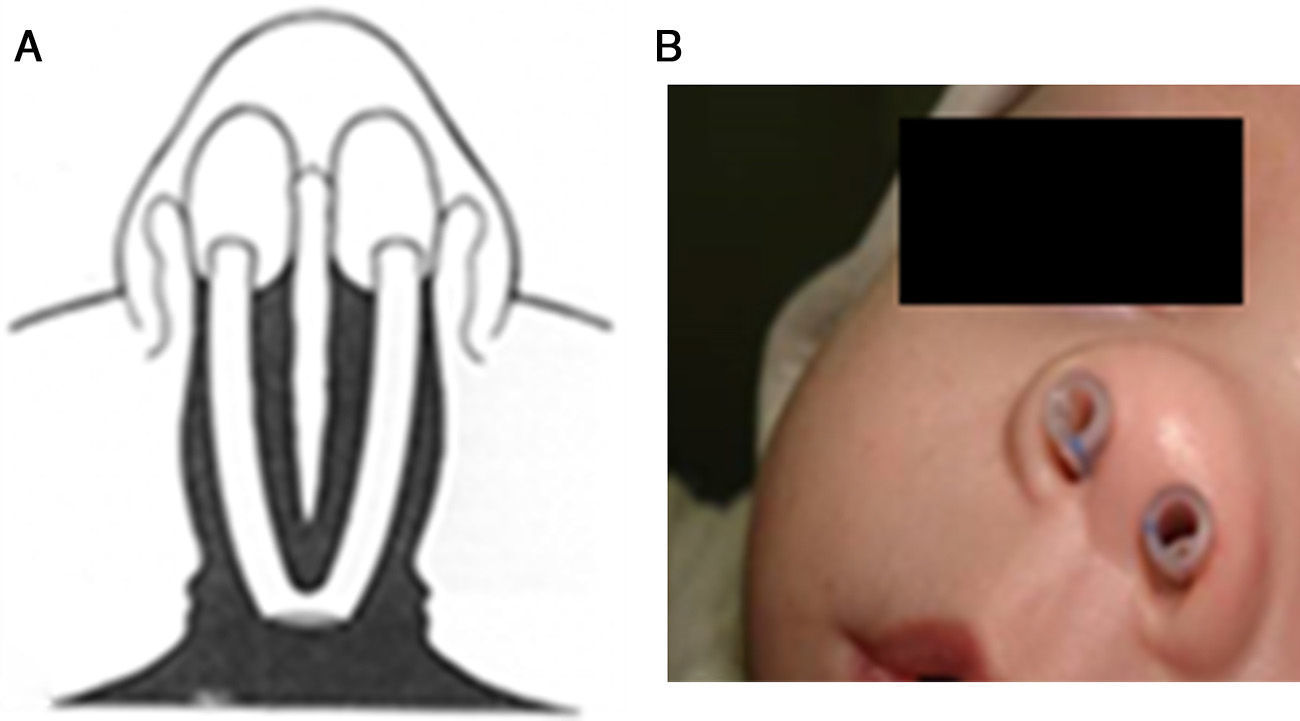
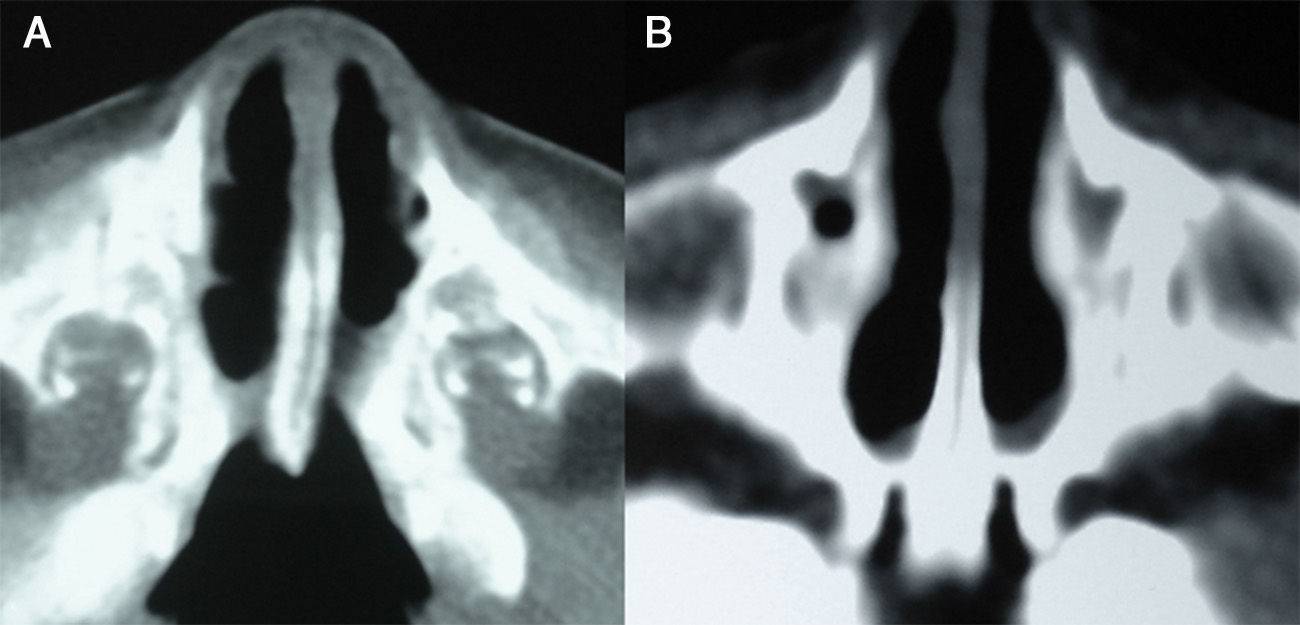
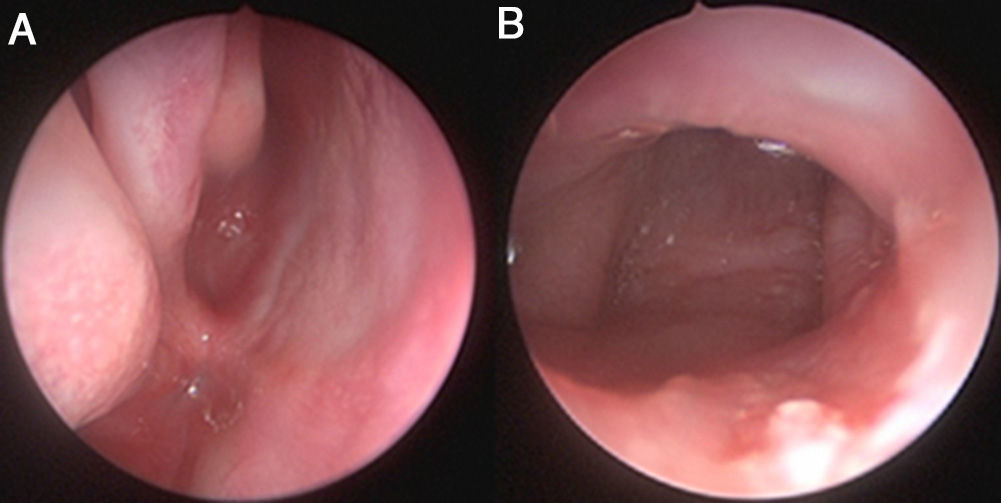
Choanal atresia is the most common congenital nasal anomaly. Diagnosis is confirmed by endoscopic examination and computed tomography. The definitive treatment is surgical, and different surgical techniques and approaches are used. We describe our experience in transnasal microsurgical treatment of congenital choanal atresia.
MethodsWe retrospectively evaluated 49 patients with congenital choanal atresia operated in the Department of Respiratory Endoscopy over a period of 20 years. The clinical variables analysed were type of atretic plate, age at diagnosis and surgery, associated malformations, maternal history of hyperthyroidism treated with methimazole during pregnancy, mode of airway stabilisation before surgery, surgical technique, complications, and outcome.
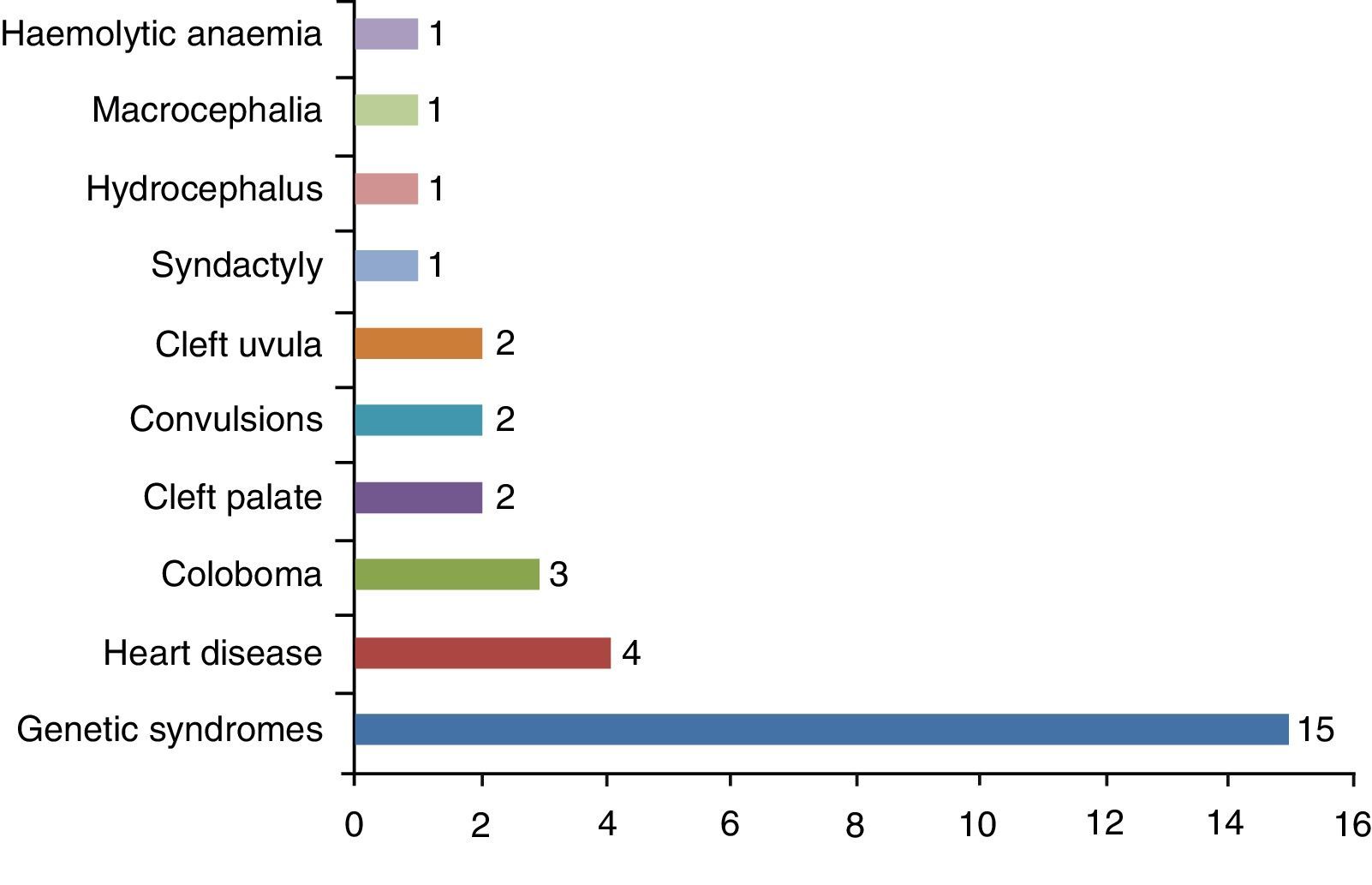
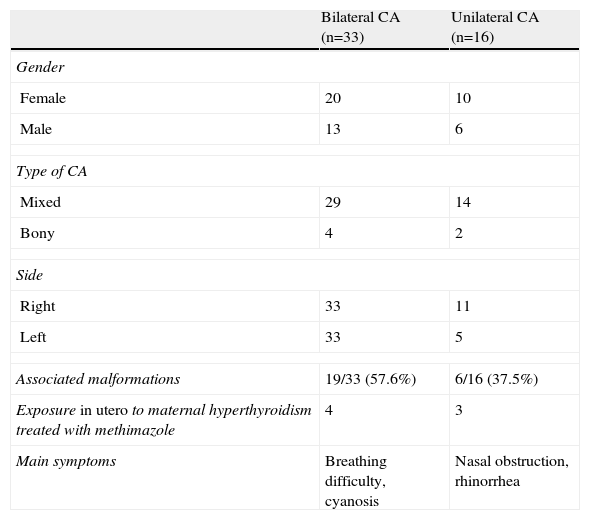
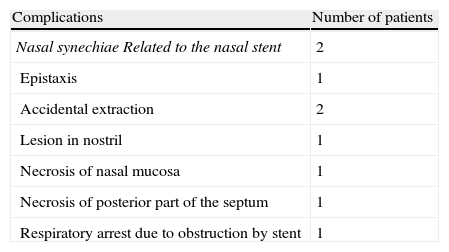
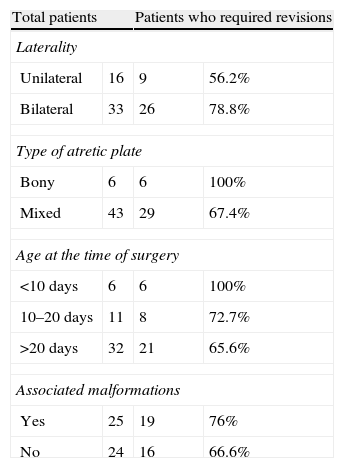
ResultsMixed bilateral choanal atresia was the most frequent (29 cases). Its incidence was higher in females (61.2%). Almost 51% of patients showed associated malformations, and 7 had a history of maternal hyperthyroidism treated with methimazole during pregnancy. The surgical procedure consisted of a transnasal microscopic approach and placement of a silicone endonasal stent for one to 12 weeks. Thirty-five patients required revision after surgery. Nine patients had complications. Suitable nasal ventilation was achieved in 46 patients (93.9%). One patient died of causes unrelated to the surgery. Two patients with permeable choanae remain with tracheotomy.
ConclusionThe transnasal microsurgical repair with endonasal stent proved to be a safe and effective procedure.
La atresia de coanas es la anomalía congénita nasal más común. El diagnóstico se confirma mediante examen endoscópico nasal y tomografía computarizada de macizo craneofacial. El tratamiento definitivo es quirúrgico, existiendo diferentes técnicas y vías de abordaje. Presentamos nuestra experiencia en el tratamiento microquirúrgico transnasal de la atresia de coanas congénita.
MétodosSe evaluaron de forma retrospectiva 49 pacientes con atresia de coanas congénita intervenidos quirúrgicamente en el Servicio de Endoscopia Respiratoria durante un periodo de 20 años. Las variables analizadas fueron el tipo de placa atrésica, la edad en el momento del diagnóstico y de la cirugía, las malformaciones asociadas, el antecedente materno de hipertiroidismo tratado con metimazol durante el embarazo, el modo de estabilización de la vía aérea previa a la cirugía, la técnica quirúrgica utilizada, las complicaciones y los resultados.
ResultadosLa atresia de coanas mixta bilateral fue la más frecuente (29 casos), siendo la incidencia mayor en el sexo femenino (61,2%). El 51% presentaba malformaciones asociadas. Siete pacientes tenían el antecedente materno de hipertiroidismo tratado con metimazol durante el embarazo. El procedimiento quirúrgico consistió en un abordaje transnasal con microscopio y colocación de stent intranasal de silicona durante una a 12 semanas. Treinta y cinco pacientes requirieron revisión posquirúrgica. Nueve pacientes presentaron complicaciones. Se logró ventilación nasal adecuada en 46 pacientes (93,9%). Un paciente falleció de causa no relacionada a la cirugía. Dos pacientes con coanas permeables permanecen con traqueotomía.
ConclusiónLa reparación microquirúrgica transnasal con colocación de stent intranasal resultó ser un procedimiento seguro y eficaz.