This is the first report dealing with immune-mediated inner ear disease (IMIED) hearing loss in a group of patients affected with autoimmune thyroid disease (AITD), whose treatment required corticosteroids, despite being treated with levothyroxine. Immunopathology linking the inner ear and the thyroid gland is also presented.
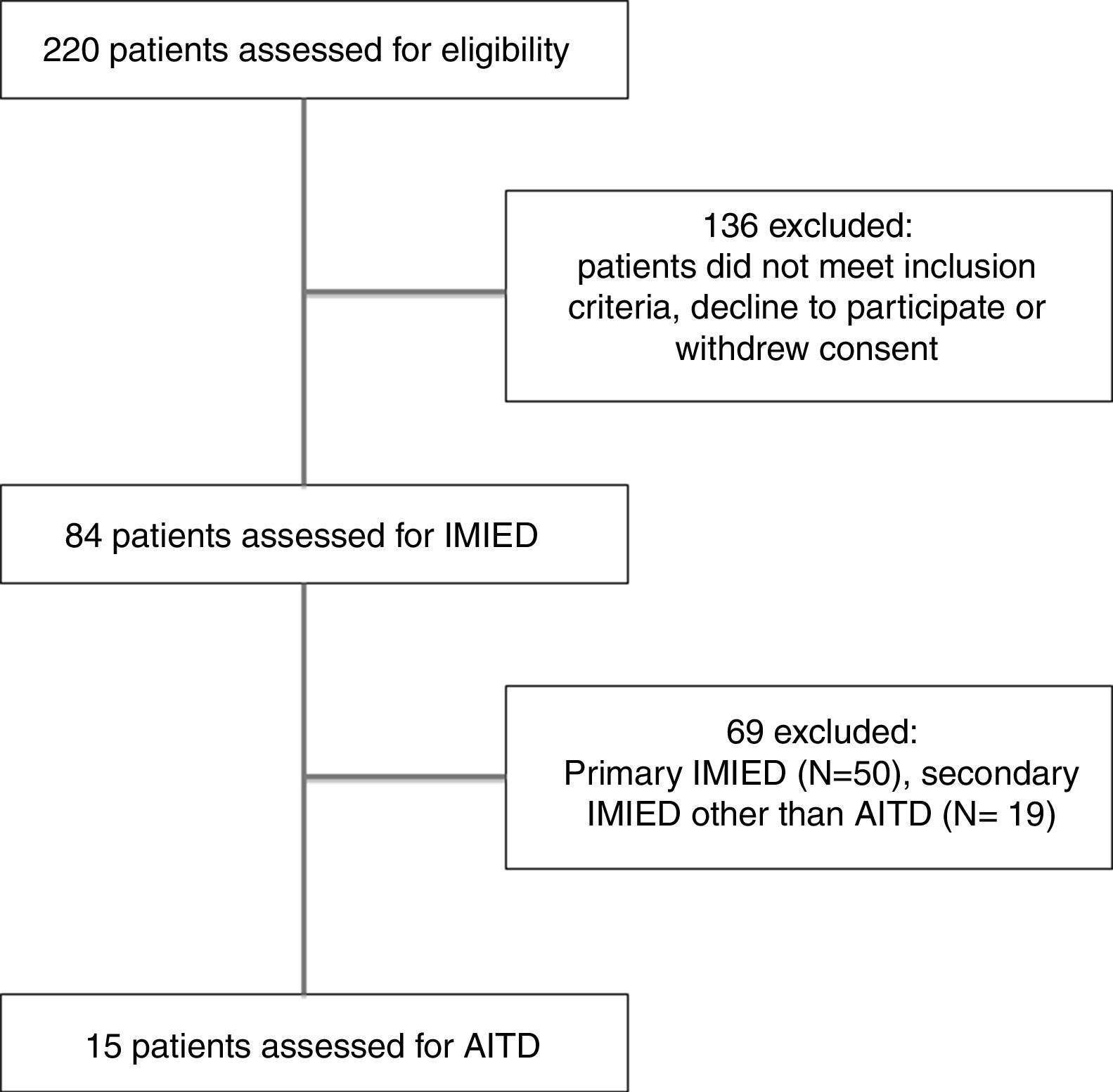
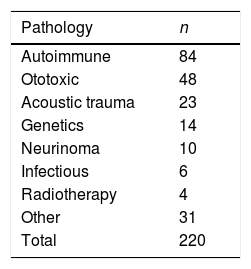
PatientsA total of 220 patients were selected with sensorineural hearing loss (SNHL) of causes other than presbycusis. Audiometry was performed and pure tone average was calculated before and after treatment with corticosteroids.
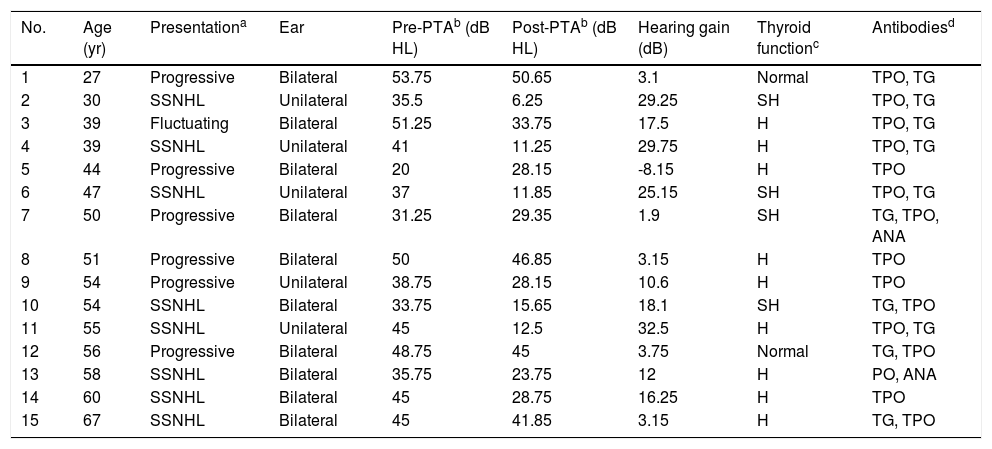
ResultsEighty-four (84) patients had SNHL of autoimmune origin, and 15 patients were diagnosed with AITD (Hashimoto's disease). Bilateral hearing loss was observed in 10 patients (66.5%). Sudden sensorineural hearing loss was the most frequent clinical form of presentation. Nine patients showed a hearing recovery greater than 10dB after corticosteroid treatment.
ConclusionsAcquired hypothyroidism is thought to affect hearing due to different mechanisms. Although specific hormonal therapy may improve peripheral or central auditory disorders associated with hypothyroidism, the presence of IMIED in AITD patients requires another approach. Altered immune regulatory mechanisms involving Treg cells and CD4+CD45RO cells have been suggested in patients with AITD and IMIED. In the present study, although all the patients with hypothyroidism and subclinical hypothyroidism were being treated with levothyroxine, immune-mediated hearing loss was observed. Therapy with corticosteroids could achieve hearing recovery. Since inner ear and thyroid gland share possible antigen targets, we highlight the existence of IMIED in AITD patients and the importance of implementing appropriate therapy with corticosteroids.
Este es el primer trabajo que trata la hipoacusia por enfermedad inmune-mediada del oído interno (IMIED) en un grupo de pacientes afectados de tiroiditis autoinmune (AITD), cuyo tratamiento requirió corticosteroides, a pesar de haber sido tratados con levotiroxina. También se presenta la inmunopatología que vincula el oído interno y la glándula tiroides.
PacientesSe seleccionó un total de 220 pacientes con hipoacusia neurosensorial (SNHL) por causas diferentes a presbiacusia. A todos los pacientes se les realizó una audiometría, calculándose la media de tonos puros antes y después del tratamiento con corticosteroides.
ResultadosOchenta y cuatro (84) pacientes tenían SNHL de origen autoinmune, y 15 pacientes fueron diagnosticados de AITD (Enfermedad de Hashimoto). Se observó hipoacusia bilateral en 10 pacientes (66,5%). La sordera súbita fue la forma de presentación clínica más frecuente. Nueve pacientes presentaron una recuperación auditiva superior a 10dB tras el tratamiento con corticosteroides.
ConclusionesSe piensa que el hipotiroidismo adquirido afecta a la audición por diferentes mecanismos. Aunque la terapia hormonal específica puede mejorar los trastornos auditivos periféricos o centrales asociados al hipotiroidismo, la presencia de IMIED en los pacientes de AITD requiere otro abordaje. Se ha sugerido una alteración de los mecanismos reguladores de la respuesta inmune que implica a las células de Treg y a las células CD4+CD45RO en los pacientes con AITD e IMIED. En el presente estudio, a pesar de que todos los pacientes con hipotiroidismo e hipotiroidismo subclínico estaban siendo tratados con levotiroxina, se observó hipoacusia inmuno-mediada. La terapia con corticosteroides podría lograr una recuperación auditiva. Dado que el oído interno y la glándula tiroides comparten posibles antígenos diana, destacamos la existencia de IMIED en los pacientes de AITD, y la instauración de una terapia adecuada con corticosteroides.