The diagnostic accuracy and reliability of the head pitch test in differentiating between different types of BPPV require further investigation. Studying the diagnostic accuracy of the head pitch test in BPPV diagnosis can aid in the development of targeted management strategies for patients presenting with BPPV.
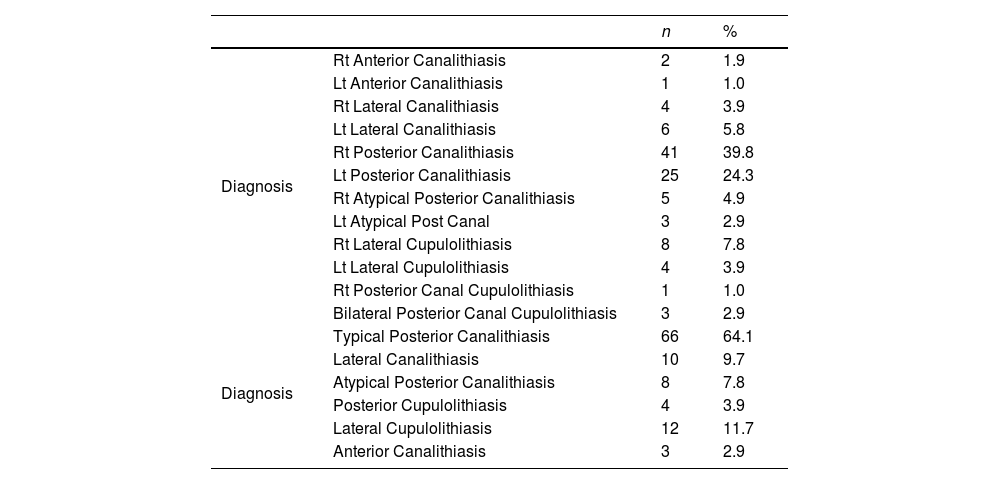
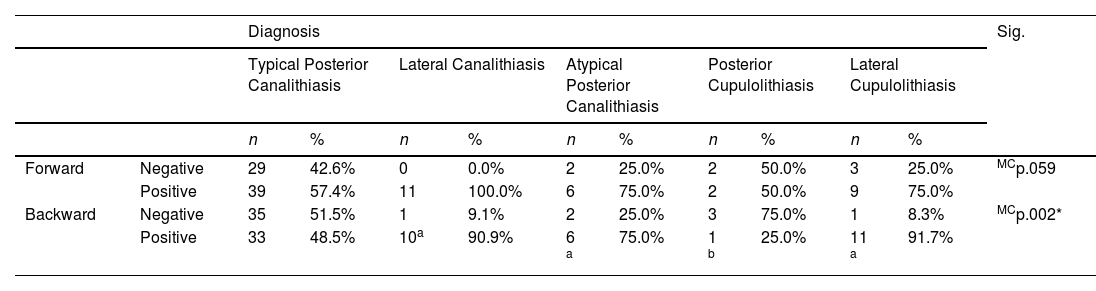
MethodsAll patients who complained of positional vertigo for seconds underwent complete videonystagmography test using ICS Chartr 200 VNG/ENG system (Otometrics, Denmark) including : spontaneous nystagmus, complete occulomotor test battery, then the head pitch test was performed in two positions: first the patient’s head was bent 90 degrees forwards, then 60 degrees backwards for approximately 1 min each. If nystagmus was observed, its direction was recorded.1 All patients then underwent gold standard tests for positional vertigo including both Dix-Hallpike maneuver and the supine roll tests.
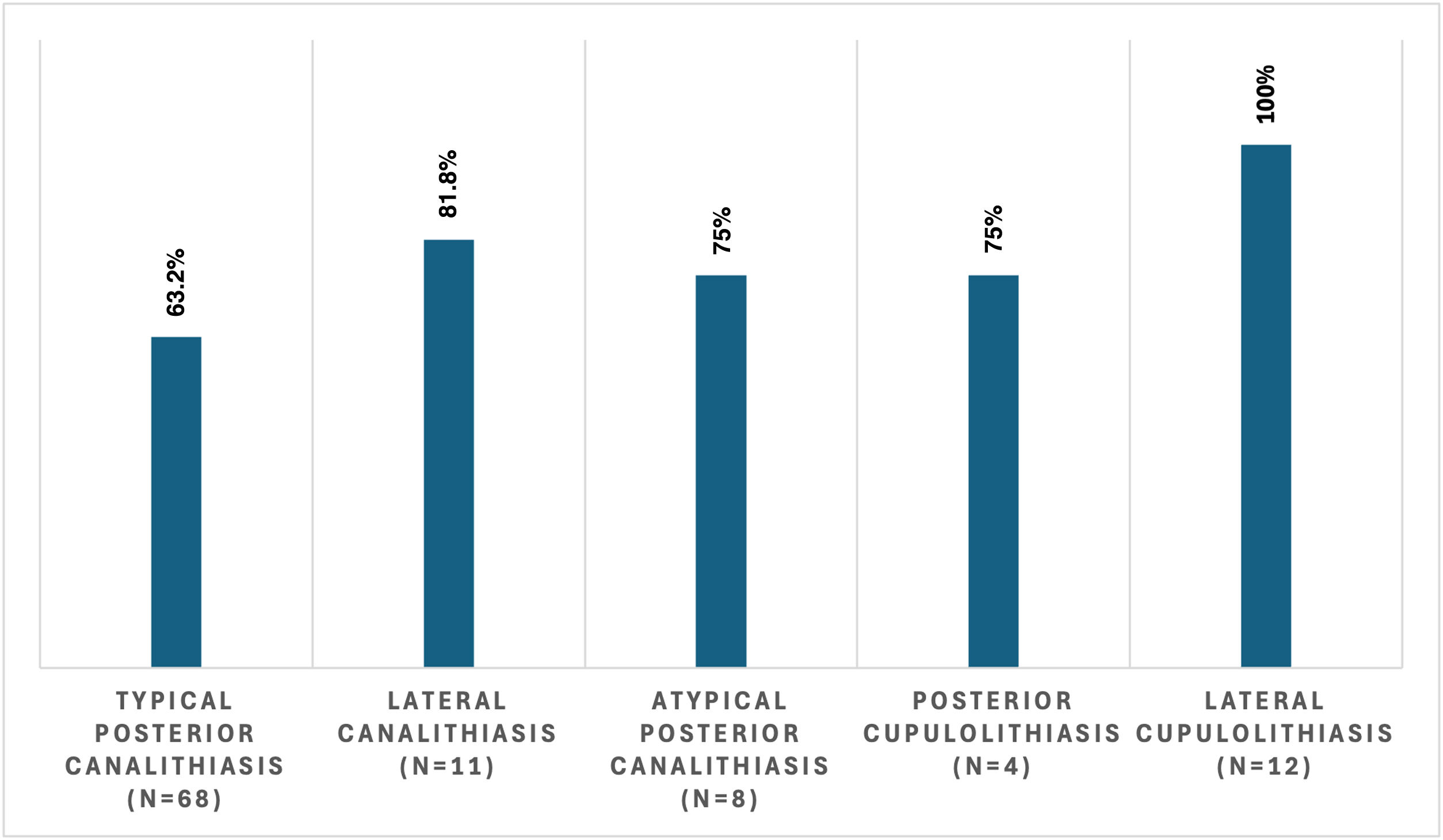
ResultsThe sensitivity (true positive cases) was defined as the head pitch (HPT) test being positive and showing the correct nystagmus for different categories of BPPV. The sensitivity of the experimental HPT was compared to the gold standard tests (100% sensitive) for diagnosis of different categories of vertical canal and lateral canal BPPV. It was highest (100%) for Lateral Cupulolithiasis patients (n = 12) and Anterior canal Canalithiasis (n = 3) and lowest (68%) for Typical Posterior Canalithiasis patients (n = 68).
ConclusionThis study supports the addition of the head pitch test in the routine assessment of patients with positional vertigo. As it could shorten the examination time and decrease the repositioning maneuvers which may cause severe autonomic symptoms.
La precisión diagnóstica y la fiabilidad de la prueba de cabeceo para diferenciar entre diferentes tipos de VPPB requieren mayor investigación. El estudio de la precisión diagnóstica de la prueba de cabeceo en el diagnóstico de VPPB puede contribuir al desarrollo de estrategias de tratamiento específicas para pacientes con VPPB.
MétodosTodos los pacientes que presentaron vértigo posicional durante segundos se sometieron a una videonistagmografía completa con el sistema ICS Chartr 200 VNG/ENG (Otometrics, Dinamarca), que incluyó: nistagmo espontáneo, batería completa de pruebas oculomotoras. Posteriormente, se realizó la prueba de cabeceo en dos posiciones: primero, con la cabeza del paciente inclinada 90 grados hacia adelante y luego 60 grados hacia atrás durante aproximadamente 1 minuto cada una. Si se observó nistagmo, se registró su dirección1. Todos los pacientes fueron sometidos a pruebas estándar de oro para el vértigo posicional, incluidas la maniobra de Dix-Hallpike y las pruebas de giro supino.
ResultadosLa sensibilidad (casos positivos verdaderos) se definió como la prueba de inclinación de la cabeza (HPT) positiva y con nistagmo correcto para diferentes categorías de VPPB. La sensibilidad de la HPT experimental se comparó con las pruebas de referencia (100%) para el diagnóstico de diferentes categorías de VPPB del conducto vertical y del conducto lateral. La sensibilidad fue máxima (100%) para los pacientes con cupulolitiasis lateral (n = 12) y canalitiasis del conducto anterior (n = 3), y mínima (68%) para los pacientes con canalitiasis posterior típica (n = 68).
ConclusiónEste estudio respalda la incorporación de la prueba de cabeceo en la evaluación rutinaria de pacientes con vértigo posicional, ya que podría acortar la duración del examen y disminuir las maniobras de reposicionamiento que pueden causar síntomas autonómicos graves.