasal irrigation (NaCl .9%) followed by a forced nasal inspiration in the IG, and after 30min of normal activities, in the CG.
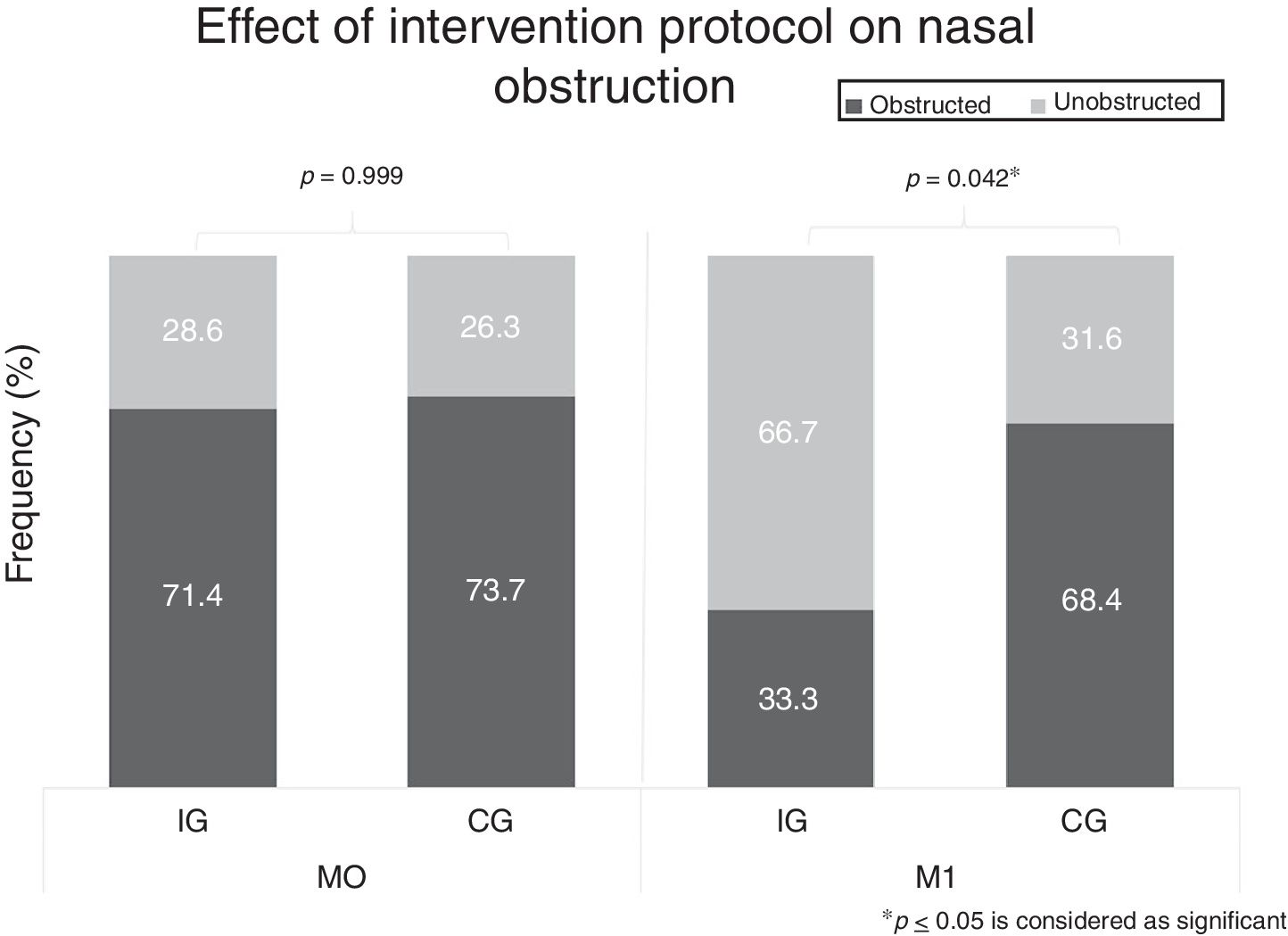
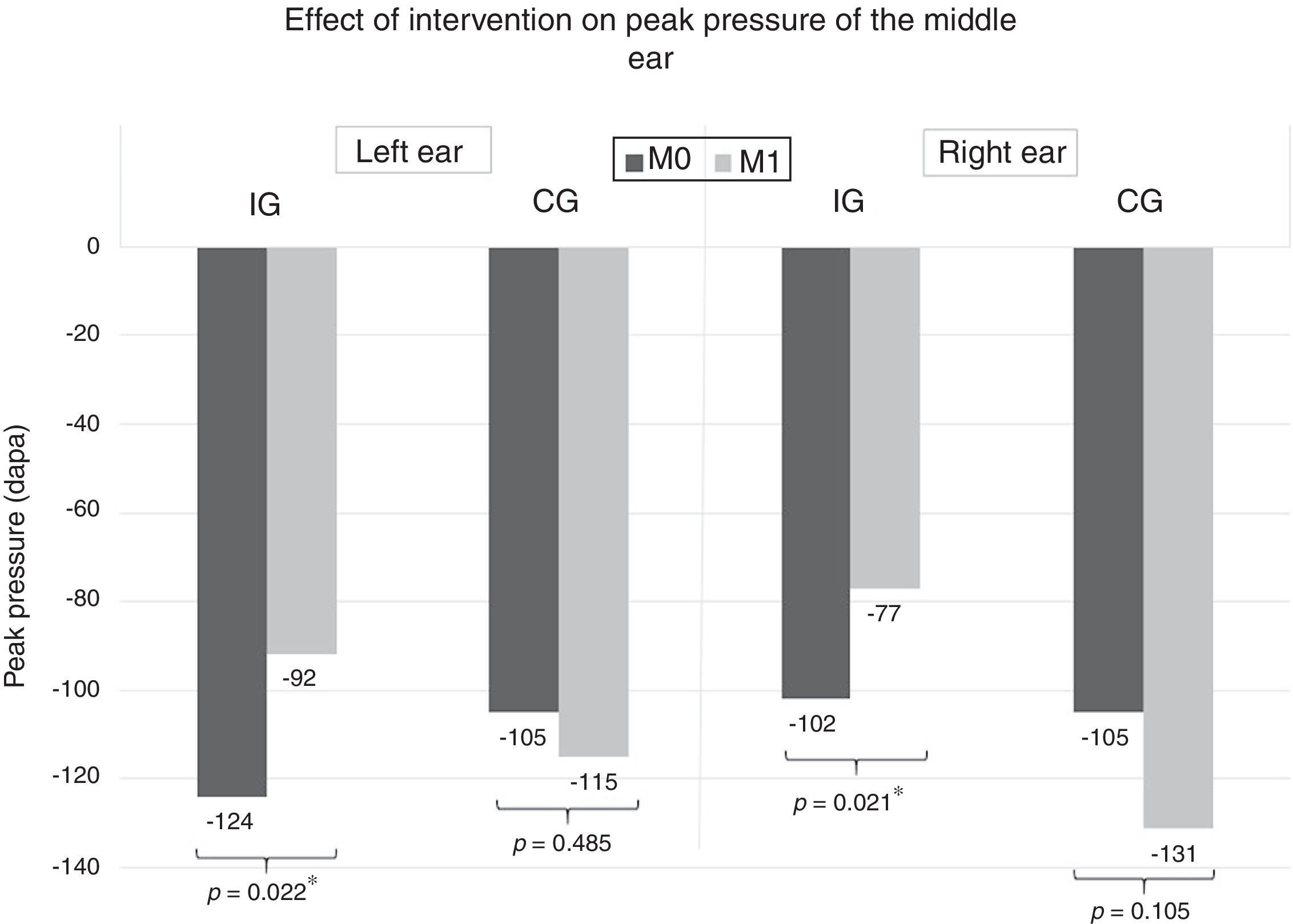
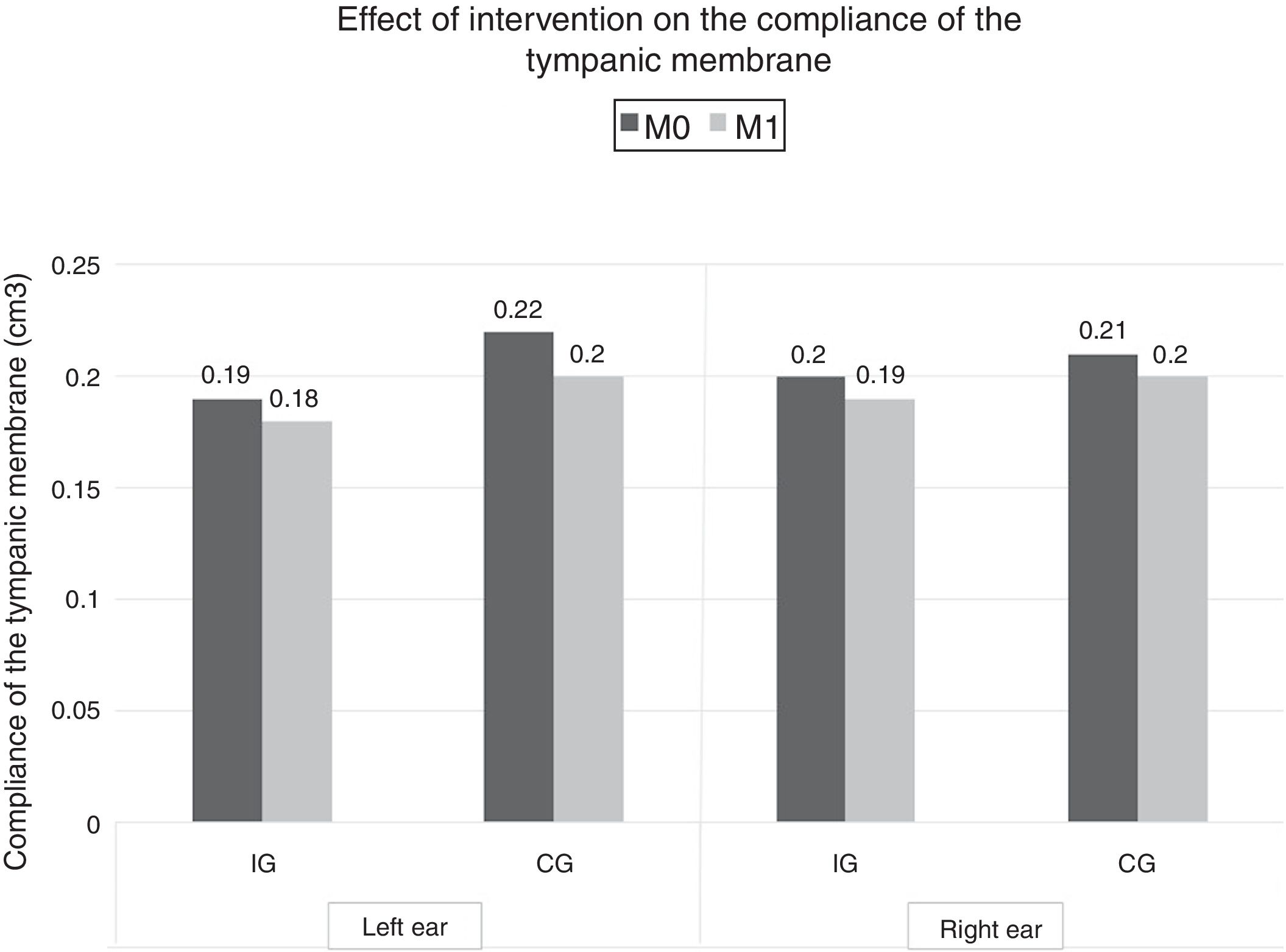
ResultsIn M1 there was a lower frequency of children classified as having an obstructed nasal sound in the IG when compared to the CG (IG=33.3%; CG=68.4%; p=0.042). We also observed an improvement of mean peak pressure (PP) in the IG (Left ear: M0=−124daPa; M1=−92daPa; p=0.022. Right ear: M0=−102daPa; M1=−77daPa; p=0.021), which was not observed in the CG (Left ear: M0=−105daPa; M1=−115daPa; p=0.485. Right ear: M0=−105daPa; M1=−131daPa; p=0.105). There were no significant results concerning the compliance of the tympanic membrane.
ConclusionsThe rhino-pharyngeal clearance improved the nasal obstruction and PP of the middle ear of children under 3 years of age with URTI.
Los niños corren un alto riesgo de infecciones respiratorias superiores (IRS) y con frecuencia se prescriben irrigaciones nasales. Hasta hoy no hay suficiente conocimiento sobre sus efectos inmediatos en la nasofaringe y el oído medio. Por lo tanto, este estudio tuvo como objetivo analizar el efecto de un protocolo de intervención de limpieza nasal en la obstrucción y en el estado del oído medio de niños menores de 3 años con IRS.
Material y métodosEnsayo controlado aleatorizado en una guardería de Oporto, incluidos 44 niños asignados al Grupo de intervención (IG) y al Grupo de control (CG). La auscultación nasal y la timpanometría se realizaron al inicio (M0) y después de la intervención (M1), que consistió en irrigación nasal (NaCl 0,9%) seguido de una inspiración nasal forzada en IG, y después de 30min de actividades normales en CG.
ResultadosEn M1 hubo una menor frecuencia de niños clasificados como con un sonido nasal obstruido en IG en comparación con CG (IG=33,3%; CG=68,4%; p=0,042). También se observó una mejora de la presión máxima media (PP) en IG (oído izquierdo: M0=−124daPa; M1=−92daPa; p=0,022; oído derecho: M0=−102daPa; M1=−77daPa; p=0,021), que no se observó en CG (oído izquierdo: M0=−105daPa; M1=−115daPa; p=0,485; oído derecho: M0=−105daPa; M1=−131daPa; p=0,105). No hubo resultados significativos con respecto al cumplimiento de la membrana timpánica.
ConclusionesLa limpieza nasal mejoró la obstrucción y la PP del oído medio de niños menores de 3 años con IRS.