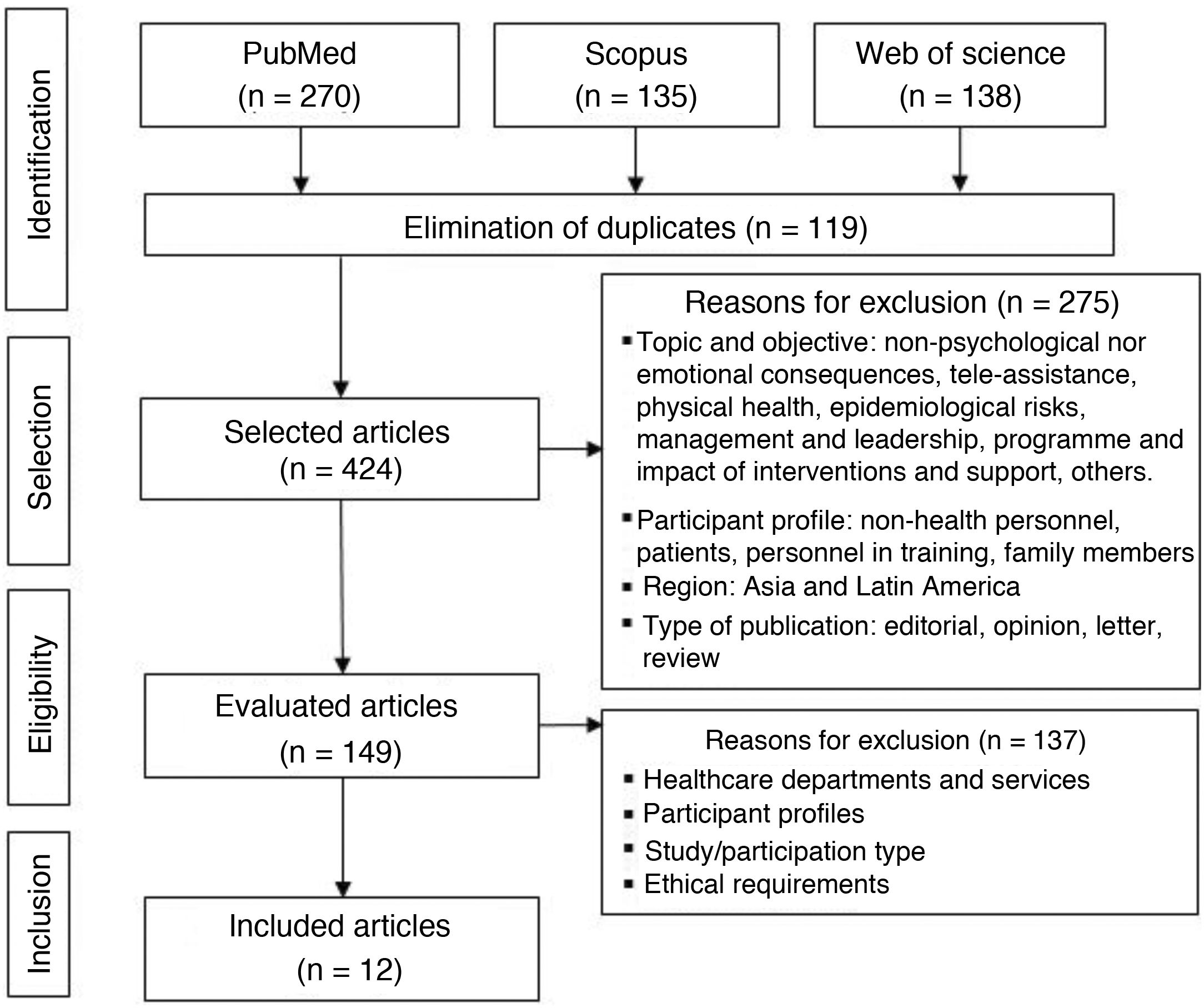
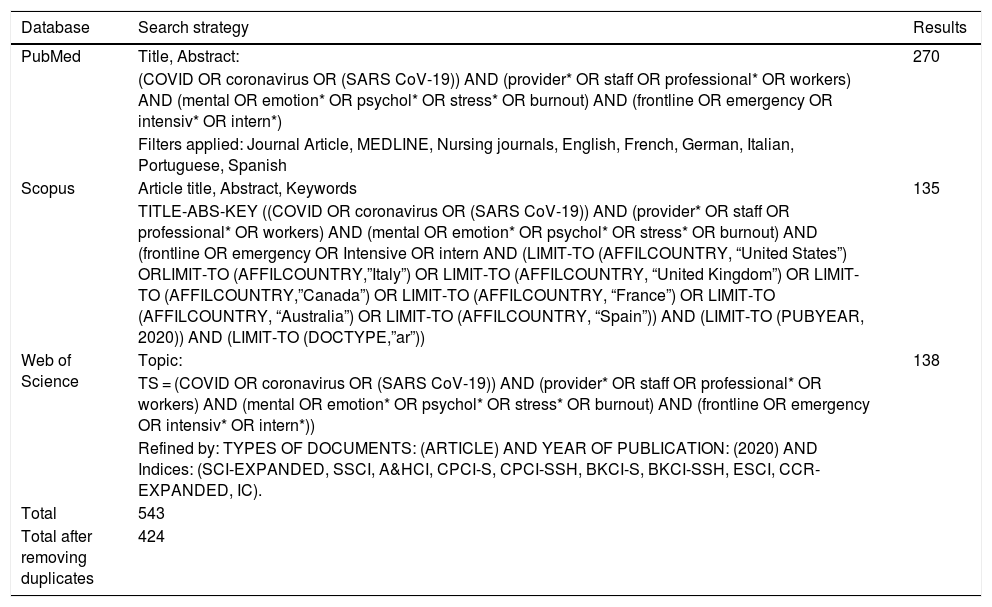
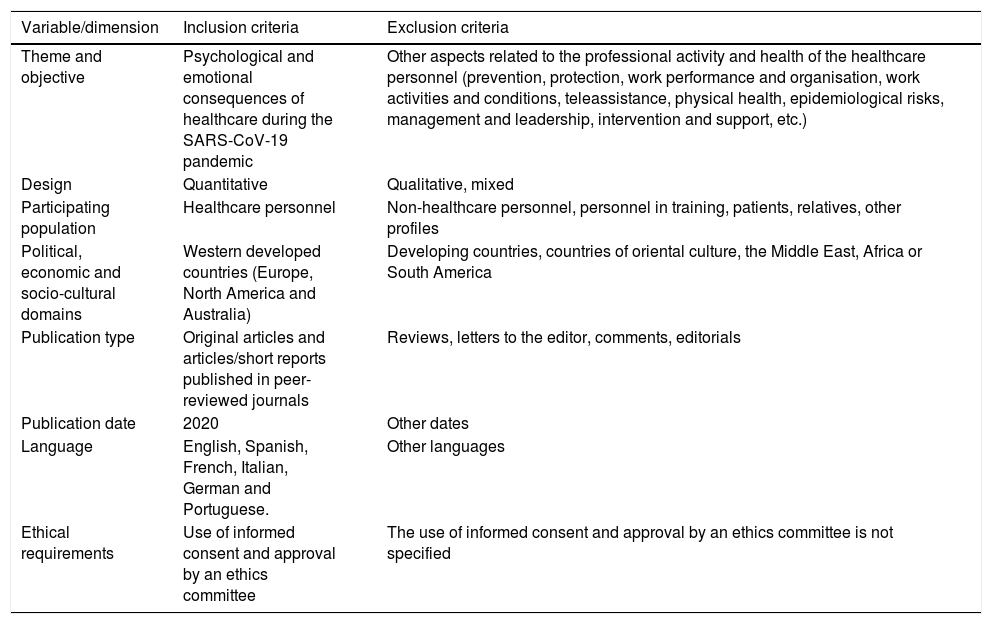
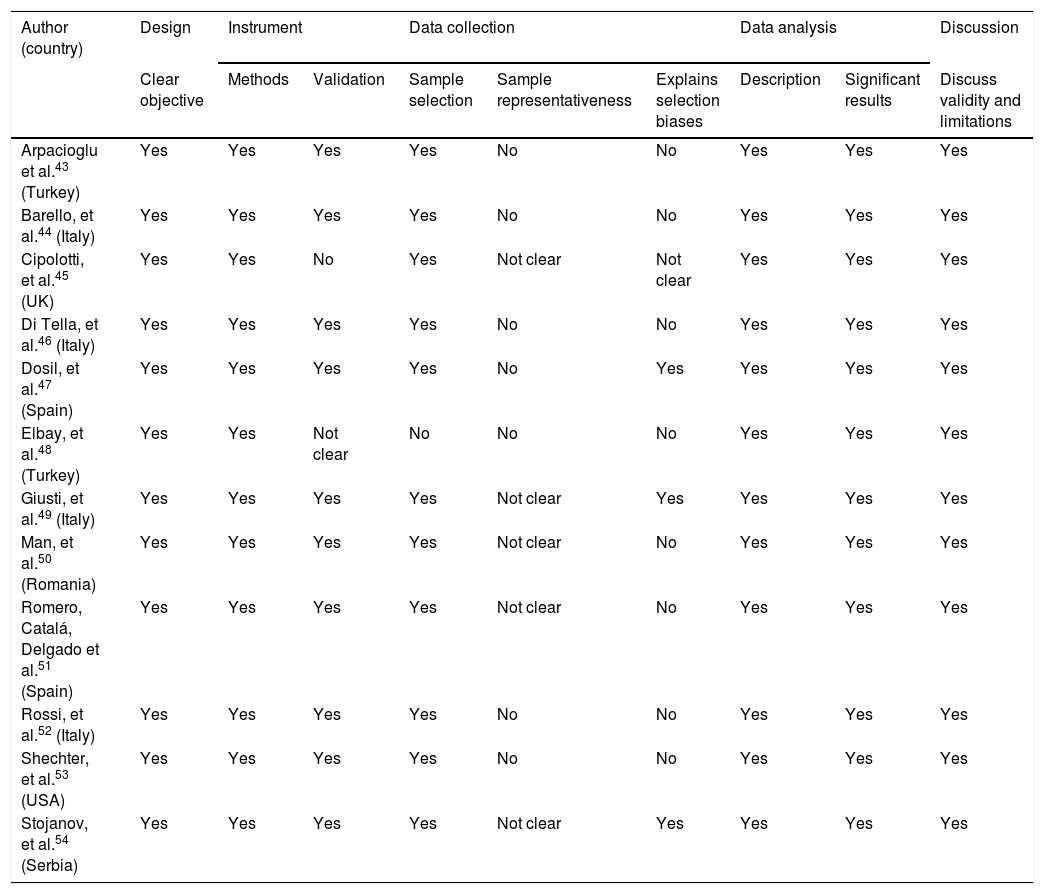
The aim of this study was to assess the psychological impact among healthcare workers who stand in the frontline of the SARS-CoV-2 crisis and to compare it with the rest of healthcare professionals, by means of a systematic review of Western publications. The systematic review was carried out in PubMed, Scopus and Web of Science databases and 12 descriptive studies were reviewed. The European and American quantitative studies reported moderate and high levels of stress, anxiety, depression, sleep disturbance and burnout, with diverse coping strategies and more frequent and intense symptoms among women and nurses, without conclusive results by age. In the first line of assistance the psychological impact was greater than in the rest of the health professionals and in the Asian area. It is necessary to go deeper into the emotional experiences and professional needs for emotional support in order to design effective interventions for protection and help.
El objetivo de este estudio fue conocer el impacto psicológico entre el personal sanitario de primera línea en la asistencia a pacientes con SARS-CoV-2 y compararlo con el resto de profesionales sanitarios, a través de una revisión sistemática de la producción científica en el ámbito occidental. La revisión se realizó en las bases PubMed, Scopus y Web of Science y se seleccionaron 12 artículos. Los estudios cuantitativos realizados en Europa y EE. UU. refirieron niveles moderados y altos de estrés, ansiedad, depresión, alteración del sueño y burnout, con estrategias de afrontamiento diversas y síntomas más frecuentes e intensos entre mujeres y enfermería, sin resultados concluyentes por edad. En la primera línea de asistencia, el impacto fue mayor que en el resto de profesionales sanitarios y que en el ámbito asiático. Se requiere profundizar en las experiencias emocionales y necesidades profesionales de apoyo emocional, para diseñar intervenciones eficaces de protección y ayuda.