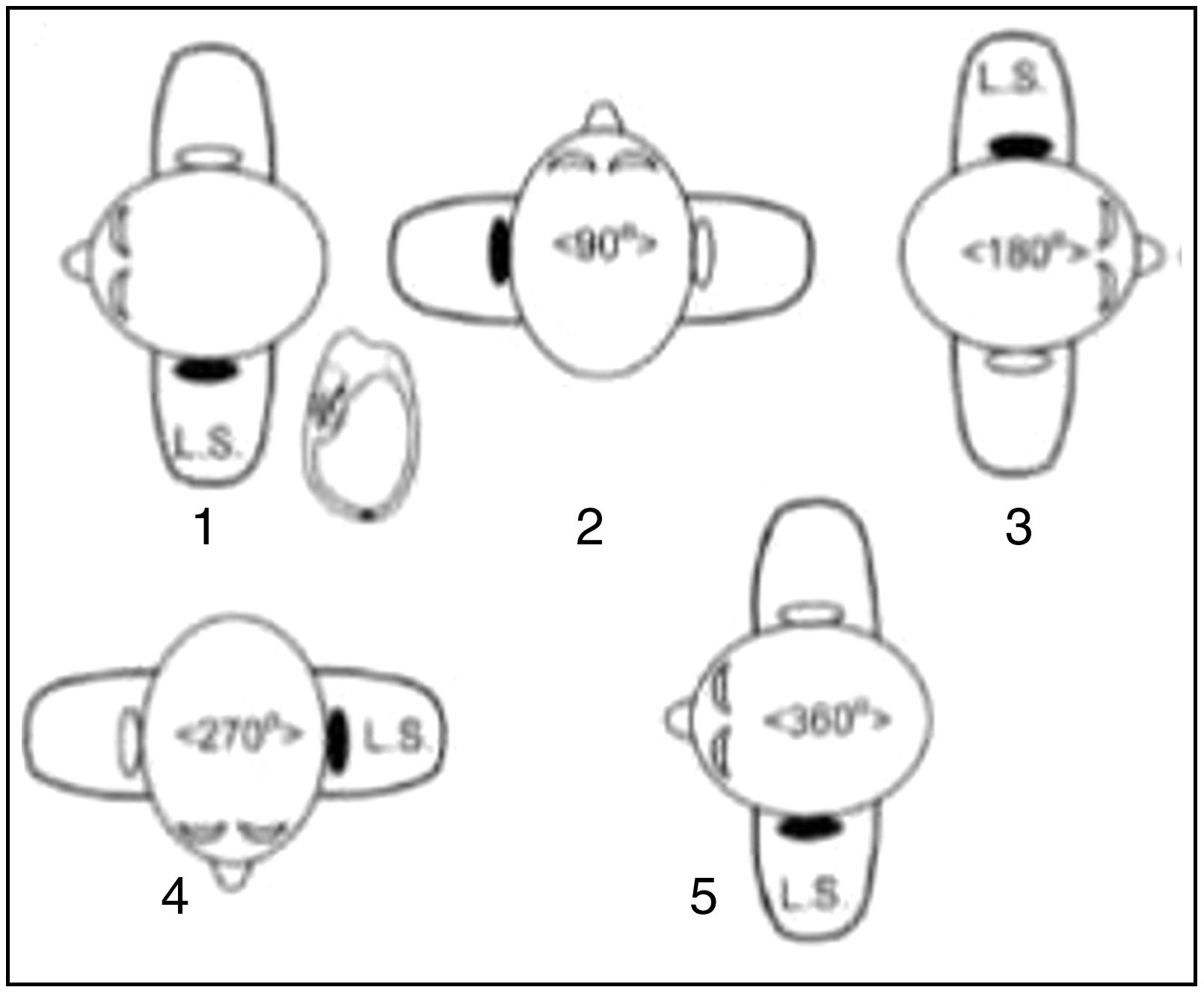
Benign paroxysmal positional vertigo is the most common peripheral vertigo disease. The aim of this paper is to review the results obtained with the different specific particle repositioning manoeuvres, evaluating the possible risk factors linked to a poorer prognosis.
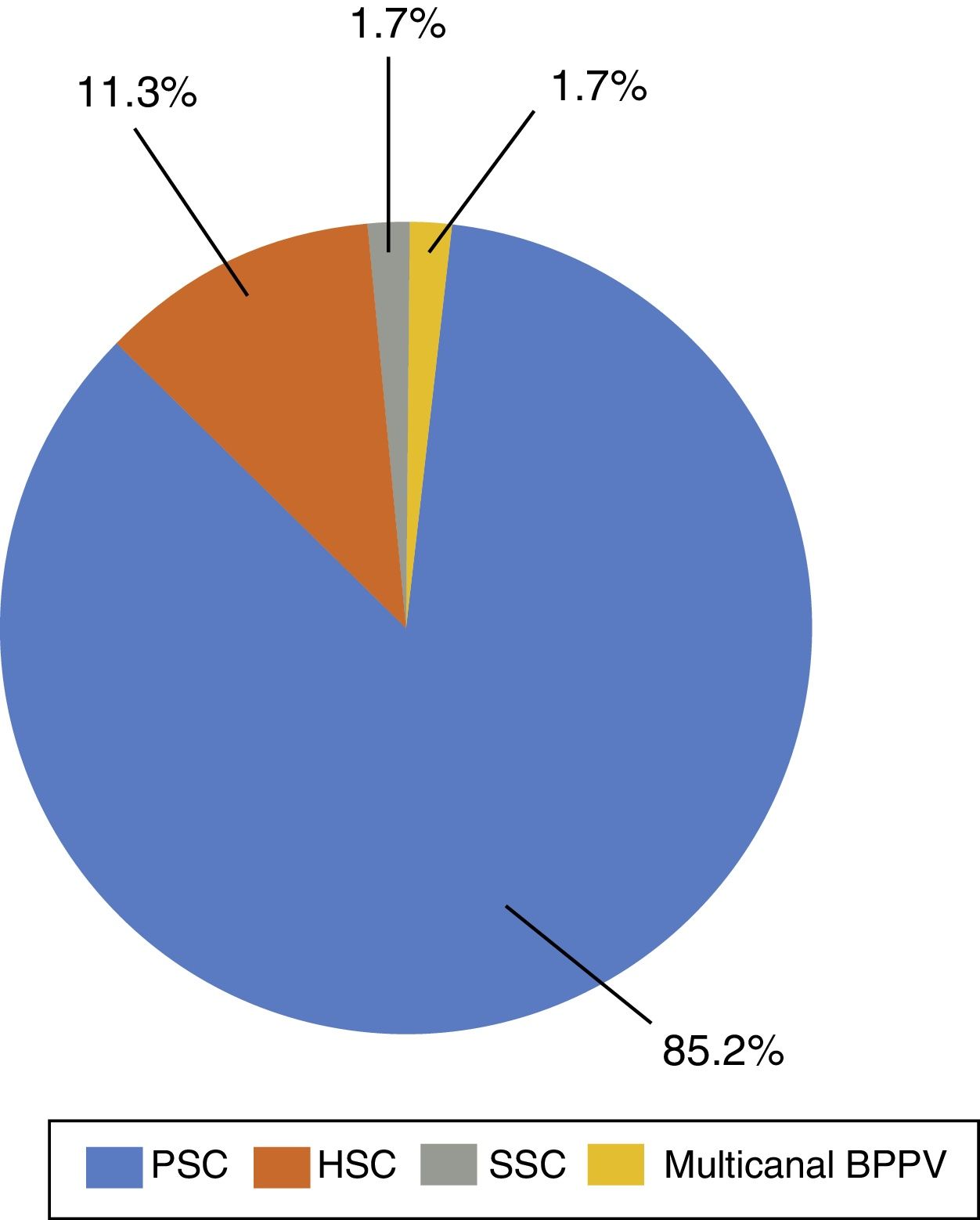
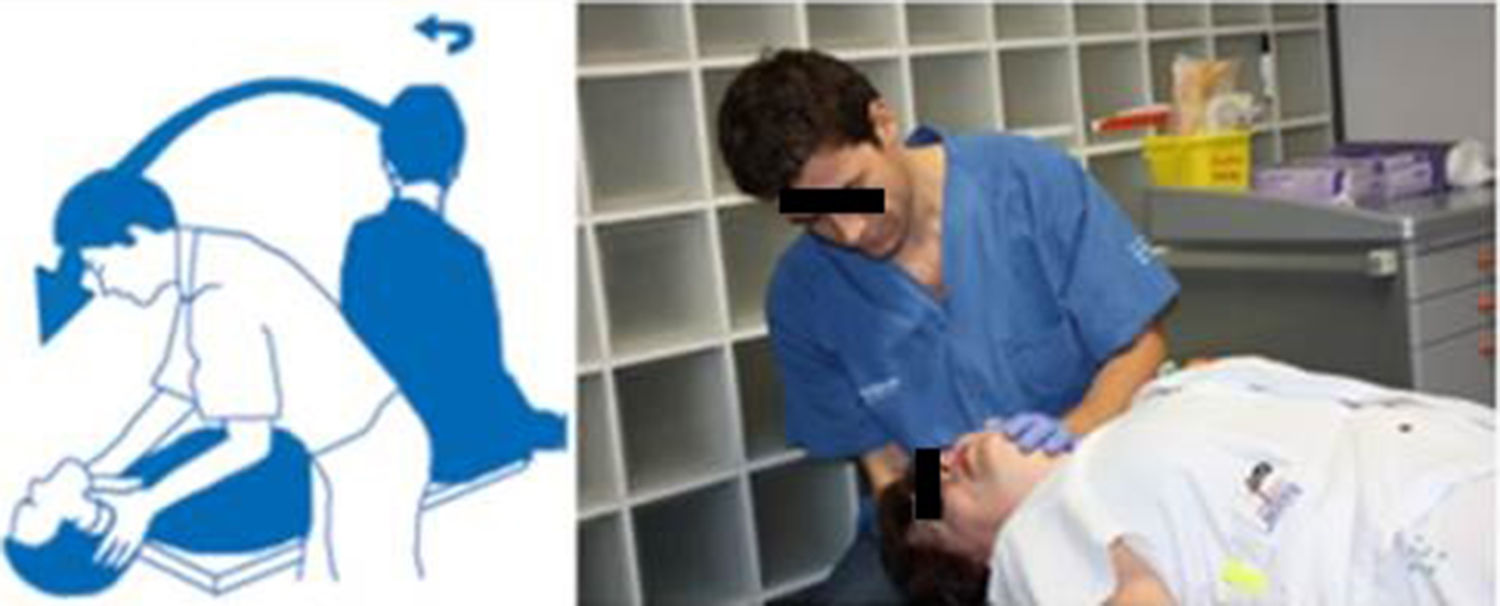
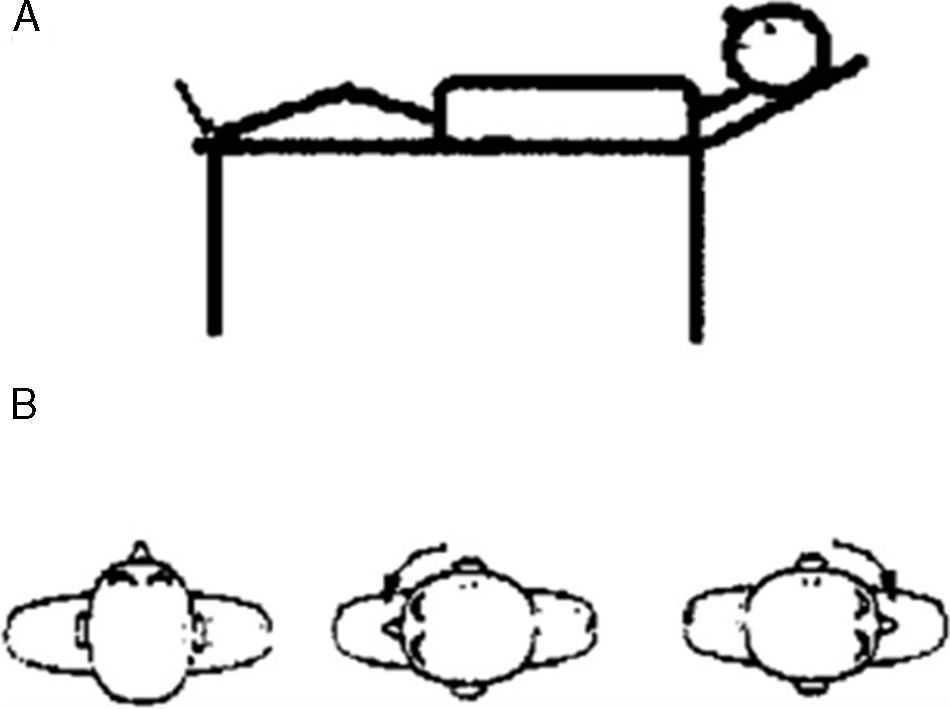
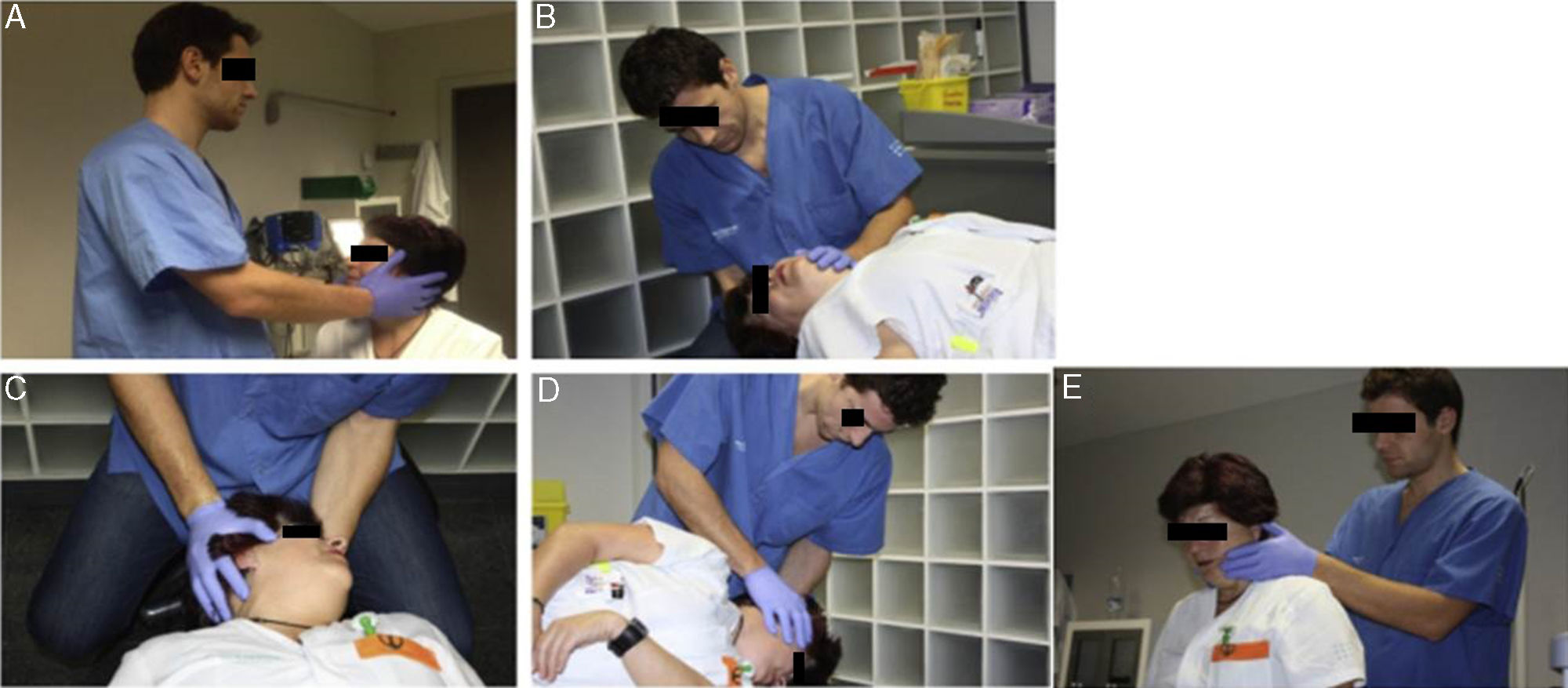
MethodsOne hundred and seventy-six patients with a diagnosis of benign paroxysmal positional vertigo were reviewed retrospectively, of whom 150 had vertigo of the posterior canal, 20 had vertigo of the horizontal canal, 3 had vertigo of the superior canal, and 3 had a double vertigo. The Epley manoeuvre was used to treat the posterior and superior canals, and Lempert manoeuvre was used to treat the horizontal canal. An imaging study by nuclear magnetic resonance with gadolin was always used in refractory cases.
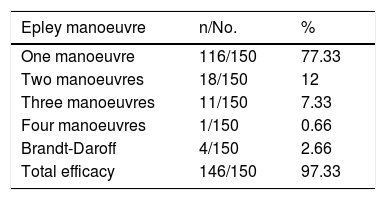
ResultsThe Epley manoeuvre showed an efficacy of 74.6 and 100% at first attempt for posterior and superior canals respectively. The efficacy of the Lempert manoeuvre for the horizontal canal was 72.72% in the patients with canalolithiasis, and 58.33% in the patients with cupulolithiasis. The treatment of patients with more than one affected canal and a history of surgery in the previous month was more difficult.
ConclusionsParticle repositioning manoeuvres show a very high success rate, allowing better results in the treatment of the posterior canal. We need more studies to confirm the suspicion that surgery may be a factor of poorer prognosis.
El vértigo posicional paroxístico benigno es la entidad más frecuente dentro de los vértigos de origen periférico. El objetivo del siguiente trabajo es revisar los resultados obtenidos con las diferentes maniobras de reposicionamiento canalicular específicas para cada tipo de canal semicircular afectado, evaluando posibles factores de riesgo relacionados con un peor pronóstico.
MétodosSe han revisado retrospectivamente 176 pacientes diagnosticados de vértigo posicional paroxístico benigno en nuestro centro, de los cuales 150 tenían vértigo del canal semicircular posterior, 20 del horizontal, 3 del superior y 3 multicanal. Se ha usado la maniobra de Epley para el tratamiento del canal posterior y del superior y la maniobra de Lempert para el tratamiento del horizontal. En los casos refractarios se ha realizado siempre un estudio de imagen cerebral con resonancia.
ResultadosLa maniobra de Epley ha mostrado una eficacia al primer intento del 74,6% para el canal posterior y del 100% para el superior. La eficacia de la maniobra de Lempert para el canal horizontal ha sido del 72,72% en los casos de canalolitiasis y del 58,33% en los de cupulolitiasis. Más complicado ha sido el tratamiento de los pacientes con más de un canal afectado y con antecedente quirúrgico en el mes previo.
ConclusionesLas maniobras de reposicionamiento canalicular permiten alcanzar una tasa de éxito muy alta, obteniendo mejores resultados en el tratamiento del canal posterior. Hacen falta más estudios para confirmar la sospecha de que la cirugía previa pueda ser un factor de peor pronóstico.