Immune-mediated inner ear disease (IMIED) is one of the few reversible forms of sensorineural hearing loss. Treatment is based on high-dose corticosteroids, although long-term therapy is associated with serious adverse effects; this has led to the use of other agents or different routes of administration such as transtympanic delivery. This study analyses the role of biological agents in IMIED management.
Material and methodsWe searched PUBMED for studies that examined the response to treatment with different biological agents in patients with IMIED. The following data were extracted from the selected studies and entered into a standardised database: exclusion and inclusion criteria, characteristics of the patients studied, treatment, outcome measures and response rates achieved.
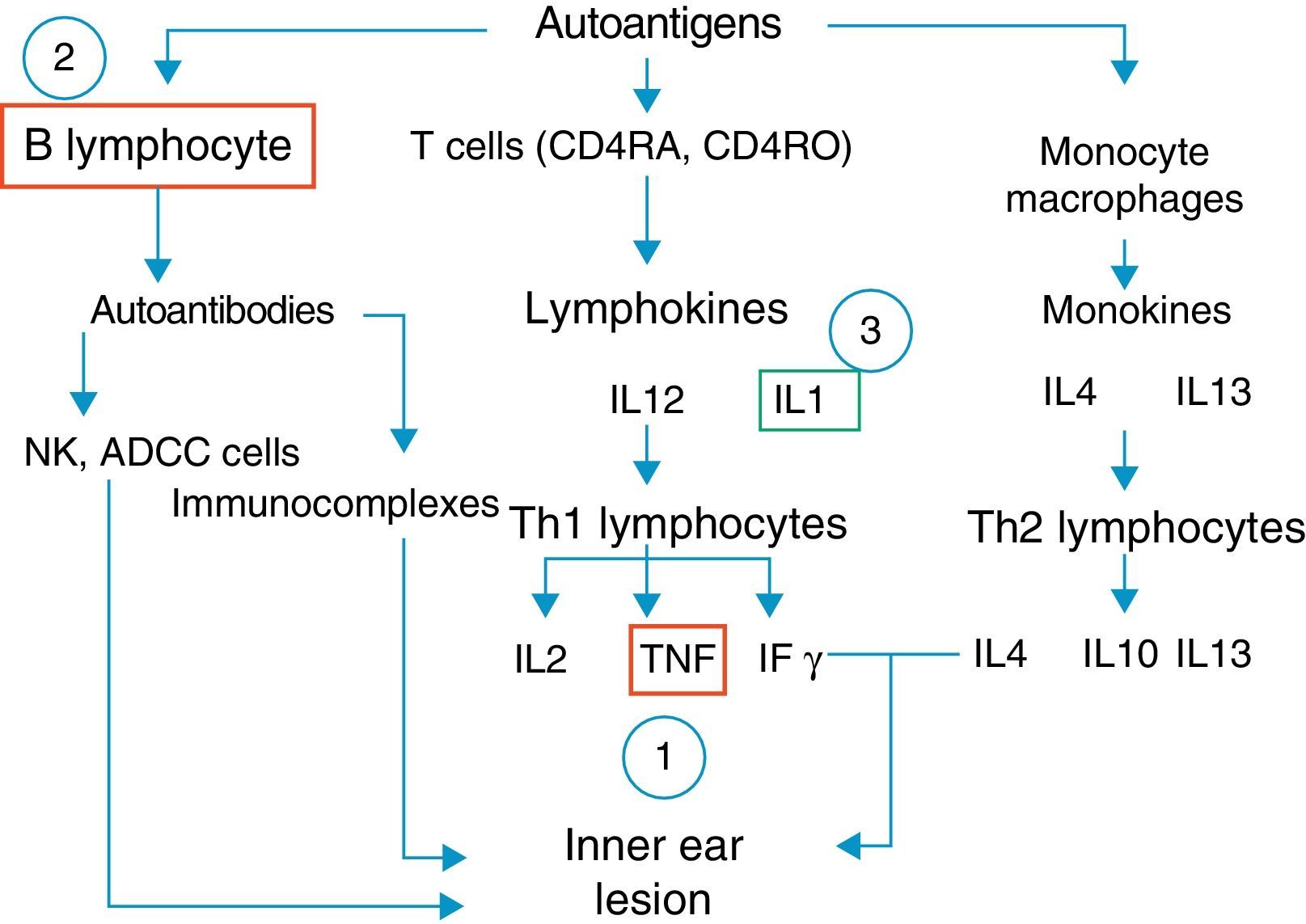
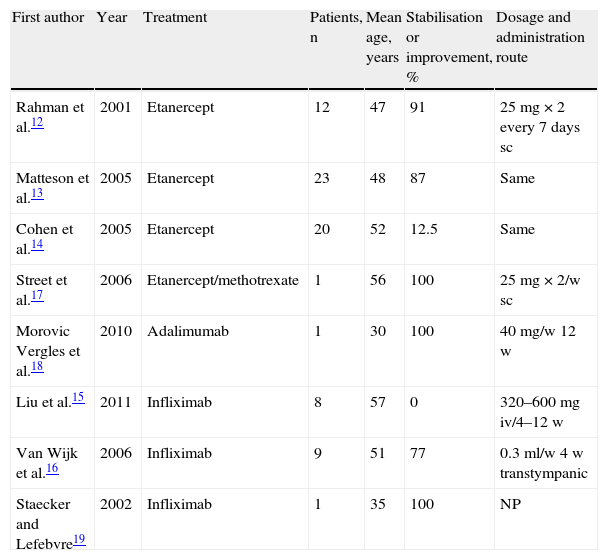
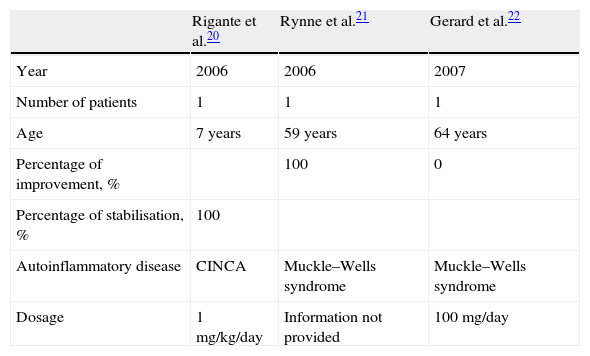
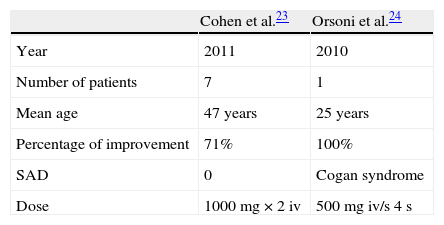
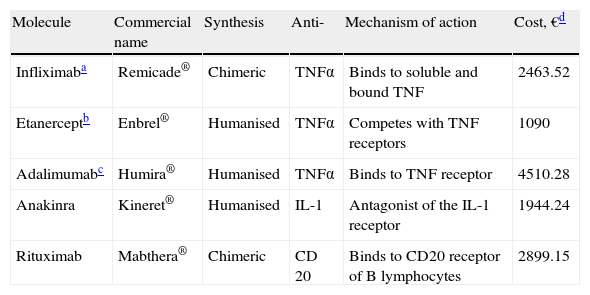
ResultsThirteen studies were included in this review. A TNF alpha inhibitor (etanercept, infliximab, adalimumab) was used in 8 studies, an IL-1 antagonist (anakinra) was used in 3 studies and rituximab, and an antibody directed against the CD20 surface antigen on B lymphocytes was evaluated in 2 studies. Most studies achieved a hearing improvement or stabilisation in more than 70% of treated patients.
ConclusionsBiological agents can play a role in the management of patients with IMIED, at least in those patients who do not respond to conventional therapy or whose hearing is not stabilised. However, specially designed randomised controlled clinical trials are needed to assess their effectiveness.
La enfermedad inmunomediada del oído interno (EIOI) es una de las escasas afecciones del oído interno que pueden revertirse con tratamiento médico. Este se basa en los corticoides, si bien el tratamiento prolongado con los mismos se asocia a serios efectos adversos, lo que ha propiciado el uso de otros fármacos o vías de administración como la intratimpánica. En este estudio se analiza el papel de las terapias biológicas en el tratamiento de la EIOI.
Material y métodosSe ha realizado una búsqueda sistemática en PUBMED de aquellos estudios que examinan la respuesta al tratamiento con distintos agentes biológicos en pacientes con EIOI. Se ha analizado los criterios de inclusión y exclusión de cada estudio, así como las características de la población estudiada, el tratamiento utilizado y, los criterios de respuesta y tasa de respuesta alcanzada.
ResultadosSe identificaron 13 estudios relevantes. En 8 estudios de utilizó un inhibidor del TNFα (etanercept, infliximab, adalimumab), en 3 un antagonista de la IL-1 (anakinra) y en el resto se empleó el rituximab, un antagonista del receptor CD20 de los linfocitos B. En la mayoría de los estudios se logró una mejoría o estabilización de la audición en más del 70% de los pacientes tratados.
ConclusionesLas terapias biológicas pueden tener un papel en el tratamiento de los pacientes con EIOI, al menos en aquellos que responden mal a los corticoides o no se consigue su estabilización. Sin embargo, son necesarios más estudios controlados y aleatorizados para conocer su eficacia.