The aim of this study was first to present the indications and results using expansion sphincter pharyngoplasty to treat obstructive sleep apnoea–hypopnoea syndrome (OSAHS). And second, to compare the findings of drug-induced sleep endoscopy (DISE) before and after the surgery.
Material and methodsThe study design was a prospective cohort of patients surgically treated between 2015 and 2016. All patients were diagnosed with mild to severe obstructive sleep apnoea and did not tolerate CPAP. All had pre- and post-surgery DISE and polysomnography. The inclusion criteria were age, between 18 years and 70 years, small tonsils (sizes 1 and 2), Friedman II and III clinical stage, and lateral collapse in preoperative DISE. We performed surgery to the palate only, using expansion sphincter pharyngoplasty.
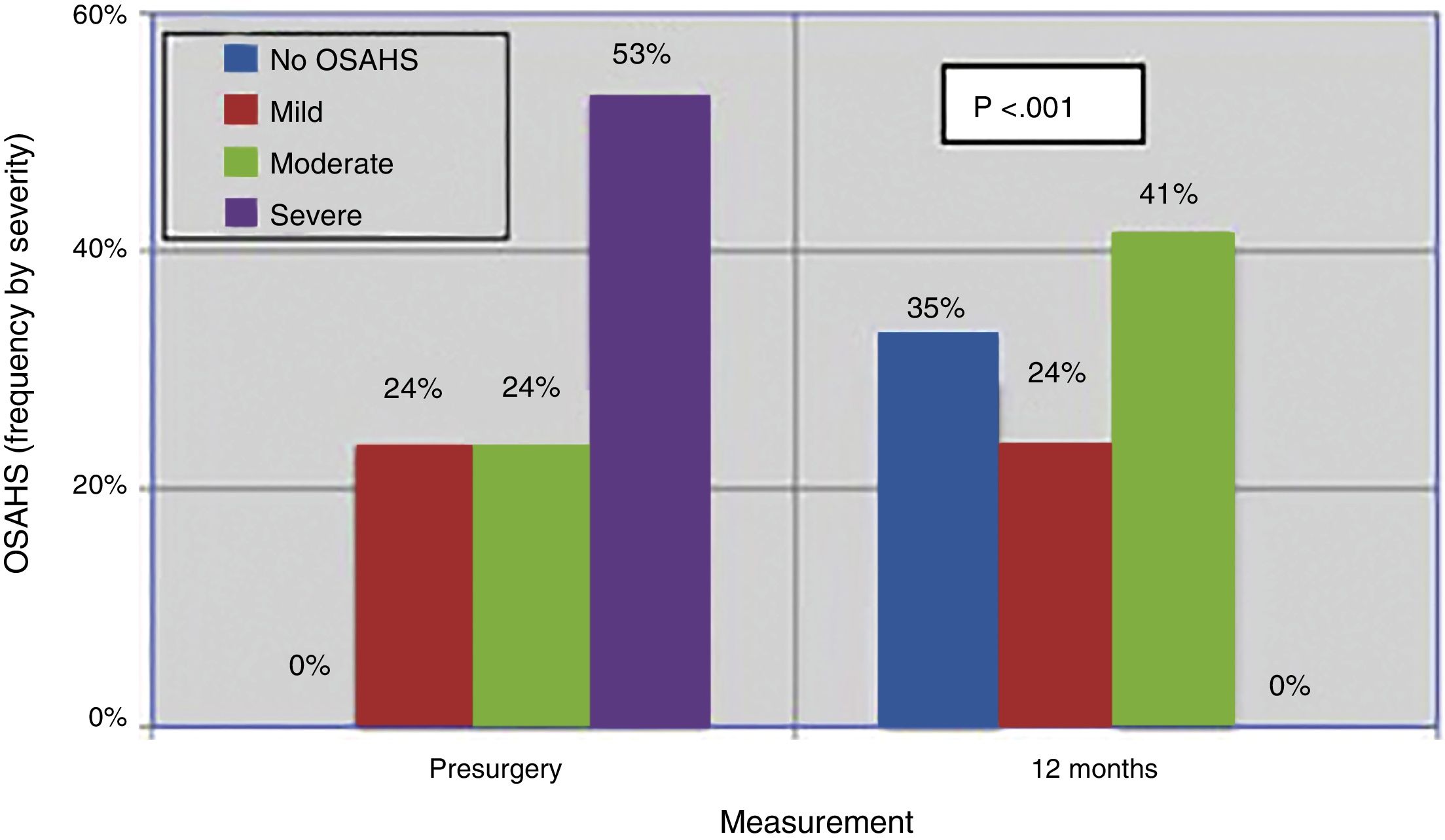
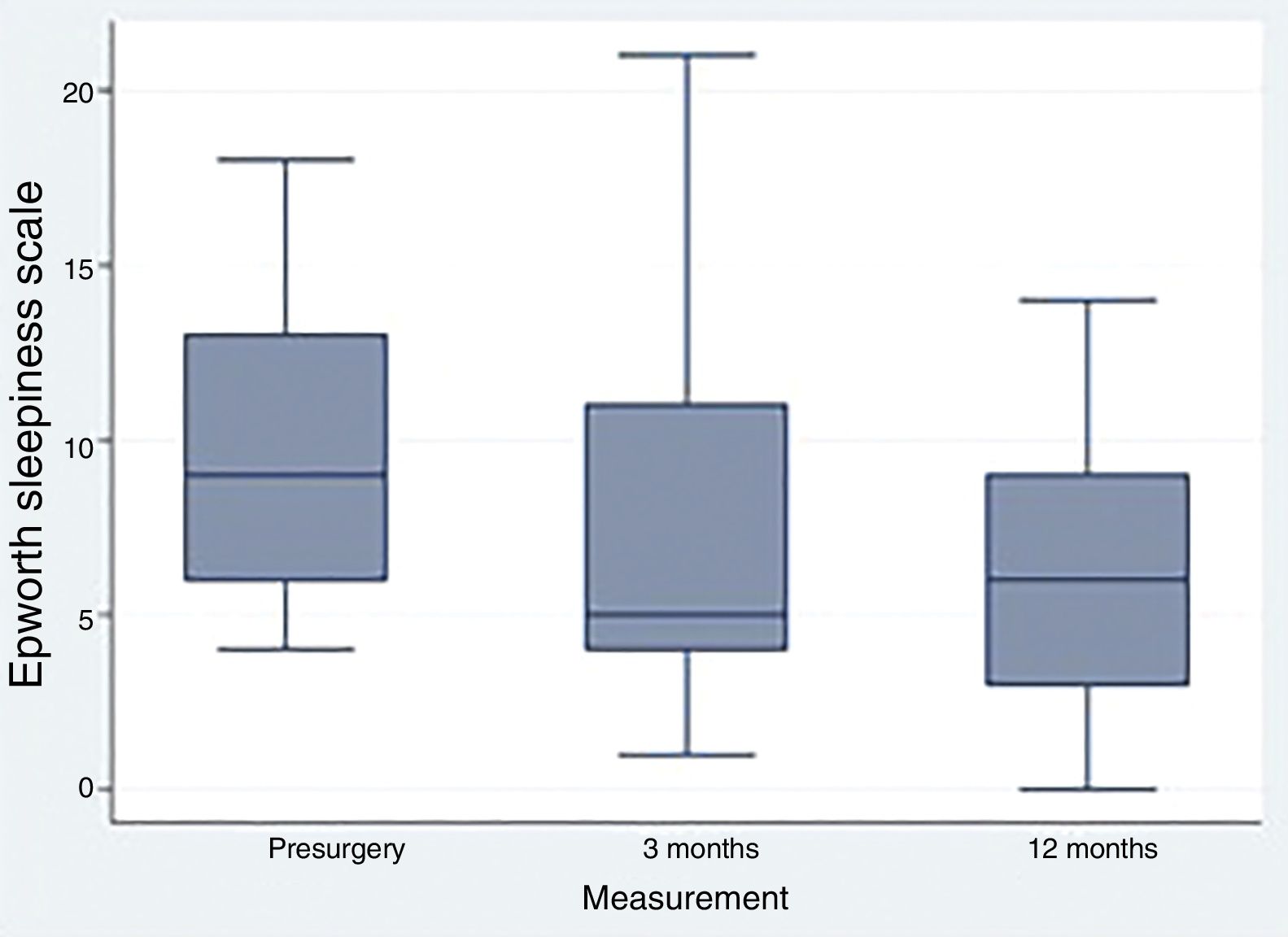
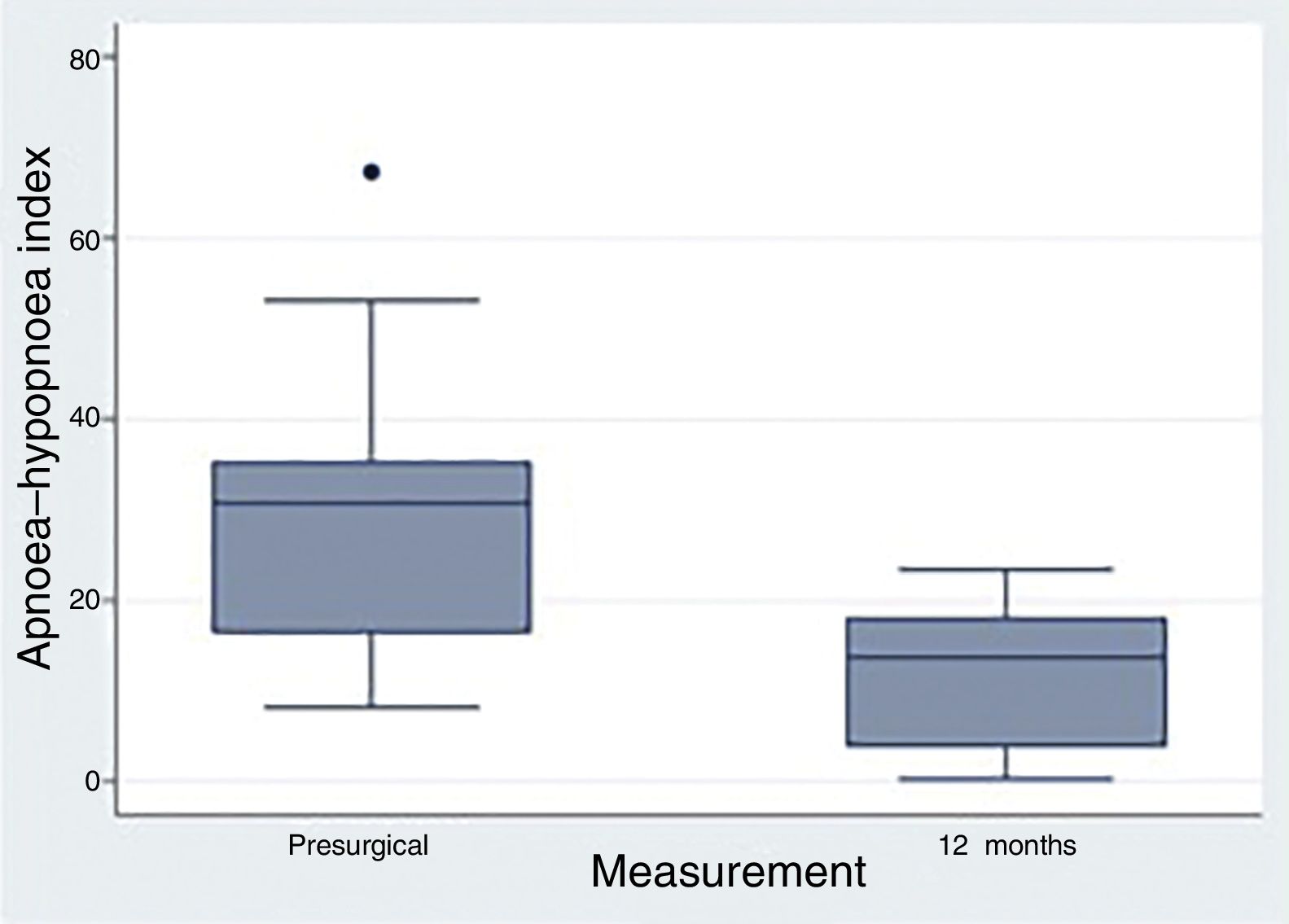
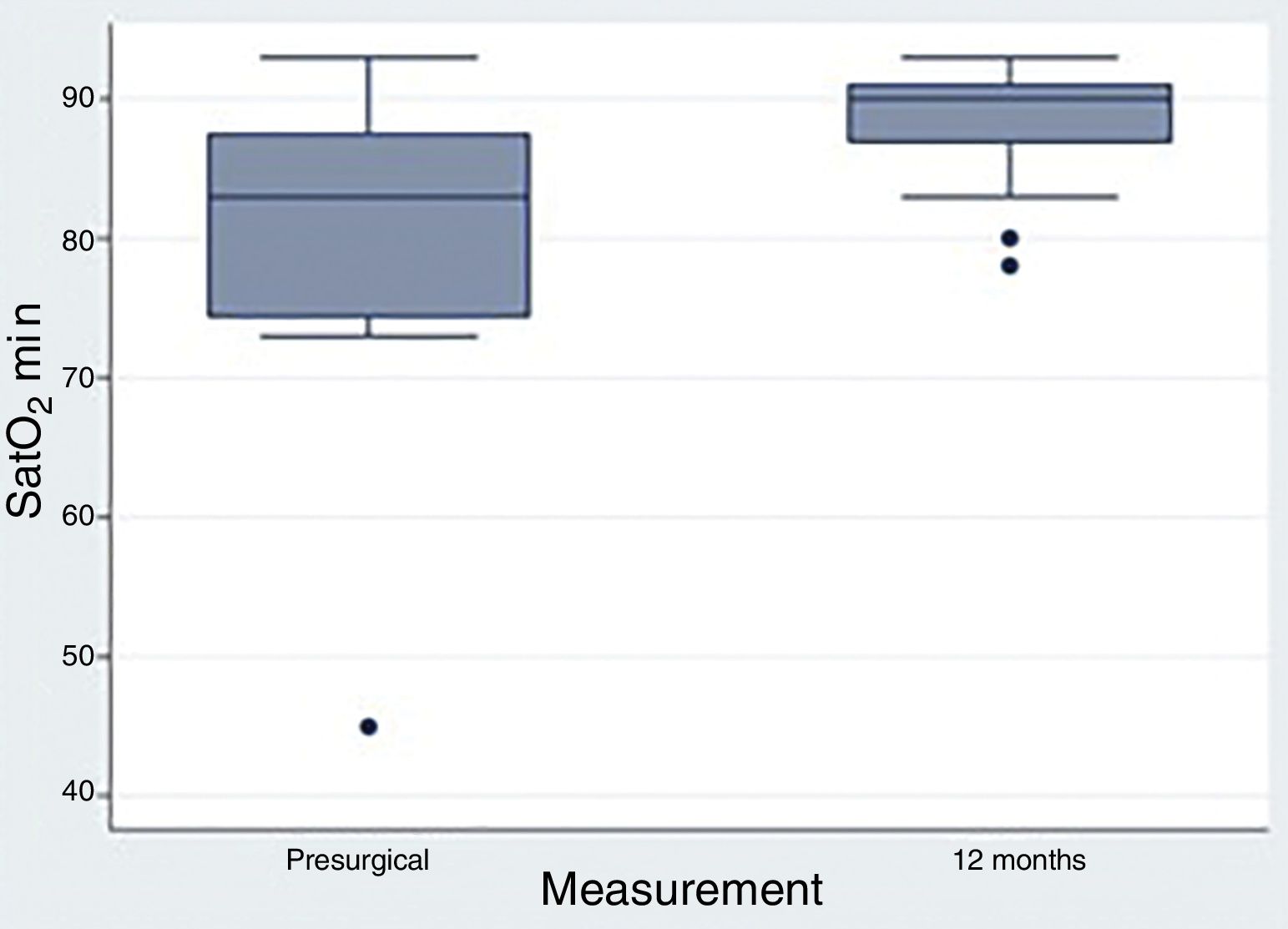
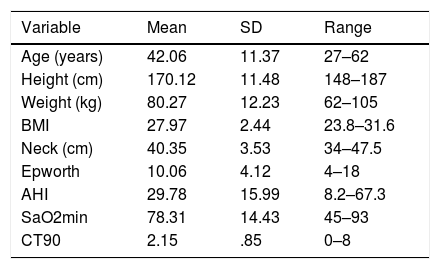
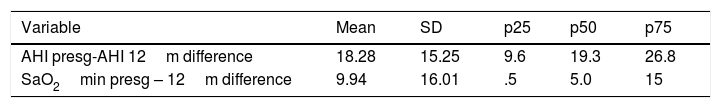
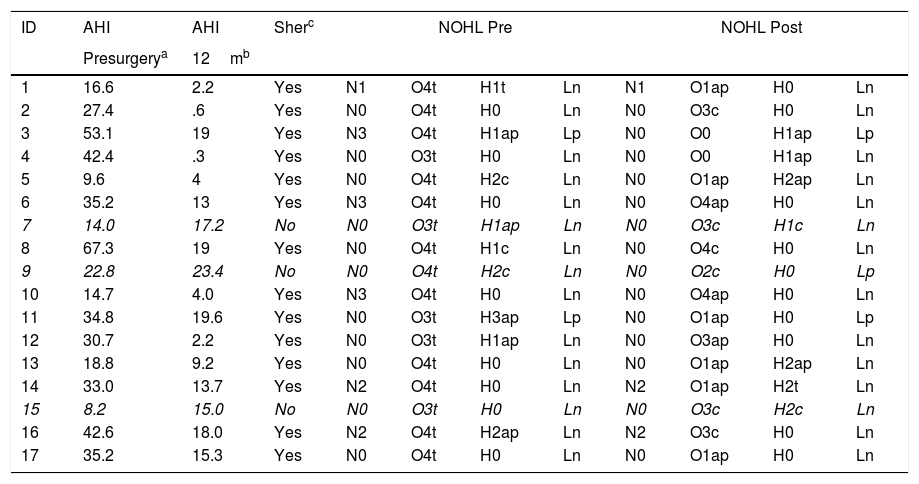
ResultsSeventeen patients were included, 52.94% had severe OSAHS. Average age was 42 years, average body mass index was 28. The surgical success rate according to Sher criteria was 82.35%. 41.17% had a postoperative apnoea–hypopnoea index of less than 10. Seventy-five percent of the patients had no further need for CPAP.
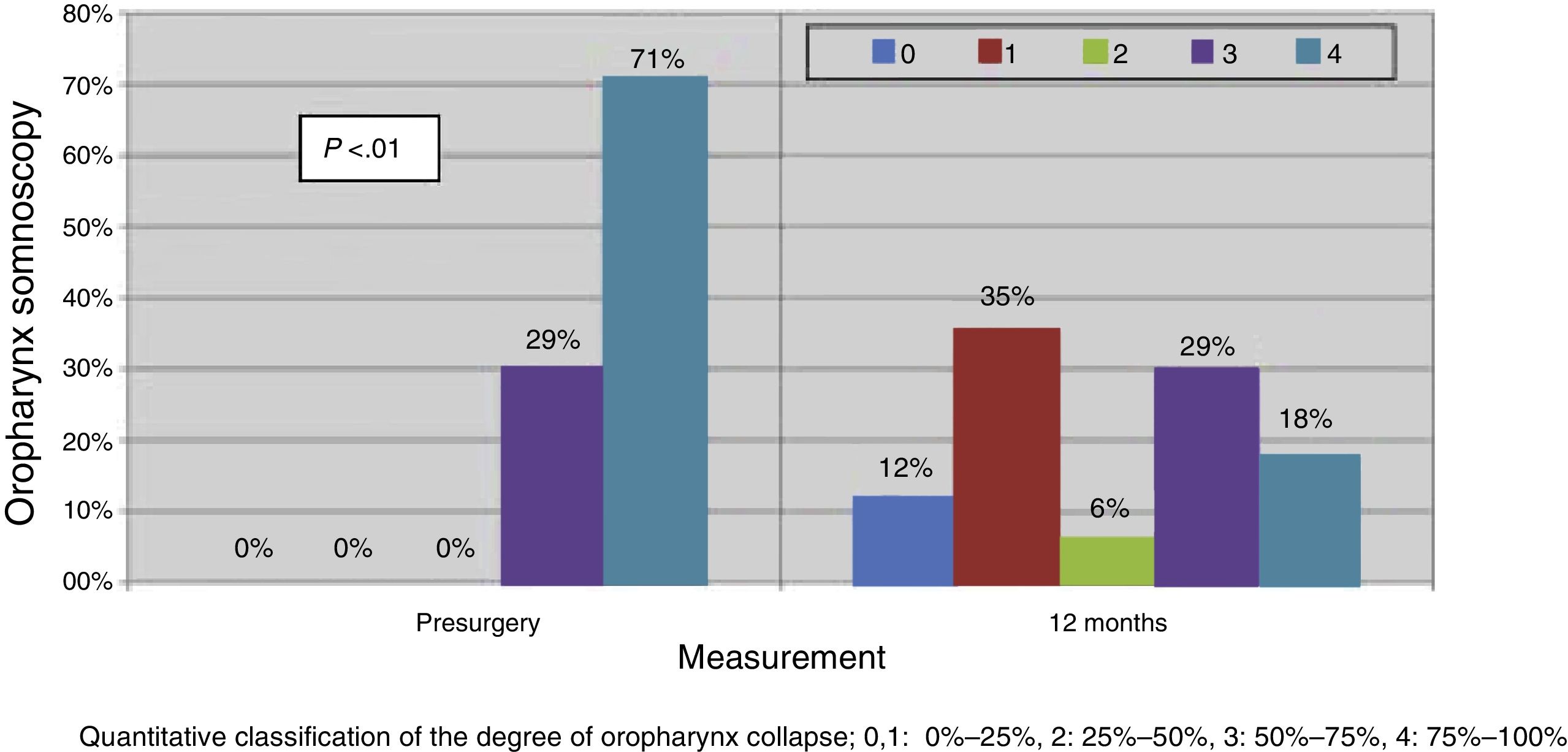
ConclusionExpansion sphincter pharyngoplasty is a safe technique for treating OSAHS, in patients with small tonsils, Friedman grade I and II and collapse of lateral walls in DISE, in the absence of multilevel collapse. The postoperative DISE showed improvement of the lateral collapse was achieved with the expansion.
El objetivo de este estudio es presentar las indicaciones y resultados de la faringoplastia de expansión como tratamiento del síndrome de apnea-hipopnea obstructiva del sueño (SAHOS). En segundo lugar, comparar los hallazgos de la somnoscopia (drug-induced sleep endoscopy –DISE–) antes y después de la cirugía.
Material y métodosEl diseño del estudio fue una cohorte prospectiva de pacientes tratados quirúrgicamente de 2015 a 2016. Todos los pacientes fueron diagnosticados de SAHOS leve a grave y no toleraban la CPAP. Todos tenían DISE y polisomnografía previa a la cirugía, y posterior a la misma. Los criterios de inclusión fueron la edad, entre 18 años y 70 años, amígdalas pequeñas (tamaños 1 y 2), estadio clínico de Friedman II y III, y colapso lateral mayoritario en la DISE preoperatoria. Se les realizó únicamente cirugía del paladar, usando la técnica de faringoplastia de expansión.
ResultadosSe incluyeron 17 pacientes, el 52,94% eran pacientes con SAHOS grave. La edad media fue de 42 años, el índice de masa corporal media fue de 28. La tasa de éxito quirúrgico según los criterios de Sher fue del 82,35%. El 41,17% presentó un índice de apnea-hipopnea postoperatoria inferior a 10. El 75% de los pacientes lograron no tener que usar la CPAP.
ConclusiónLa faringoplastia de expansión es una técnica segura como tratamiento del SAHOS en pacientes con amígdalas pequeñas, grado Friedman I y II y colapso de paredes laterales en somnoscopia, en ausencia de colapso multinivel. La DISE postoperatoria demostró la mejoría del colapso lateral obtenida con la expansión.