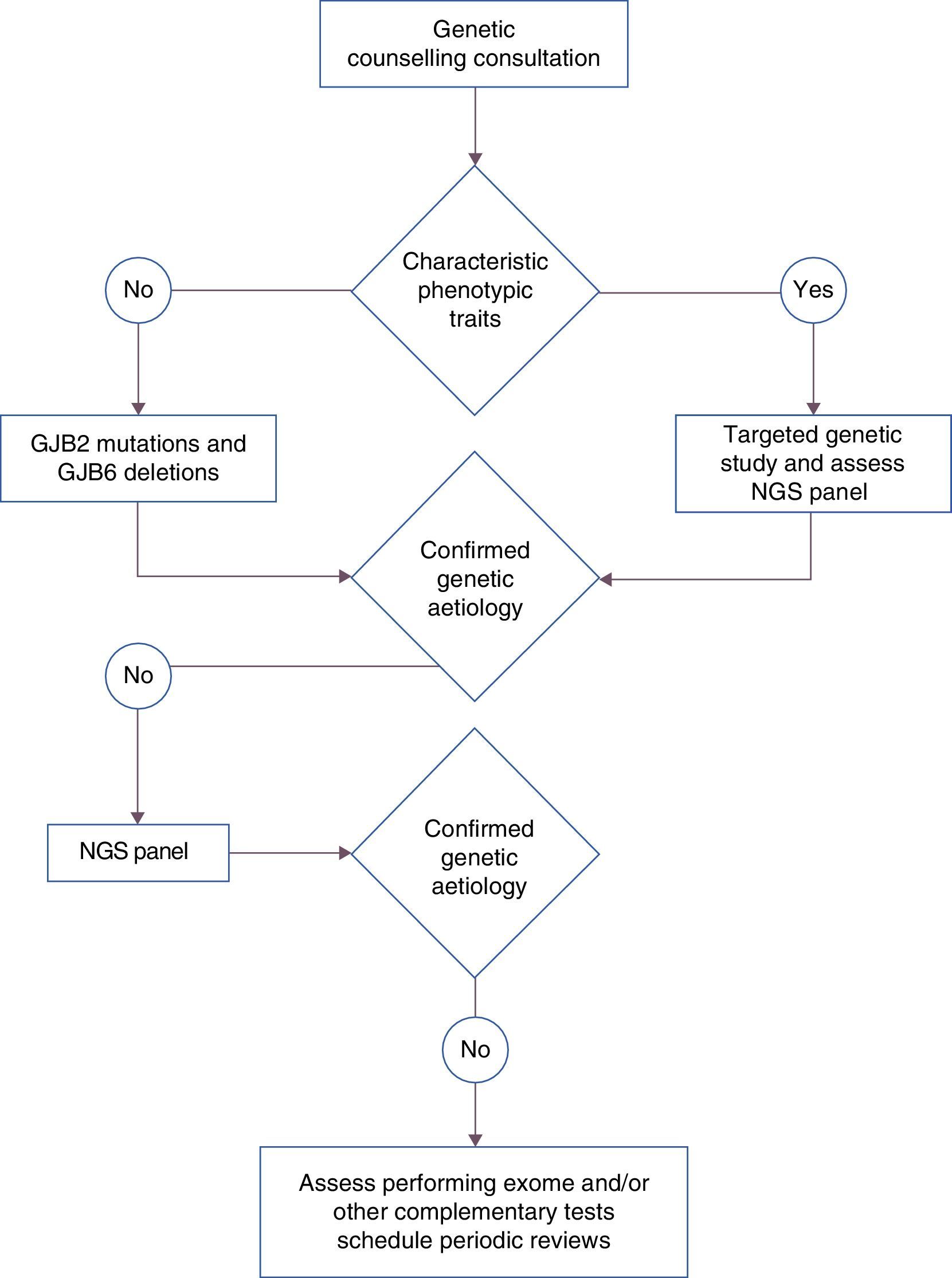
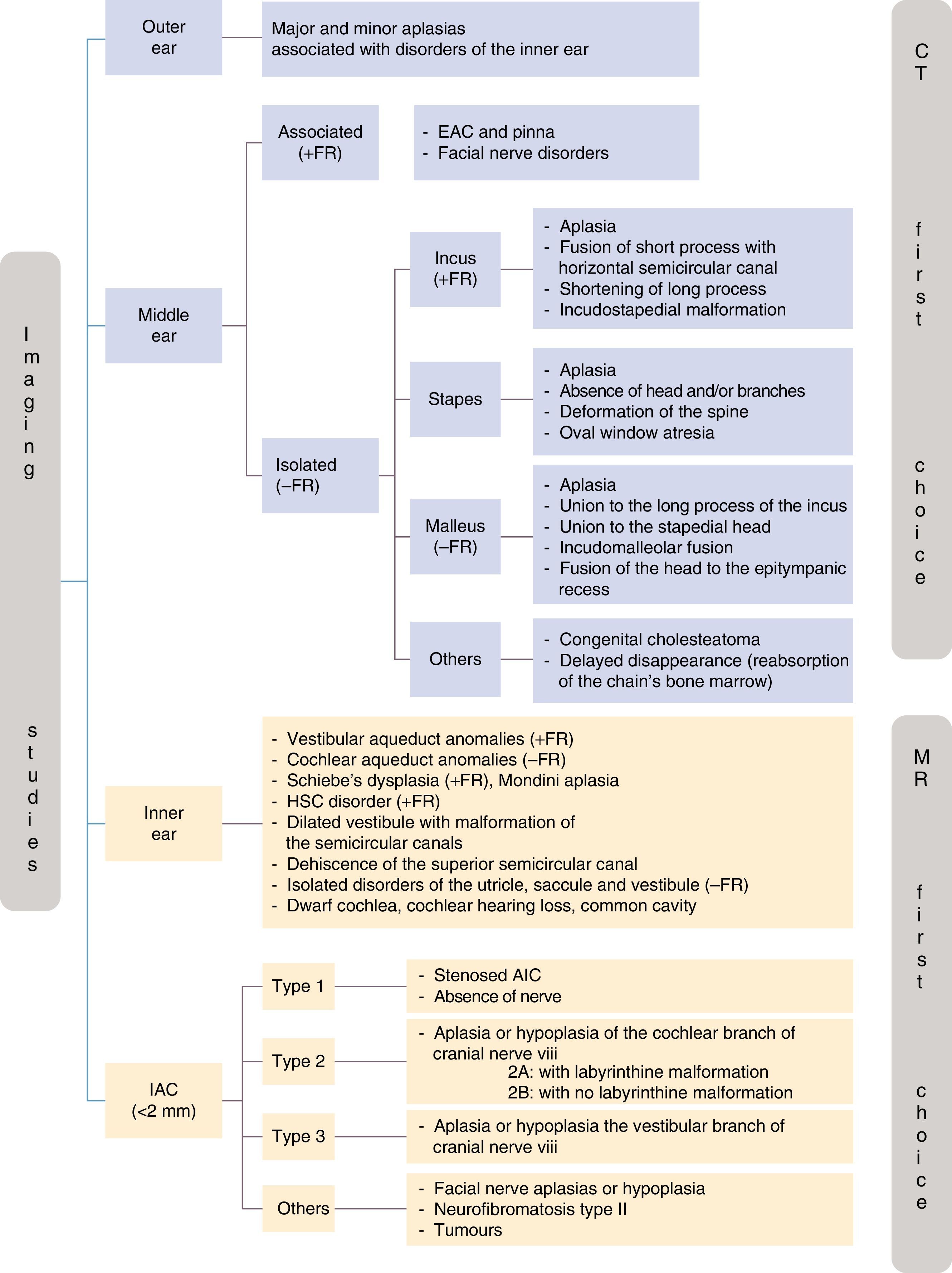
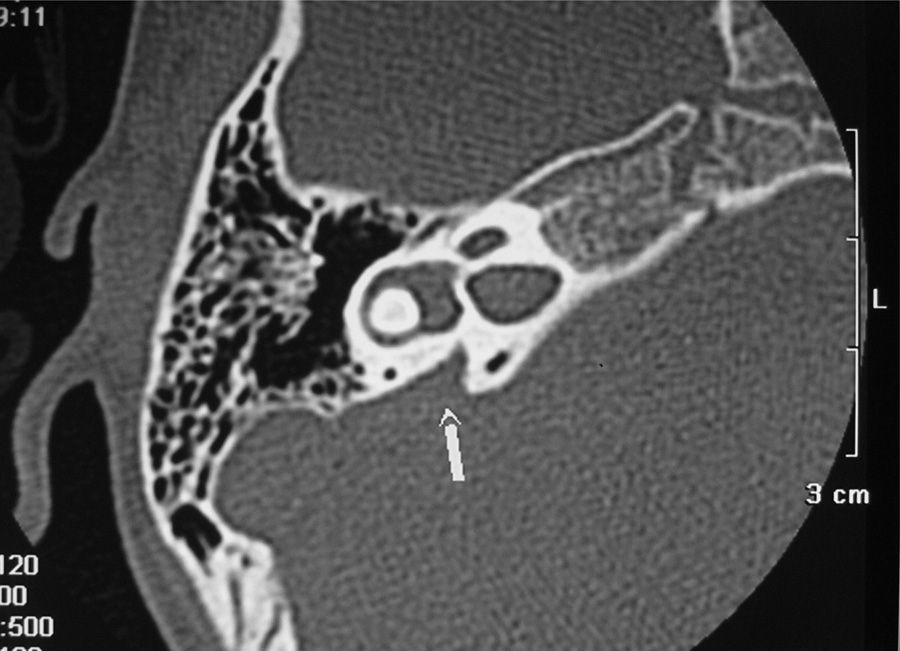
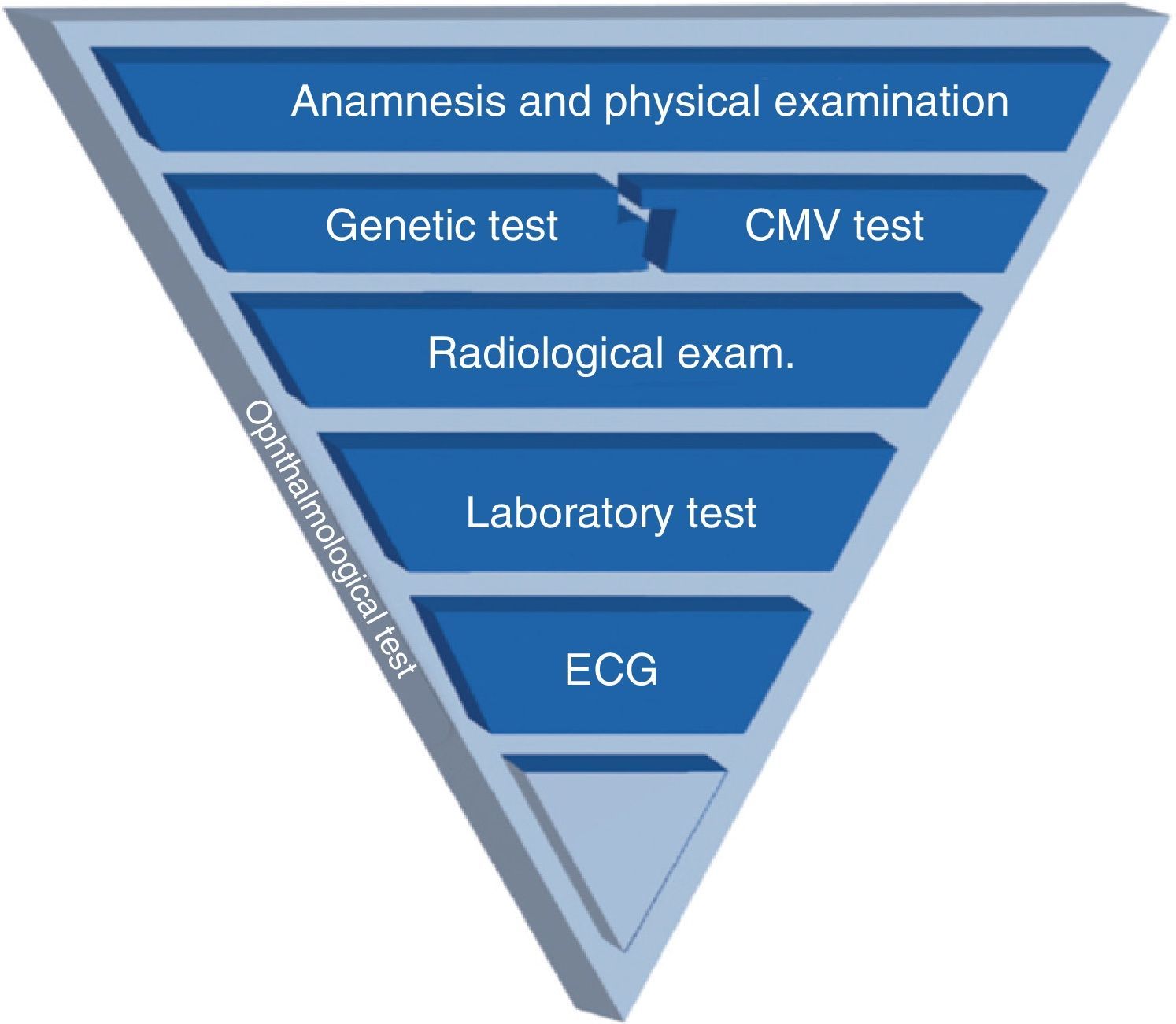
Important progress in the fields of molecular genetics (principally) and diagnostic imaging, together with the lack of a consensus protocol for guiding the diagnostic process after confirming deafness by neonatal screening, have led to this new work document drafted by the Spanish Commission for the Early Detection of Child Deafness (Spanish acronym: CODEPEH). This 2015 Recommendations Document, which is based on the most recent scientific evidence, provides guidance to professionals to support them in making decisions regarding aetiological diagnosis. Such diagnosis should be performed without delay and without impeding early intervention. Early identification of the causes of deafness offers many advantages: it prevents unnecessary trouble for the families, reduces health system expenses caused by performing different tests, and provides prognostic information that may guide therapeutic actions.
El importante avance en el campo de la genética molecular, fundamentalmente, así como en el diagnóstico por imagen, junto a la ausencia de un protocolo consensuado que oriente el proceso diagnóstico una vez confirmada la presencia de una sordera tras el cribado neonatal, motivan este nuevo trabajo de la Comisión para la Detección Precoz de la Hipoacusia Infantil (CODEPEH). El Documento de Recomendaciones sobre el diagnóstico etiológico de la sordera, que se basa en la más reciente evidencia científica, ofrece orientaciones de apoyo al profesional en la toma de decisiones que, en todo caso, deben llevarse a cabo sin entorpecer ni retrasar la intervención temprana. Identificar precozmente la causa de la hipoacusia aporta numerosas ventajas: evita molestias innecesarias a las familias, reduce el gasto sanitario derivado de la realización de numerosas pruebas y proporciona información pronóstica, que puede guiar la actuación terapéutica.