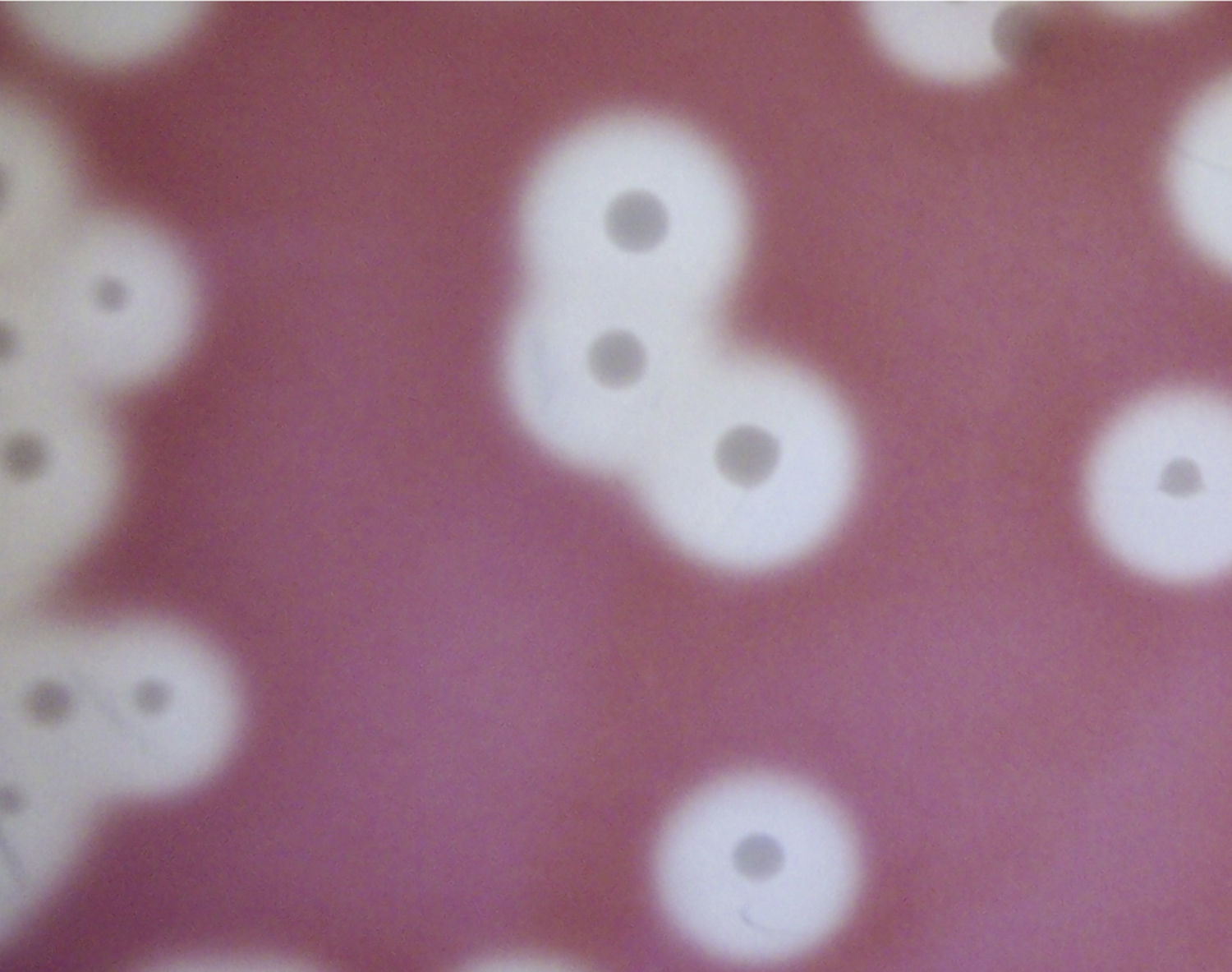
Streptococcus equi subsp. equi (S. equi) of Lancefield group C and beta-hemolytic streptococci (Fig. 1) causes strangles, an acute and contagious lymphadenopathy of young horses.1-3S. equi is host-adapted to equine but, unlike Streptococcus equi subsp. zooepidemicus, does not colonize the nasopharynx in healthy horses.2,3
The hyaluronic acid capsule is an important virulence factor for many streptococci1–4 and it is a high molecular weight polymer consisting of alternating residues of N-acetylglucosamine and glucuronic acid. The capsule reduces the phagocytic function of neutrophils and is required for the activity of proteases, toxins and the SeM protein.3 Furthermore, this capsule mimics the molecule in animal tissue and protects the bacterium from immune recognition.3
Virulent isolates of S. equi are usually highly encapsulated1,3 and nonencapsulated mutants are not able to progress from tonsillar tissue to the lymph nodes.2 However, the high levels of capsule may reduce adhesion to the mucosal surface.2
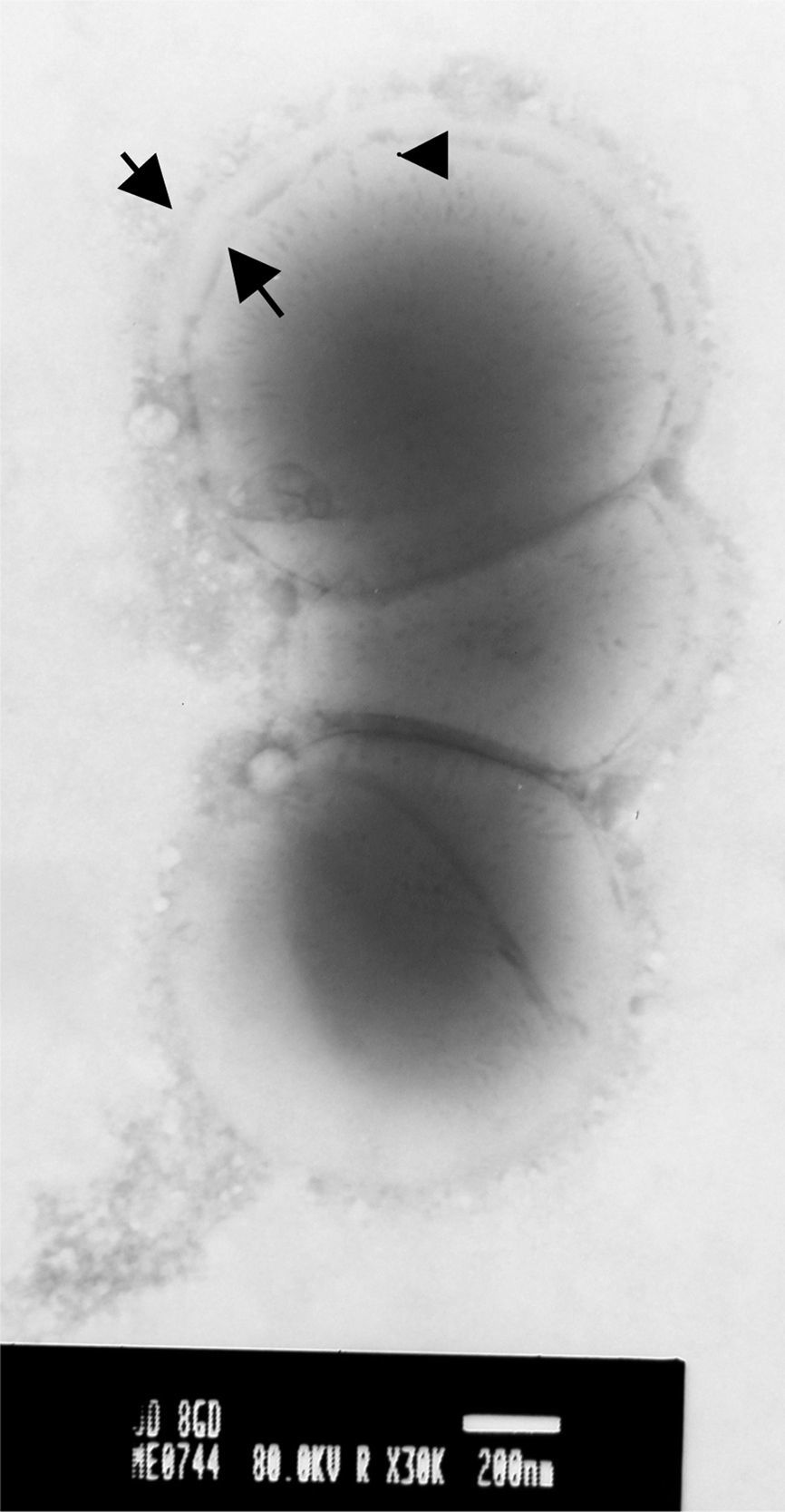
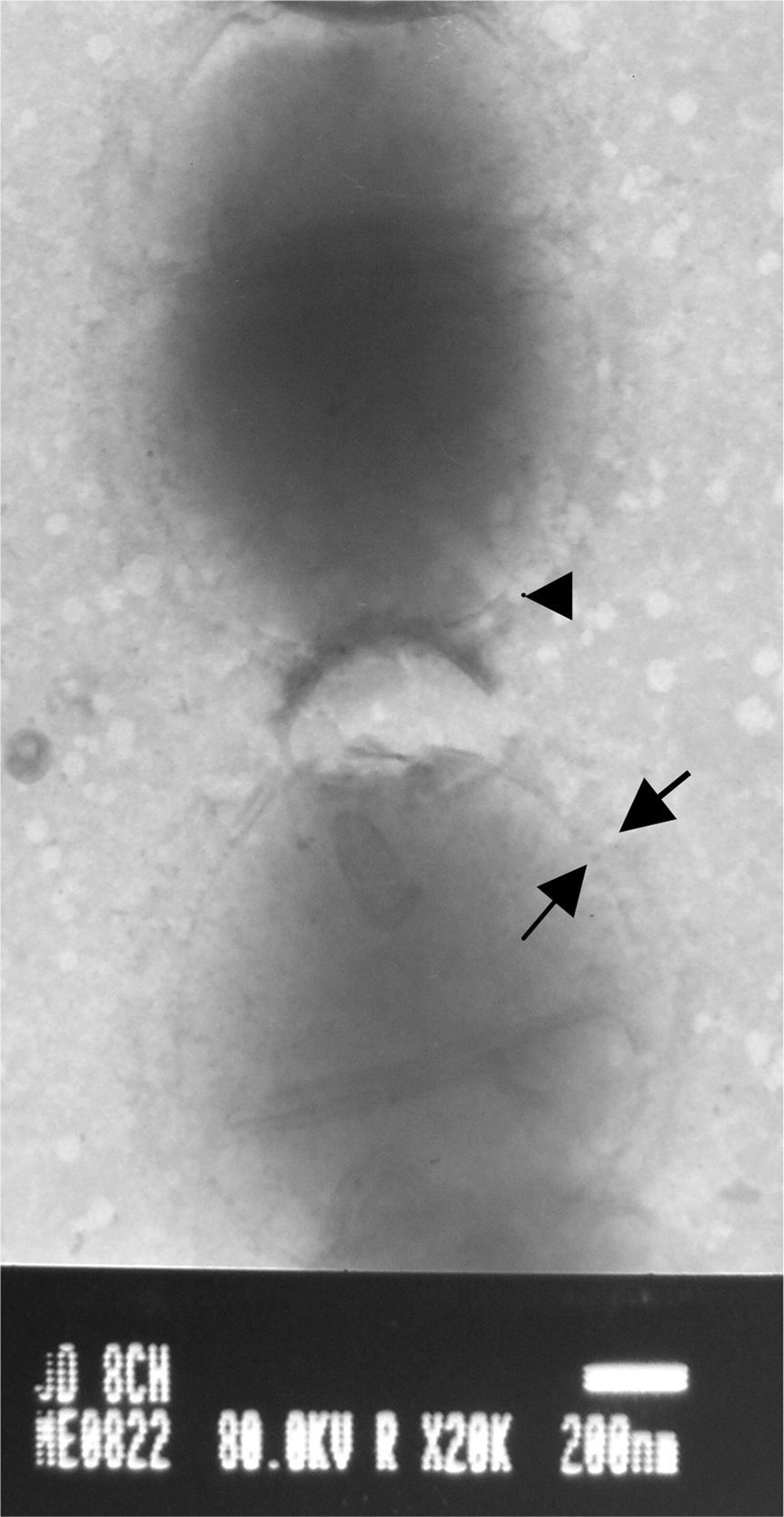
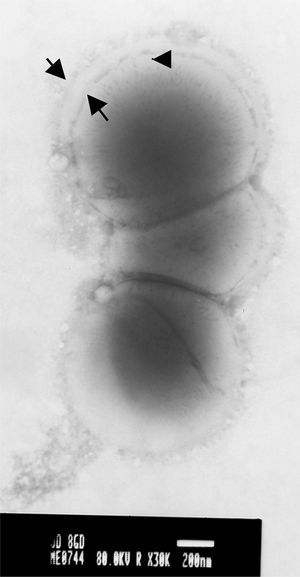
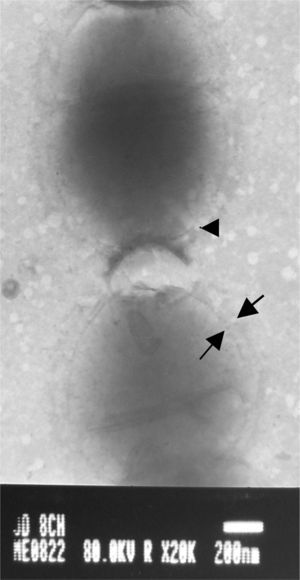
S. equi isolates (Fig. 1) were obtained from horses suffering from clinical strangles and guttural pouch empyema in Buenos Aires. The isolates were cultured for 24h at 37°C in 5ml of Todd Hewitt broth supplemented with 0.2% yeast extract and 10% adult horse serum. Then, capsules were observed with phosphotungstic acid (PTA) using a JEOL 1200EX II transmission electronic microscope at 50,000 magnification. The photographs were taken at 80 KV (Figs. 2 and 3).
High (Fig. 2) and low (Fig. 3) levels of capsule expression were observed, even in isolates from the same sample.
Ethical responsibilitiesProtection of human and animal subjectsThe authors declare that no experiments were performed on humans or animals for this study.
Confidentiality of dataThe authors declare that no patient data appear in this article.
Right to privacy and informed consentThe authors declare that no patient data appear in this article.
This work was supported by Secretaría de Ciencia y Técnica, Universidad de Buenos Aires (Research Project UBA CyT 20020100100149).