La hipoacusia neurosensorial (HNS) es el déficit sensorial más prevalente en nuestro medio. La secuenciación genómica de nueva generación (NGS) permite obtener un diagnóstico etiológico en un alto porcentaje de pacientes. Nuestro estudio piloto muestra los resultados de la aplicación sistemática de la NGS en una Unidad de Hipoacusia Infantil, así como sus implicaciones en el manejo clínico de los pacientes y sus familiares.
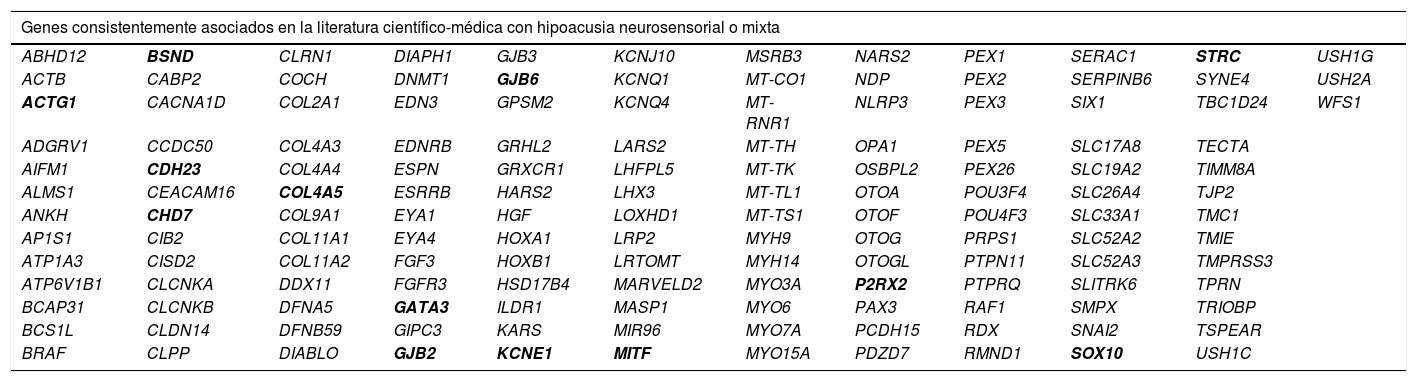
Material y métodoSe incluyó a 27 pacientes diagnosticados de HNS entre 2014 y 2017 en los que se descartó una causa ambiental. El test genético consistió en un panel de genes analizados mediante NGS (panel OTOgenicsTM). Este panel ha sido diseñado para incluir genes asociados con hipoacusia neurosensorial o mixta, de inicio precoz o tardío, sindrómica y no sindrómica, independientemente de su patrón de herencia.
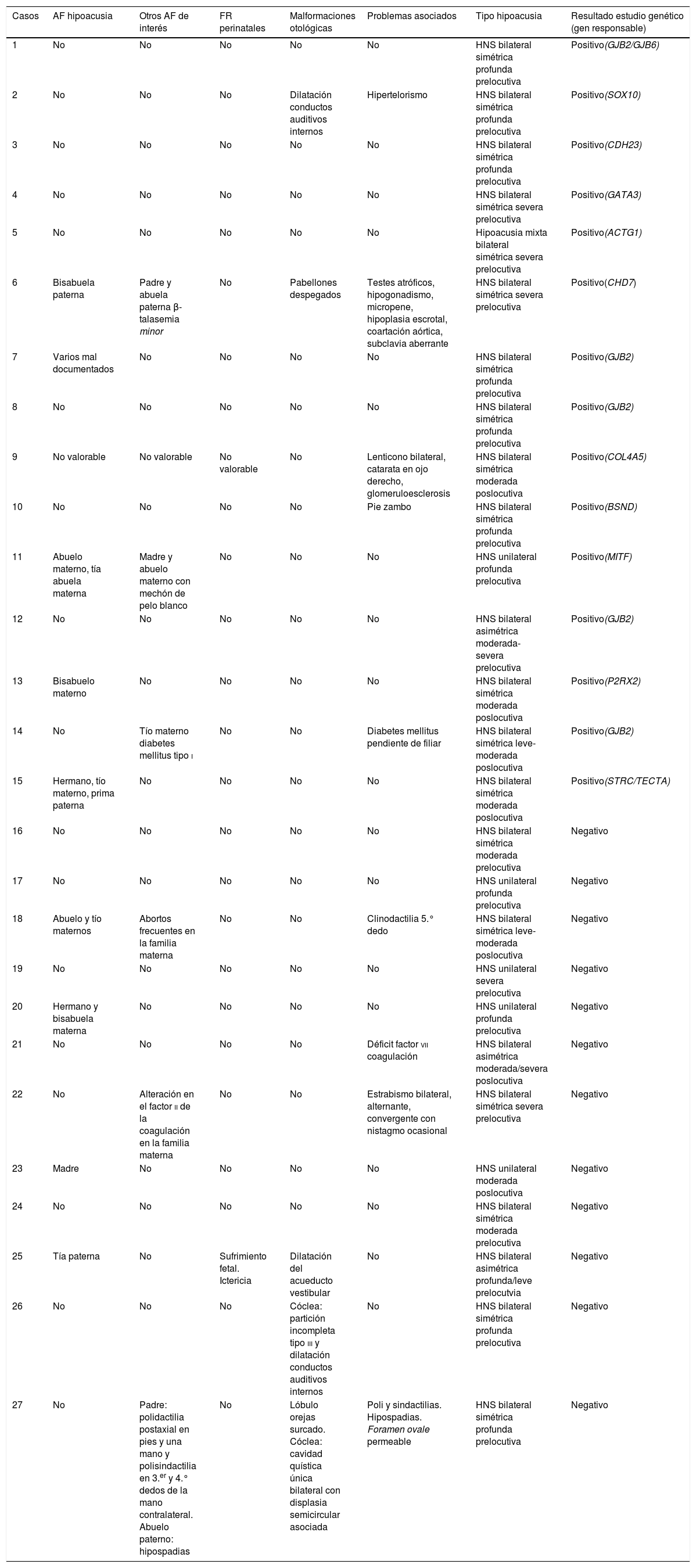
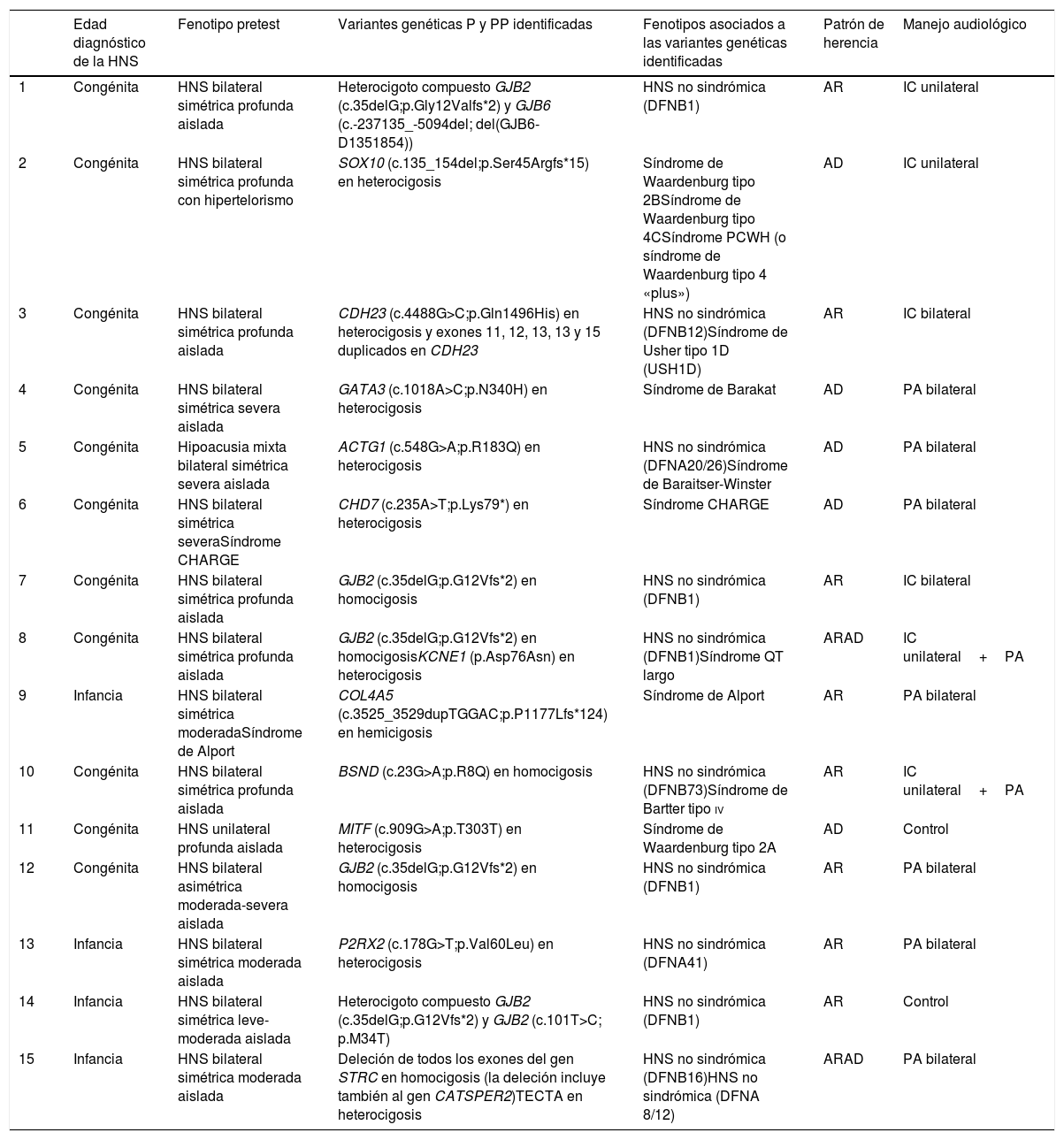
ResultadosSe obtuvo un diagnóstico genético en el 56% (15/27) de los pacientes (62% en el caso de las HNS bilaterales); 5/27 (19%) presentaron variantes patogénicas en el gen GJB2 y el resto variantes patogénicas o probablemente patogénicas en otros genes asociados con HNS aislada (PR2X2, TECTA y STRC), con HNS sindrómicas (CHD7, GATA3, COL4A5, MITF y SOX10) o con HNS sindrómicas y no sindrómicas (BSND, ACTG1 y CDH23).
DiscusiónEl diagnóstico etiológico de la HNS supone un desafío en la práctica clínica. Nuestra serie demuestra que es posible implementar el diagnóstico genético en la rutina asistencial y que esta información tiene implicaciones pronósticas y terapéuticas.
Sensorineural hearing loss (SNL) is the most prevalent sensory deficit in our environment. Next generation genomic sequencing (NGS) enables an aetiological diagnosis in a high percentage of patients. Our pilot study shows the results of the systematic application of NGS in a Childhood Hearing Loss Unit, as well as its implications for the clinical management of patients and their families.
Material and methodWe included 27 patients diagnosed with SNL between 2014 and 2017, in which an environmental cause was ruled out. The genetic test consisted of a panel of genes analyzed by NGS (OTOgenicsTM panel). This panel has been designed to include genes associated with sensorineural or mixed hearing loss, early onset or late, syndromic and non-syndromic, regardless of their inheritance pattern.
ResultsA genetic diagnosis was obtained in 56% (15/27) of the patients (62% in the case of bilateral SNL). Of the patients, 5/27 (19%) presented pathogenic variants in the GJB2 gene and the rest pathogenic and / or probably pathogenic variants in other genes associated with isolated SNL (PR2X2, TECTA and STRC), with syndromic SNL (CHD7, GATA3, COL4A5, MITF and SOX10) or with syndromic and non-syndromic SNL (BSND, ACTG1 and CDH23).
DiscussionThe aetiological diagnosis of SNL is a challenge in clinical practice. Our series demonstrates that it is possible to implement genetic diagnosis in the care routine and that this information has prognostic and therapeutic implications.