Human papillomavirus (HPV) infection is the most common human sexually transmitted disease. It is clinically relevant because this condition is necessary for the development of epithelial cervical cancer, and it is also a factor closely associated with the occurrence of diverse tumours and various benign and malignant lesions of the head and neck area. The infective mechanism in most of these cases is associated with sexual intercourse, but there is recent scientific evidence suggesting that HPV infection may also be acquired by other routes of infection not necessarily linked to sexual contact. One of them is vertical transmission from mother to child, either during pregnancy or at the time of delivery.
The aim of our research was to study maternal–foetal HPV transmission during childbirth in detail, establishing the rate of oropharyngeal neonatal HPV in vaginal deliveries.
MethodThe presence and type of HPV viral DNA at the time of delivery in samples of maternal cervical secretions, amniotic fluid, venous cord blood samples and neonatal oropharynx in pregnant women (and their babies) were determined.
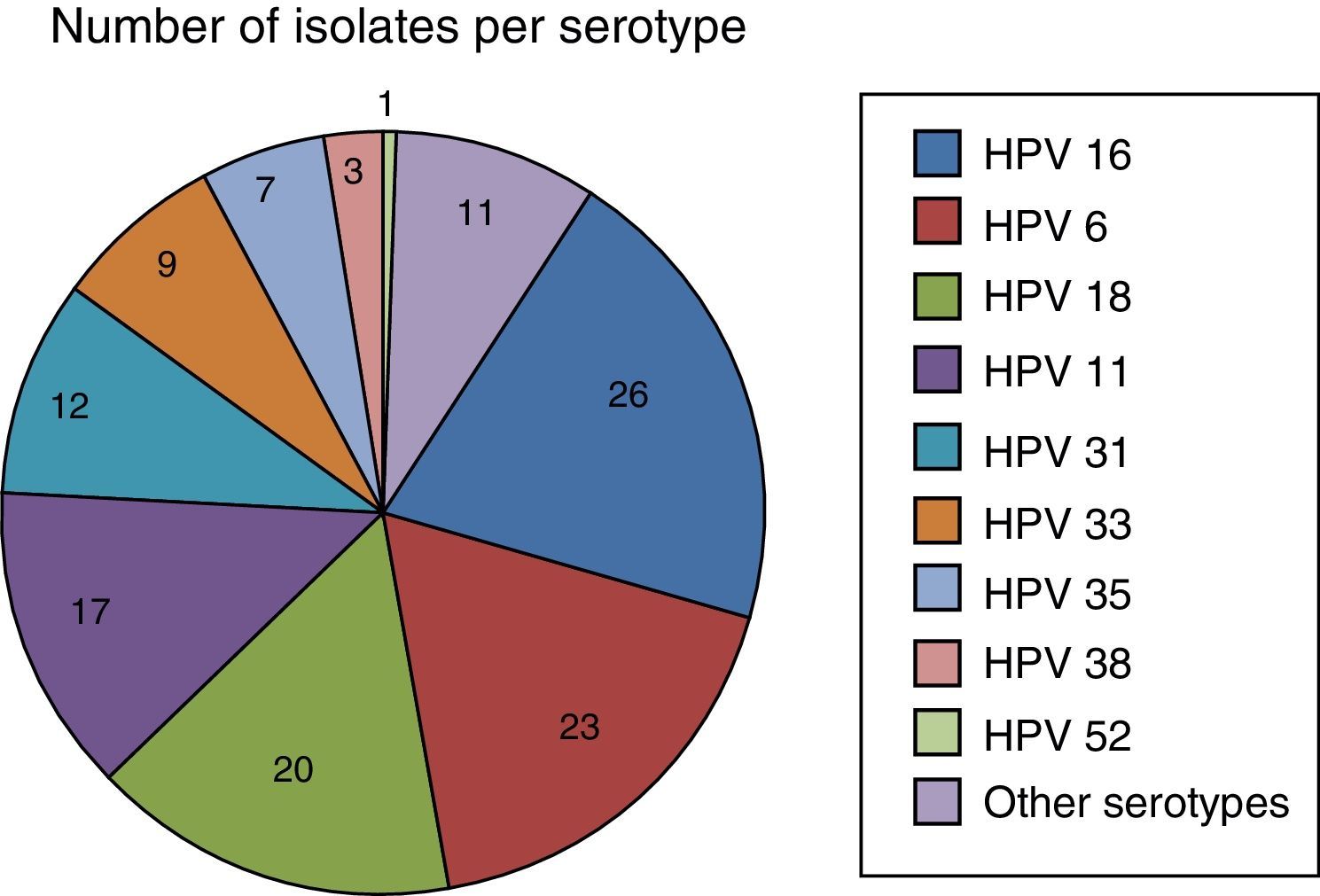
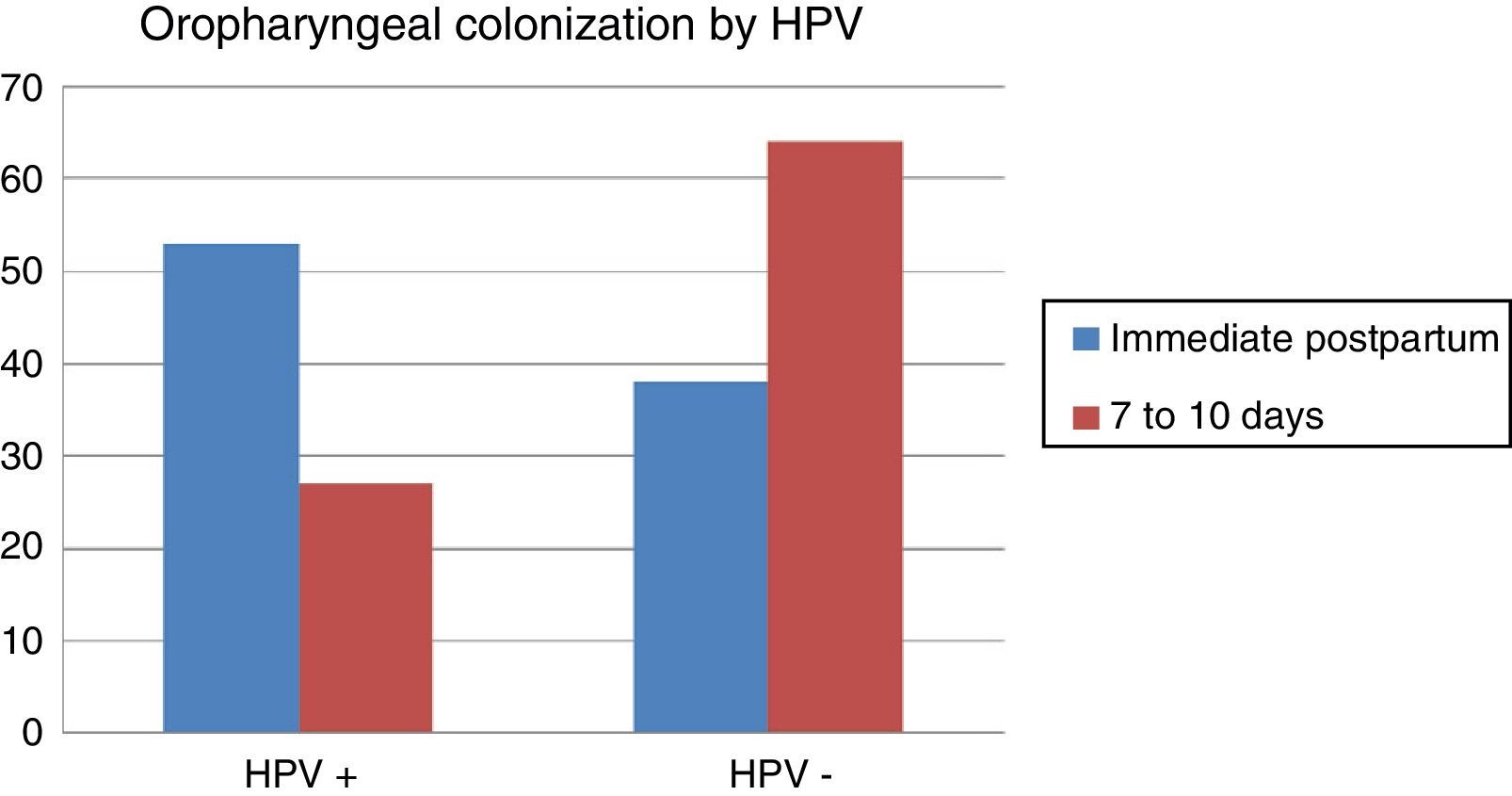
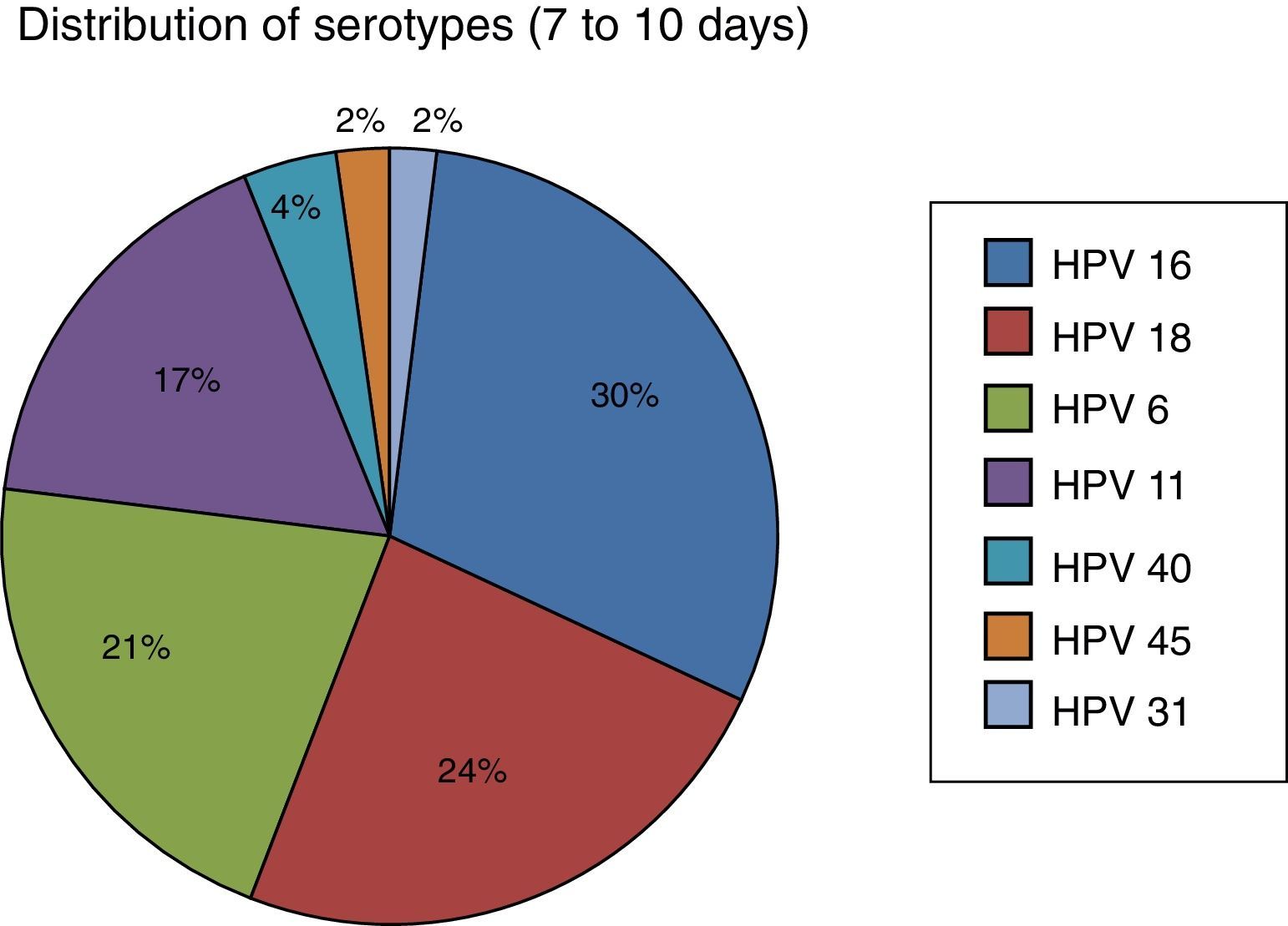
ResultsThe rate of oropharyngeal neonatal HPV colonization in vaginal deliveries was 58.24%.
ConclusionsThe maternal and neonatal HPV colonization mechanism is essentially, but not exclusively, transvaginal.
La infección por el virus del papiloma humano (VPH) es la enfermedad de transmisión sexual más frecuente del ser humano. Su relevancia clínica radica en que tal condición es causa necesaria para el desarrollo de cáncer epitelial de cuello uterino y también un factor estrechamente asociado a la aparición de tumores y diversas lesiones benignas y malignas del área cráneo-cervical. El mecanismo infectivo para la mayoría de estos casos está asociado a la participación del individuo en prácticas sexuales de diverso tipo, pero existen en la actualidad evidencias científicas que indican la posibilidad de que dicha infección pueda ser también adquirida por otras vías de contagio no necesariamente ligadas al contacto sexual. Una de ellas es la transmisión desde la madre al hijo, bien durante la gestación, bien en el momento del parto.
El objetivo de nuestra investigación es profundizar en el estudio de la transmisión materno-foetal de VPH durante el parto, estableciendo la tasa de colonización orofaríngea neonatal por VPH en los partos vaginales.
MétodoSe determinó la presencia y tipo de ADN viral de VPH en el momento del parto en las muestras obtenidas de las secreciones cervicales maternas, líquido amniótico, sangre venosa de cordón y orofaringe neonatal en las embarazadas (y sus recién nacidos).
ResultadosLa tasa de colonización orofaríngea neonatal por VPH en los partos vaginales de madres inmunocompetentes portadoras del germen fue del 58,24%.
ConclusionesEl mecanismo de contaminación materno-neonatal por VPH es esencialmente, que no exclusivamente, transvaginal.