Sensory neural hearing loss (SNHL) is a disorder characterized by an important deterioration of the auditory function. Re-establishing normal ion homeostasis of the endolymph could be related to hearing recovery and it might be mediated by mineralocorticoids.
The main purpose of this preliminary, randomized controlled clinical trial was assessing the recovery of idiopathic sensory neural cochlear hearing loss (SNHL) by comparing the efficacy of 2 types of steroids versus vasodilators.
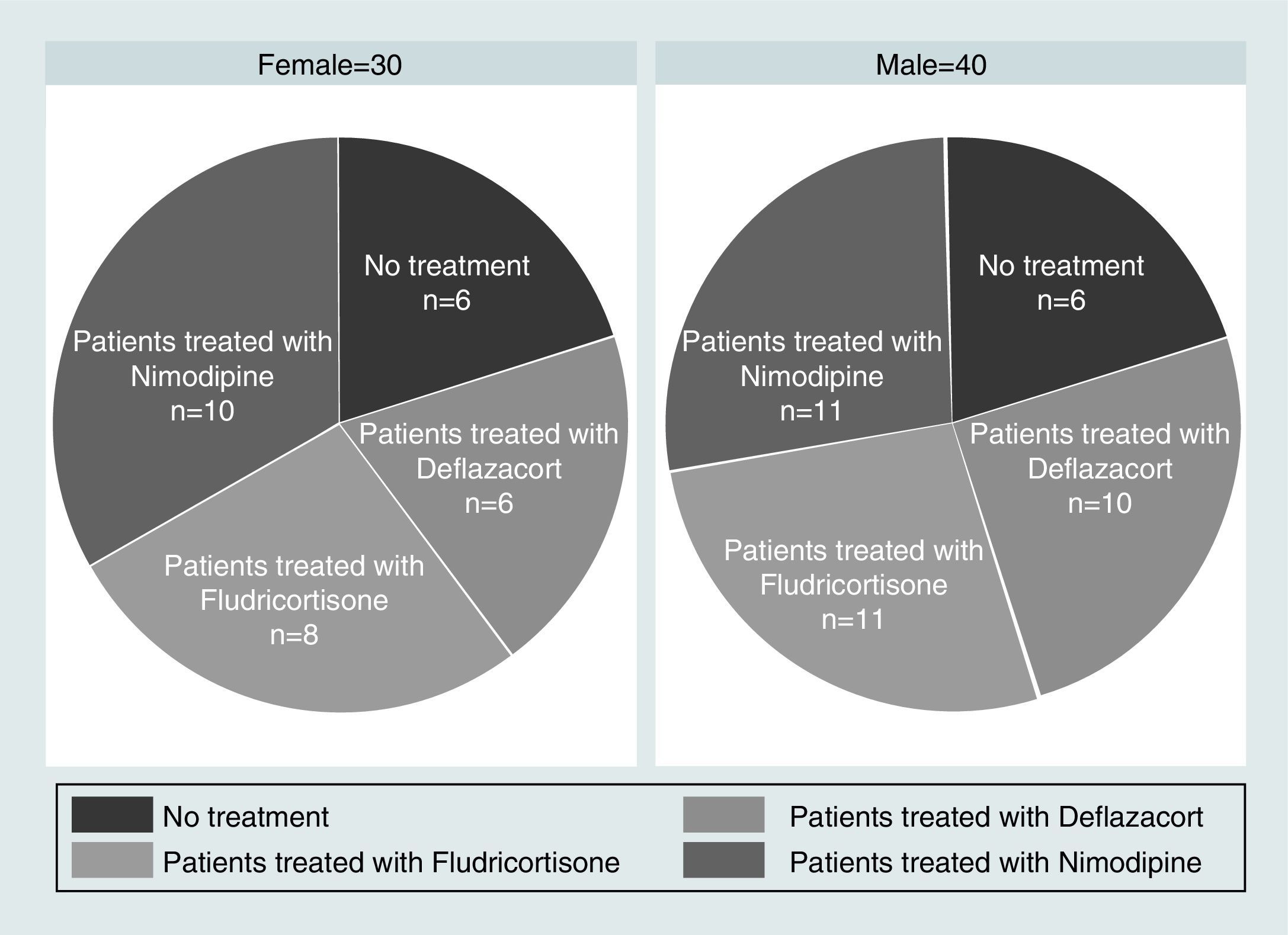
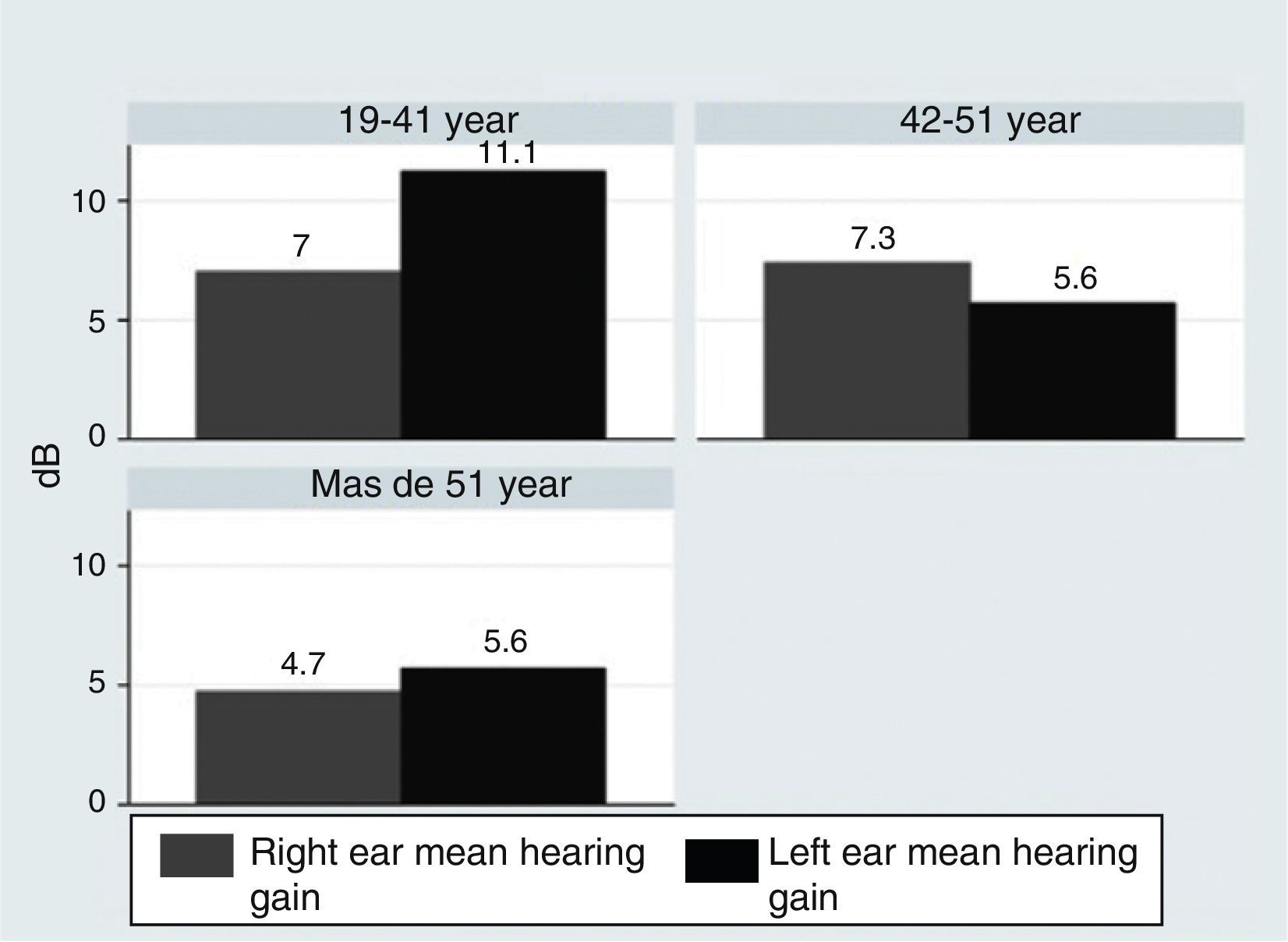
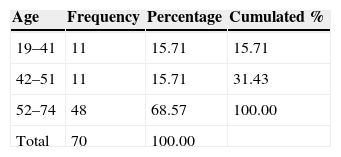
Materials and MethodsThe 3-month intervention involved 70 patients, allocated into 4 different groups: a control with no medication, consisting of 14 patients (8 men and 6 women); a vasodilator group of 21 patients (11 men and 10 women); a glucocorticoid group with 16 patients (10 men and 6 women); and a mineralocorticoid therapy group, consisting of 19 patients (11 men and 8 women). The level of hearing loss and its topography were estimated using Liminal Tone Audiometry (LTA) and Auditory Brainstem Response (ABR).
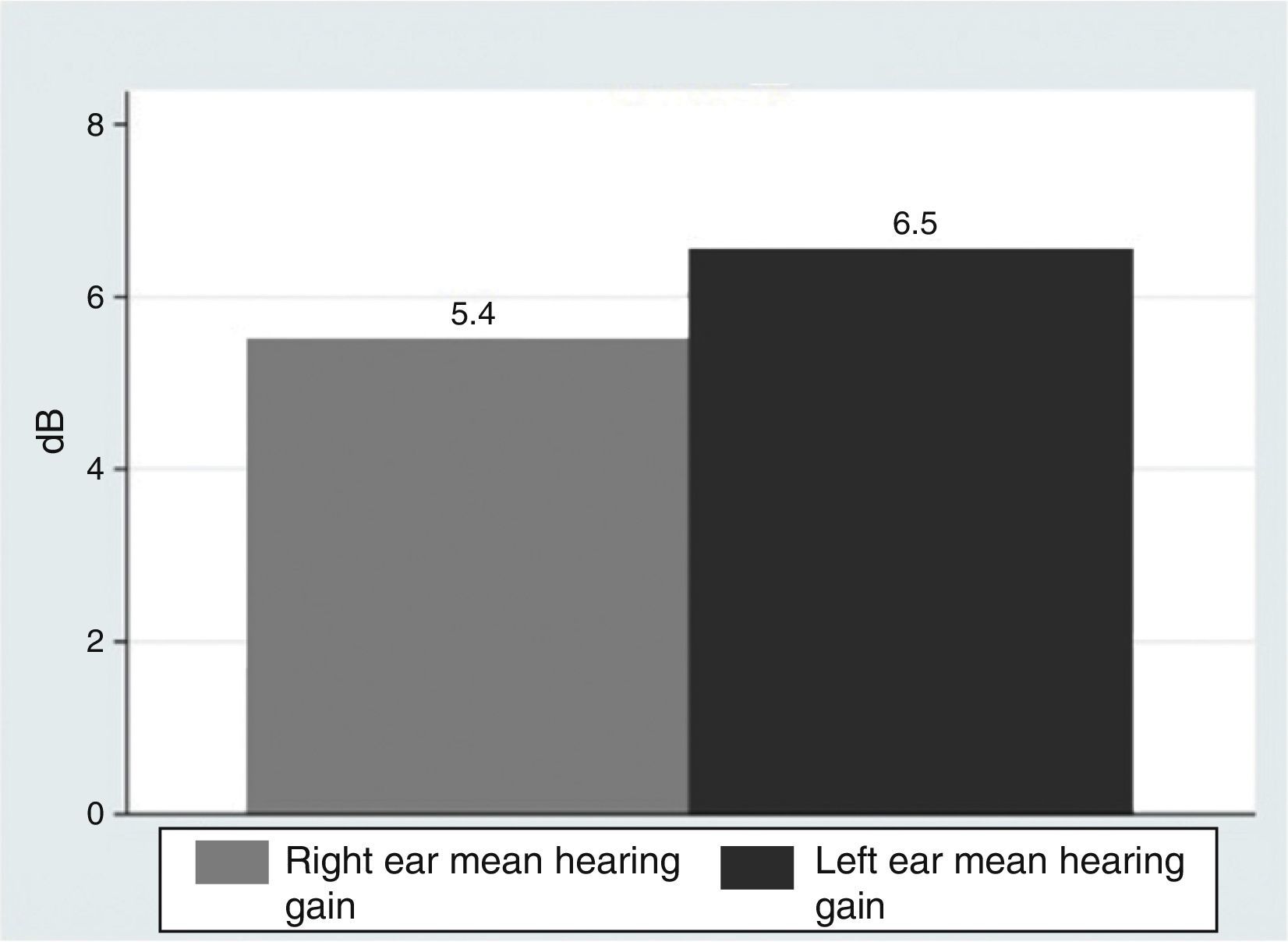
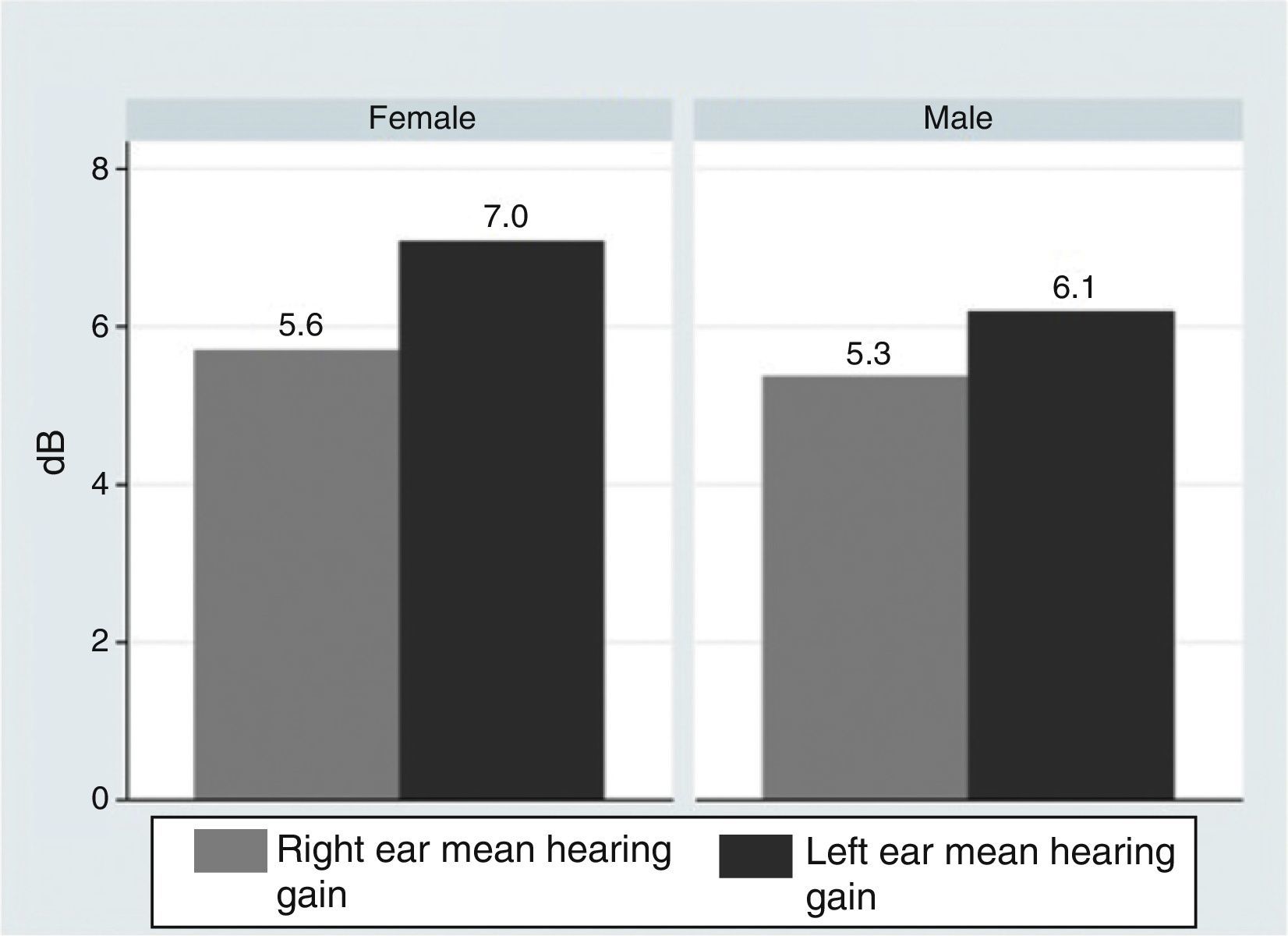
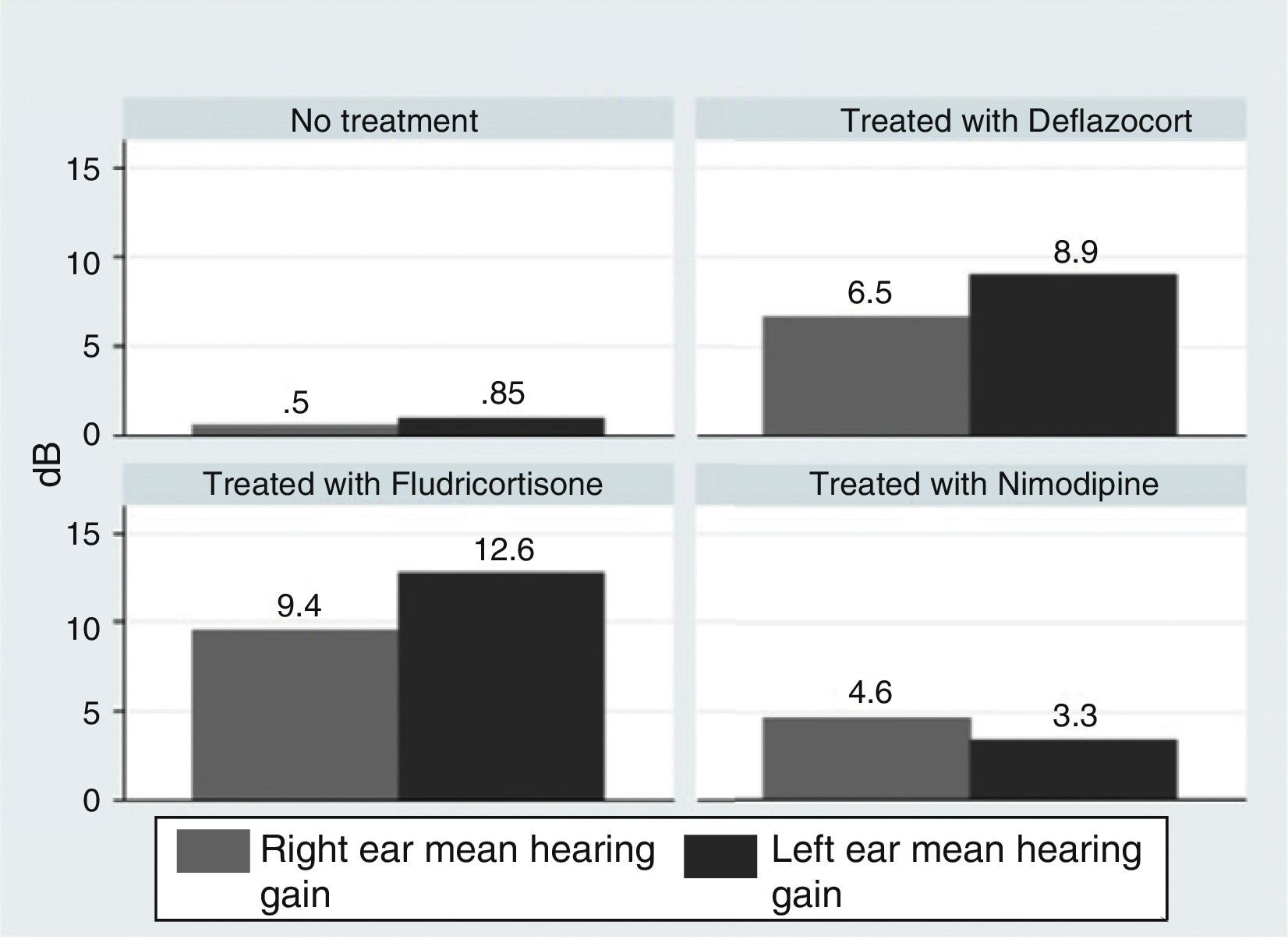
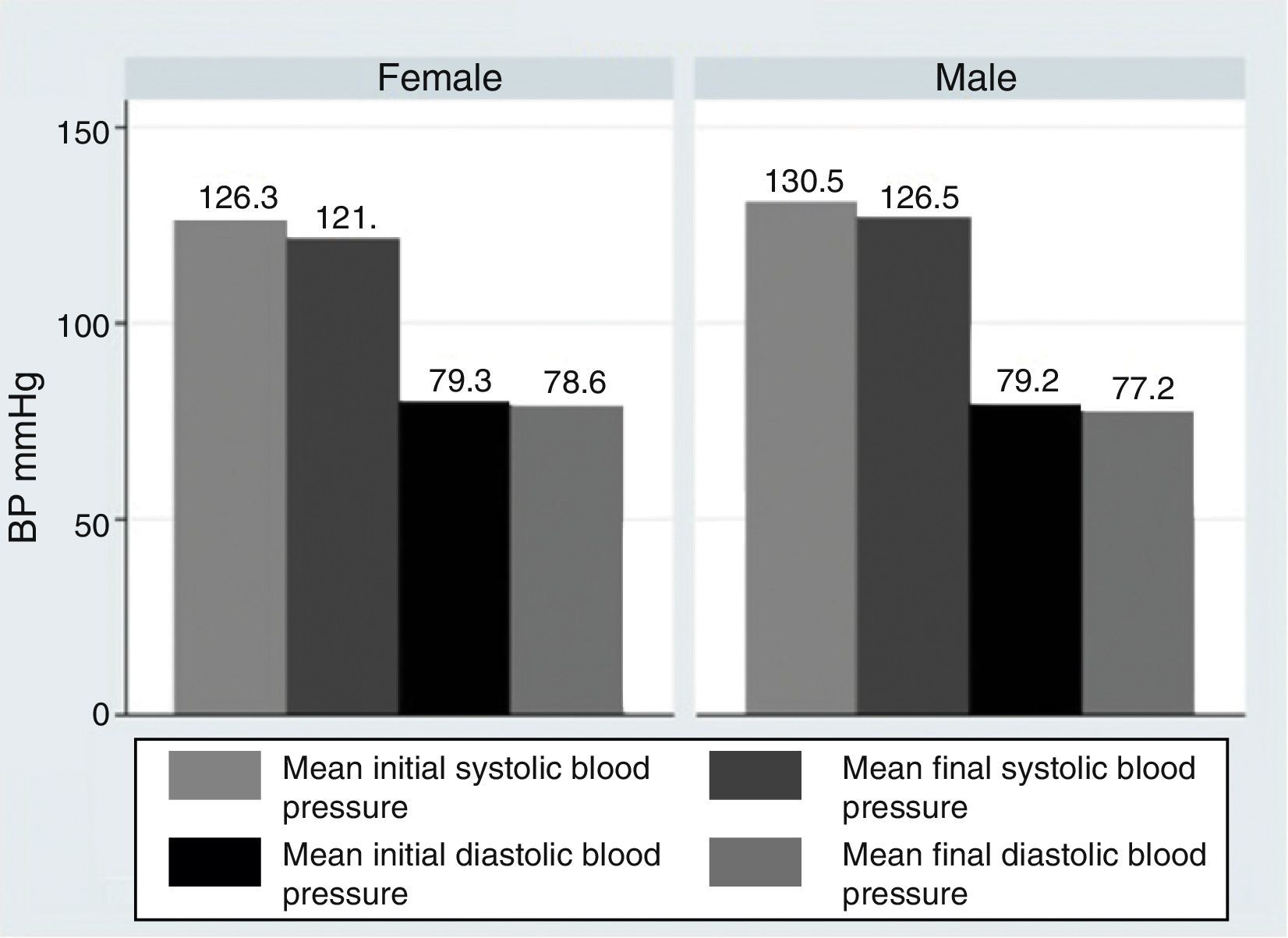
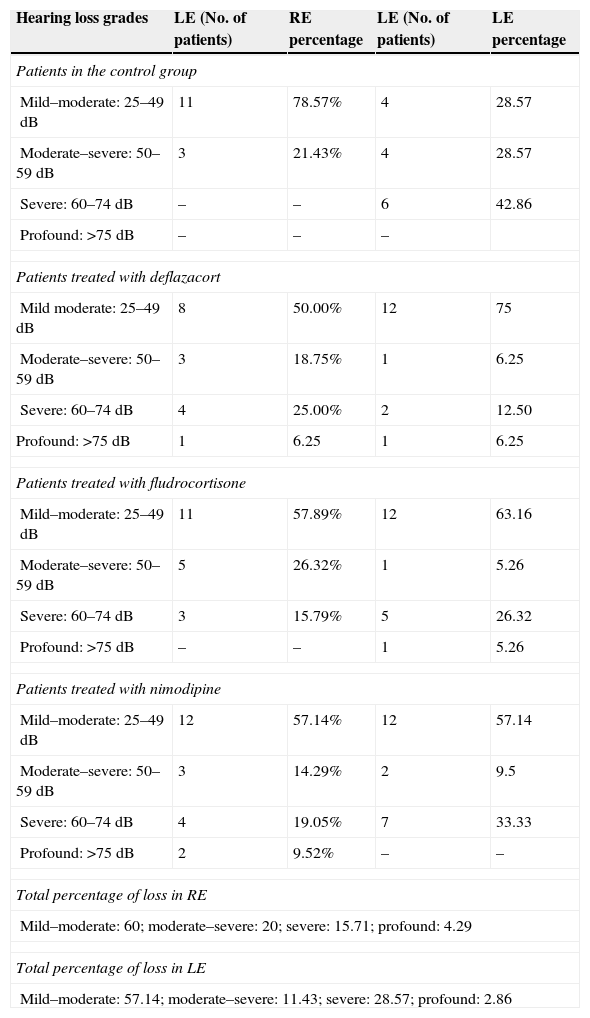
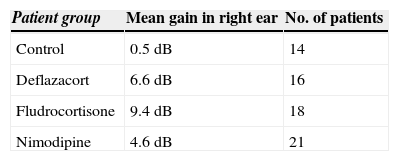
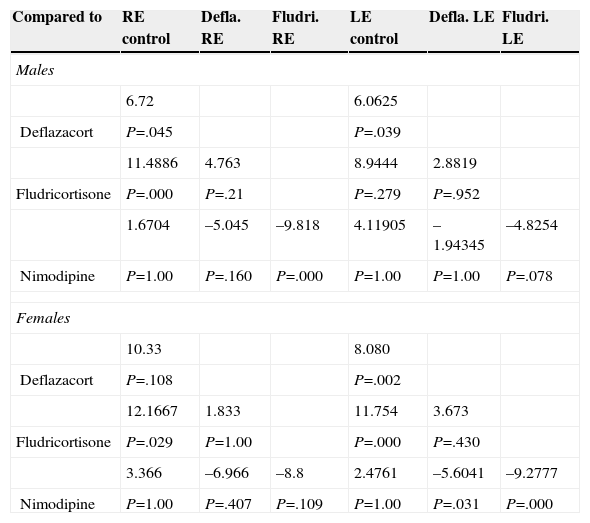
ResultsOur research found overall greater efficacy of mineralocorticoids versus glucocorticoids and vasodilators. There was better response in women than in men and it was higher from the left ear, regardless of patient gender.
ConclusionsThe hearing gain was significantly superior in the mineralocorticoid group, followed by the glucocorticoid group. However, the responses to vasodilators were lesser and of low statistical significance.
La hipoacusia neurosensorial (HNS) puede conducir a causar grave deterioro auditivo. Su recuperación funcional parece relacionarse con el control de la homeostasis iónica coclear experimentalmente dependiente de los mineralocorticoides.
El objetivo de este trabajo es valorar la eficacia terapéutica comparando 2 modalidades de corticoides frente a los vasodilatadores en pacientes con HNS idopática coclear (HNSIC).
Material y métodosEl ensayo dura 3 meses, se realiza en 70 pacientes asignados aleatoriamente en 4 grupos: grupo control, sin medicación, formado por 14 pacientes (8 varones y 6 mujeres); grupo tratado con vasodilatadores formado por 21 pacientes (11 hombres y 10 mujeres); grupo sometido a terapia glucocorticoidea formado por 16 pacientes (10 varones y 6 mujeres); y grupo sometido a terapia mineralocorticoidea formado por 19 pacientes (11 varones y 8 mujeres). La valoración del nivel de pérdida auditiva y su topografía se estiman mediante audiometría tonal liminal (ATL) y potenciales auditivos de tronco cerebral (PEATC).
ResultadosEncontramos mejor respuesta al tratamiento con los mineralocorticoides que con los glucocorticoides, siendo la respuesta más pobre para los vasodilatadores. Esta respuesta es mayor en las mujeres que en los hombres, y en general observamos mejor respuesta por parte del oído izquierdo, con independencia del sexo del paciente.
ConclusionesLas ganancias auditivas son significativamente mayores con los mineralocorticoides, seguidas por los glucocorticoides, mientras que con los vasodilatadores las respuestas son pobres y no significativas.