Identificar las situaciones que puedan hacer variar en algún sentido los resultados de las herramientas Pad test 1 y 24horas e ICIQ-SF.
ParticipantesCinco fisioterapeutas que realizaron las entrevistas y tratamiento a 81 pacientes intervenidos de prostatectomía radical.
MétodoSe realizó un estudio cualitativo fenomenológico descriptivo, mediante técnica de grupo focal de 5 personas (4 mujeres y un hombre) responsables del tratamiento y valoración de pacientes con incontinencia urinaria tras prostatectomía. Se transcribieron las grabaciones realizadas y se utilizó el programa Atlas.ti7 para codificar las variables.
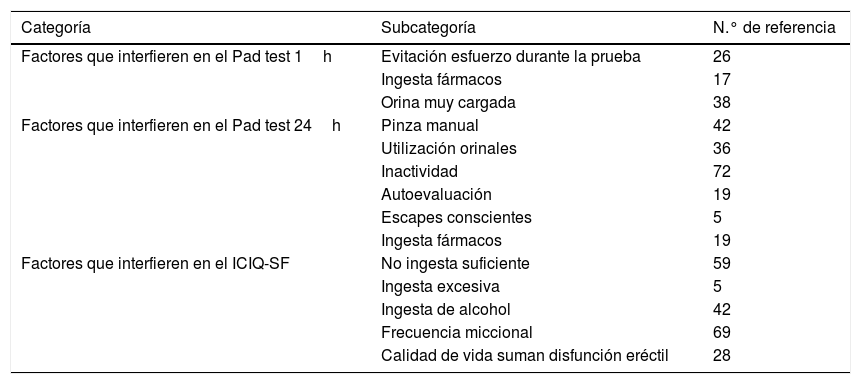
ResultadosSe identificaron importantes factores a tener en cuenta en el uso de los instrumentos de medida para el diagnóstico y valoración de la incontinencia urinaria en todas las herramientas utilizadas.
ConclusionesExisten situaciones que pueden modificar la objetividad de las distintas pruebas para la valoración de la incontinencia urinaria. Así se ha detectado, entre otras, una menor ingesta de líquidos, una menor actividad, utilización de pinza manual o de orinales para evitar las pérdidas, así como la interferencia con el uso de determinados fármacos.
To identify situations that may alter the results of the 1-hour and 24-hour Pad test and the short-form International Consultation in Incontinence Questionnaire (SF-ICIQ).
ParticipantsFive physiotherapists, who conducted the interviews and treatment of 81 patients undergoing radical prostatectomy.
MethodA qualitative descriptive phenomenological study was carried out, using a focus group technique with five people (4 women and 1 man) responsible for the treatment and assessment of patients with urinary incontinence after prostatectomy. Recordings were transcribed and the Atlas.ti7 programme was used to carry out the coding of the variables.
ResultsImportant factors were identified in the use of measuring instruments for the diagnosis and assessment of urinary incontinence in all the tools used.
ConclusionsSome situations can modify the objectivity of the various tests for the assessment of urinary incontinence. Some of the factors identified were lower fluid intake, less activity, use of manual clamp or urinals to avoid leakage, as well as the interference of certain drugs.