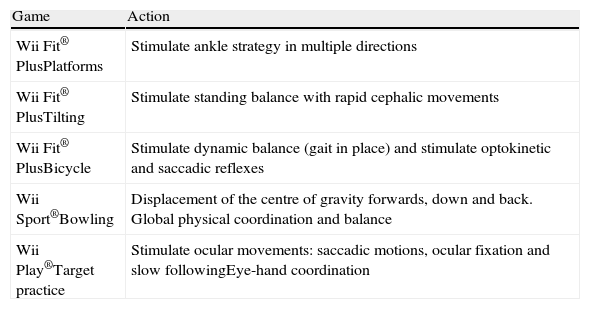
Vestibular rehabilitation therapy is an exercise-based programme designed to promote central nervous system compensation for inner ear deficit. The objective of the present study was to analyse the differences in the perception of handicap, the risk of falls, and gaze stability in patients diagnosed with chronic unilateral vestibular hypofunction before and after vestibular rehabilitation treatment with complementary Wii® therapy.
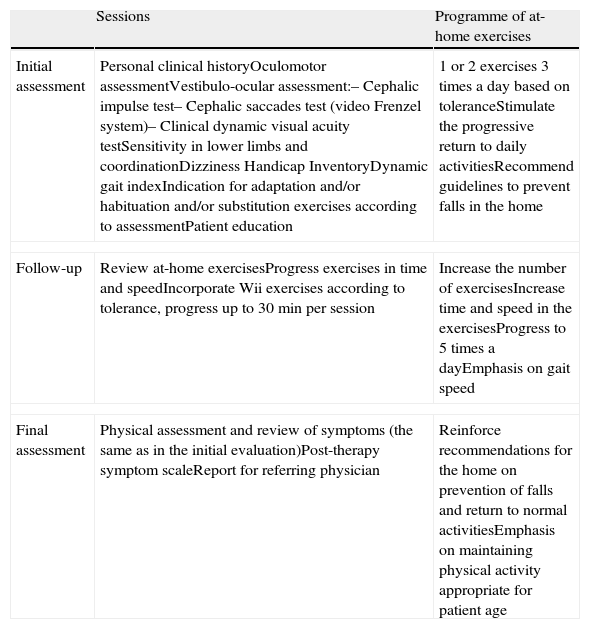
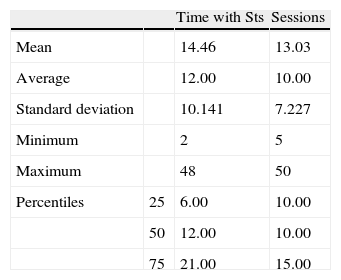
Materials and methodsA review was performed on the clinical histories of patients in the vestibular rehabilitation area of a university hospital between April 2009 and May 2011. The variables studied were the Dizziness Handicap Inventory, the Dynamic Gait Index and dynamic visual acuity. All subjects received complementary Wii® therapy.
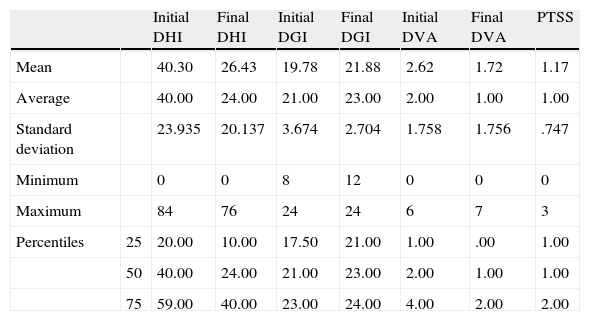
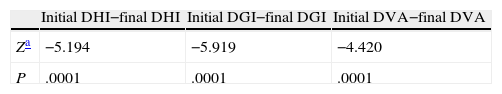
ResultsThere were 69 cases (41 woman and 28 men), with a median age of 64 years. The initial median Dizziness Handicap Inventory score was 40 points (range 0–84, percentile 25–75=20–59) and the final, 24 points (range 0–76, percentile 25–75=10.40), P<.0001. The initial median for the Dynamic Gait Index score was 21 points (range 8–24, percentile 25–75=17.5–2.3) and the final, 23 (range 12–24, percentile 25–75=21–23), P<.0001. The initial median for dynamic visual acuity was 2 (range 0–6, percentile 25–75=1–4) and the final, 1 (range 0–3, percentile 25–75=0–2), P<.0001.
ConclusionA reduction was observed in the Dizziness Handicap Inventory Values. Values for the Dynamic Gait Index increased and dynamic visual acuity improved. All these variations were statistically significant.
La rehabilitación vestibular está destinada a maximizar la compensación central de la enfermedad vestibular periférica. El objetivo del presente estudio fue analizar las diferencias de la percepción de discapacidad, el riesgo de caídas y la estabilidad de la mirada antes y después de un tratamiento de rehabilitación vestibular con el uso complementario de terapia Wii® en pacientes con diagnóstico de hipofunción vestibular unilateral crónica.
Materiales y métodosSe revisaron registros de pacientes entre abril de 2009 y mayo de 2011 del área de rehabilitación vestibular de un hospital universitario. Las variables estudiadas fueron el Dizziness Handicap Inventory, el índice dinámico de la marcha y la agudeza visual dinámica. Todos los sujetos usaron Wii® como complemento.
ResultadosSesenta y nueve casos (41 mujeres y 28 hombres). La mediana de edad fue 64 años. La mediana de Dizziness Handicap Inventory inicial fue de 40 puntos (rango 0-84, percentil 25-75=20-59) y final de 24 (rango 0-76, percentil 25-75=10-40) p<0,0001. La mediana del índice dinámico de la marcha inicial fue 21 puntos (rango 8-24, percentil 25-75=17,5-23) y final de 23 (rango 12-24, percentil 25-75=21-23) p<0,0001. La mediana de la agudeza visual dinámica inicial fue 2 (rango 0-6, percentil 25-75=1-4) y final de 1 (rango 0-3, percentil 25-75=0-2) p<0,0001.
ConclusiónSe observó una disminución de los valores del Dizziness Handicap Inventory, un aumento de los valores del índice dinámico de la marcha y una mejoría en la agudeza visual dinámica; todas estas variaciones fueron estadísticamente significativas.