This was a retrospective study reviewing 93 cases of retrosternal goitre (RG) operated in our department, with the aim of describing epidemiological and clinical data and discussing the surgical challenges of RG.
Patients and methodsFrom January 2004 to December 2012, 35 men and 58 women presenting with RG had surgery. Eighty-nine cases (95.7%) underwent cervicotomy, and a sternotomy was mandatory in 4 cases (4.3%). Laryngoscopy was performed in all cases. A second preoperative laryngoscopy by a senior was mandatory for patients with hoarseness or dyspnea even if the initial laryngeal exam was normal.
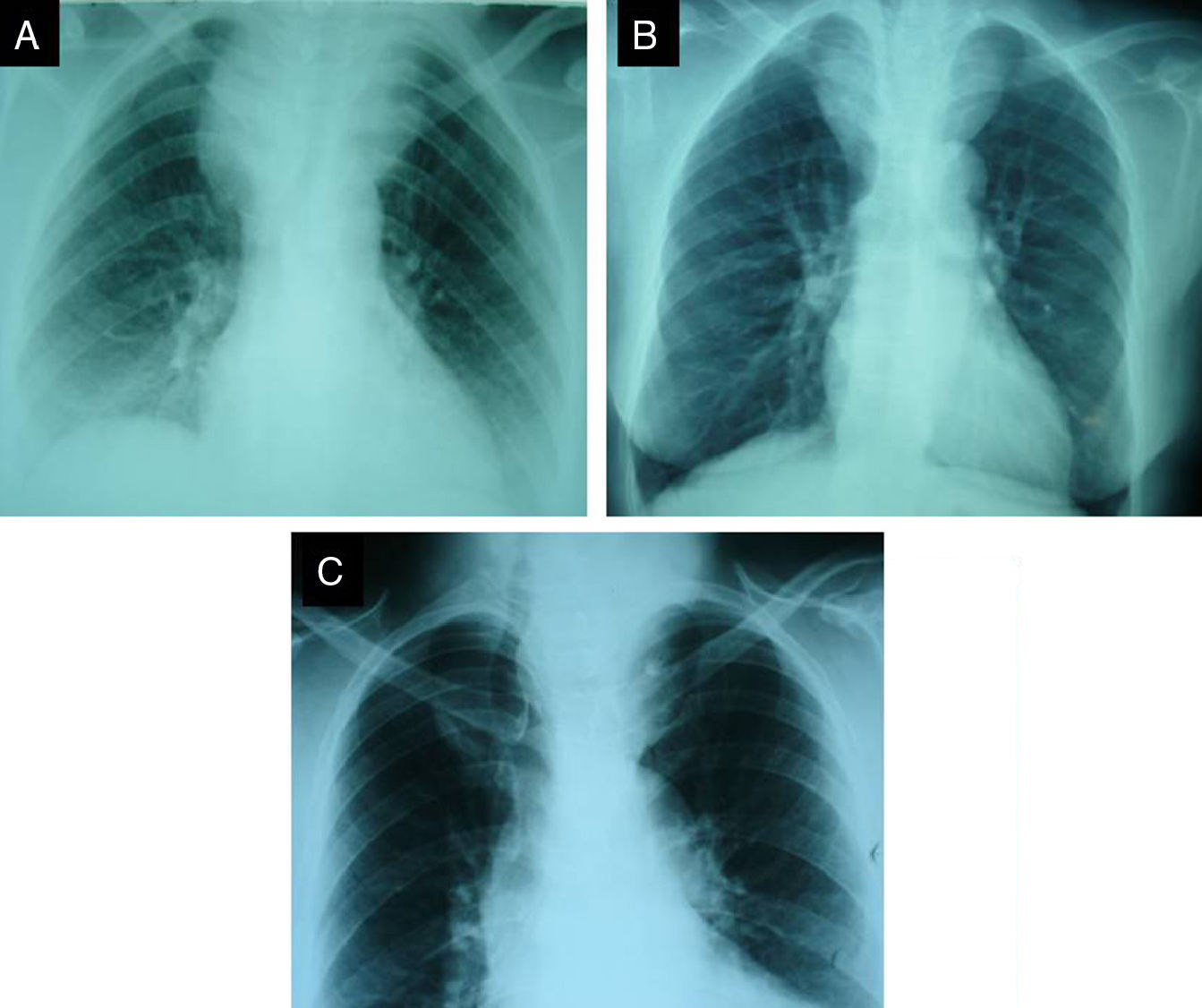
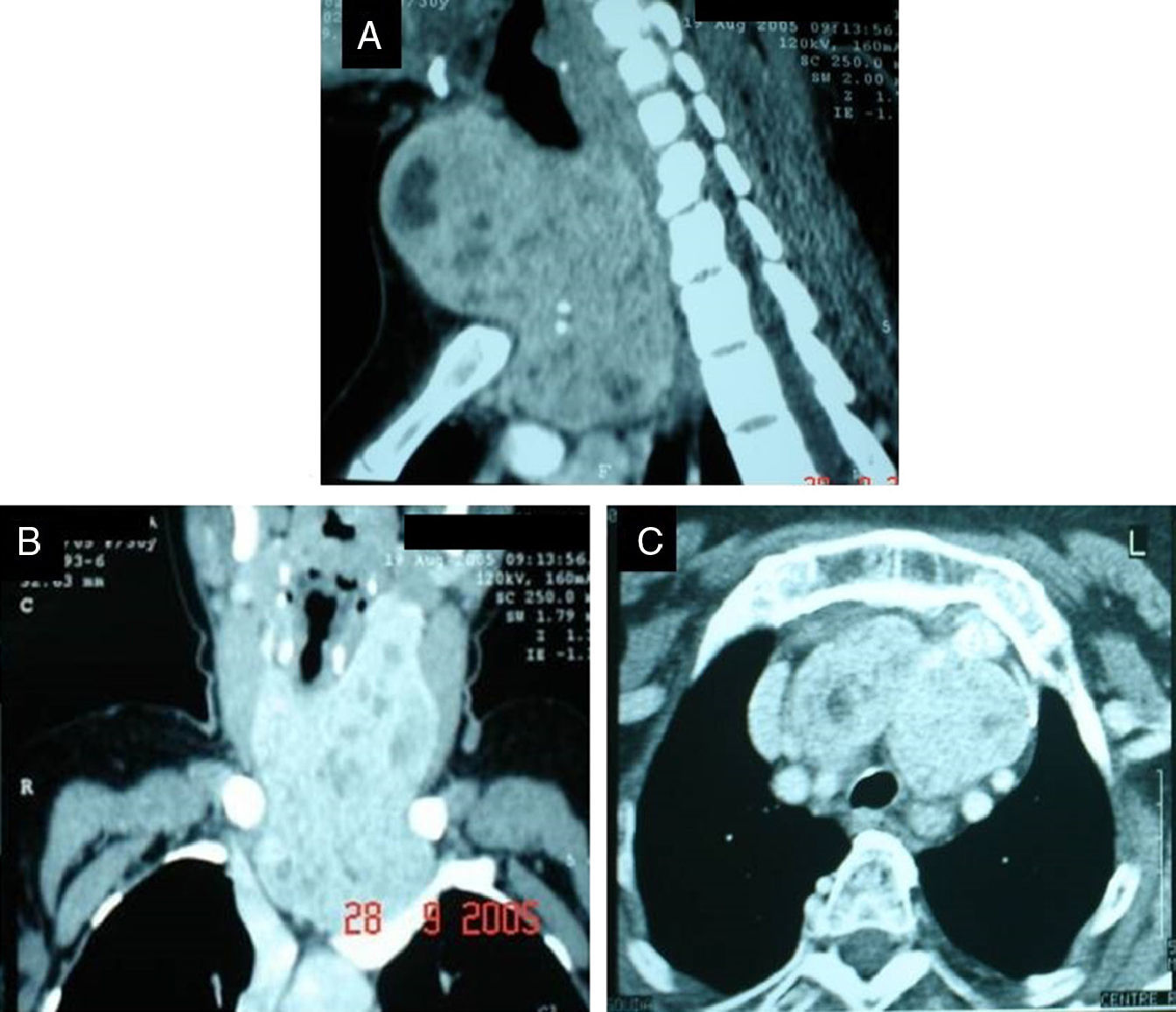
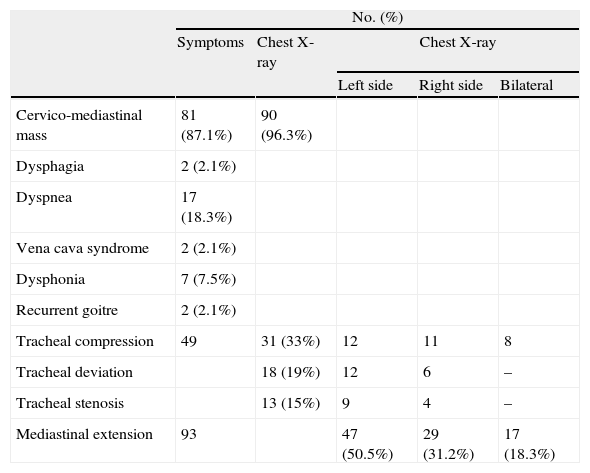
ResultsA cervical mass was noted in 81 cases (87.1%), dyspnea in 17 cases (18.3%), dysphagia in 2 cases (2.1%), hoarseness in 7 cases (7.5%), partial vena cava syndrome in 2 cases and recurrent goitre was noted in 2 cases (2.1%) after previous thyroid resection. Mediastinal extension was on the left side in 47 cases (50.5%), on the right side in 29 cases (31.2%) and bilateral in 17 cases (18.3%).
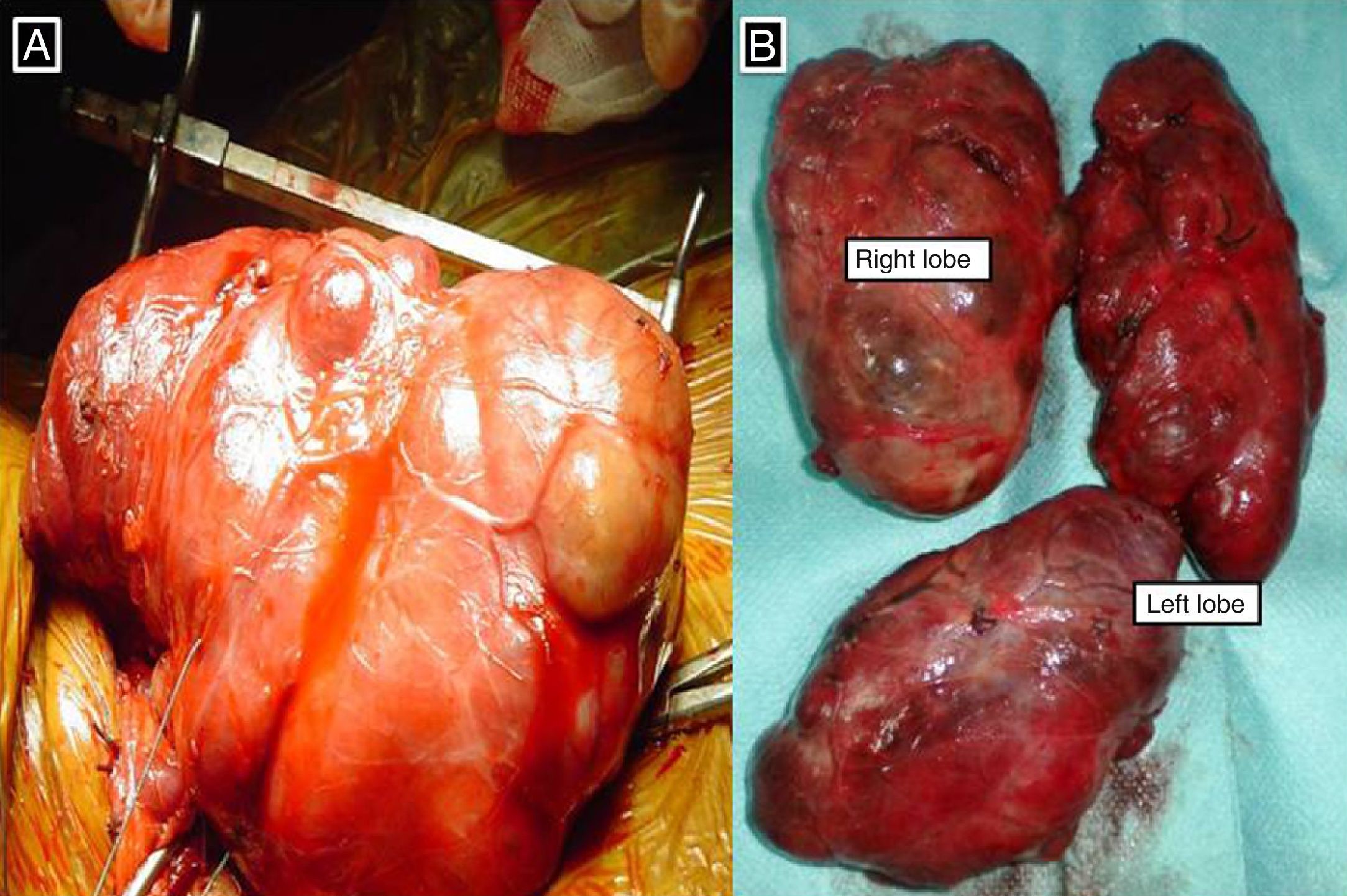
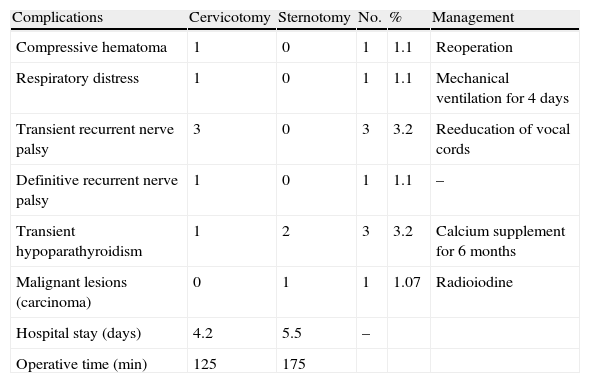
A total thyroidectomy was performed in 86 cases (92.5%) and a unilateral isthmo-lobectomy was performed in 7 cases (7.5%). Mean goitre size was 9.3cm. Postoperative complications were present in 9 cases (9.7%), 3 cases with hypoparathyroidism (3.2%) and 4 cases (4.3%) of recurrent nerve injury. There was no postoperative death. The histological study objectified 88 cases of multiheteronodular goitre, 4 cases of Basedow thyroid, and 1 case of thyroid carcinoma (papillary carcinoma).
ConclusionOur experience confirms that cervicotomy often allows removing goitre with a mediastinal extension. However, intraoperative enlargement may be necessary, with increased operating time, hospital stay and morbidity.
Se realiza un estudio retrospectivo para la revisión de 93 casos de bocio retroesternal (BR) operados en nuestro departamento, a fin de describir los datos epidemiológicos y clínicos y tratar los retos quirúrgicos de los BR.
Pacientes y métodosDe enero de 2004 a diciembre de 2012, tratamos quirúrgicamente a 35 varones y 58 mujeres con BR. Realizamos cervicotomía en 89 casos (95,7%), y la esternotomía fue necesaria en 4 casos (4,3%). Se realizó laringoscopia en todos los casos. Fue imperativa una segunda laringoscopia preoperatoria realizada por un especialista para los pacientes con ronquera o disnea, incluso cuando el examen laríngeo inicial era normal.
ResultadosSe observó una masa cervical en 81 casos (87,1%), disnea en 17 casos (18,3%), disfagia en 2 casos (2,1%), ronquera en 7 casos (7,5%), síndrome parcial de la vena cava en 2 casos y bocio recurrente en 2 casos (2,1%) tras la resección tiroidea previa. La extensión mediastínica se localizó en el lado izquierdo en 47 casos (50,5%), en el lado derecho en 29 casos (31,2%), y bilateralmente en 17 casos (18,3%).
Se practicó tiroidectomía total en 86 casos (92,5%), e istmo-lobectomía unilateral en 7 casos (7,5%). El tamaño medio del bocio fue de 9,3cm. Se presentaron complicaciones postoperatorias en 9 casos (9,7%), 3 casos con hipoparatiroidismo (3,2%) y 4 casos (4,3%) de lesión del nervio recurrente. No se produjeron muertes postoperatorias. El estudio histológico detectó 88 casos de bocio multiheteronodular, 4 casos de enfermedad de Graves-Basedow, y un caso de carcinoma tiroideo (carcinoma papilar).
ConclusiónNuestra experiencia confirma que la cervicotomía permite a menudo la extirpación del bocio con extensión mediastínica. Sin embargo, puede requerirse una esternotomía, alargándose el tiempo quirúrgico, la estancia hospitalaria y la morbilidad.