Hand hygiene (HH) is the simplest and most effective measure for the prevention of infection related to healthcare. Despite this, compliance in healthcare professionals continues to be suboptimal. The aim of this study is to assess the impact of an expanded WHO multimodal strategy on hand hygiene compliance in healthcare personnel.
Material and methodsA quasi experimental before-after study was designed, carrying out the expanded WHO multimodal strategy in 2018, aimed at professionals in a tertiary hospital. In this strategy, apart from applying the 5 pillars of the WHO, a video was made, the administration of the WHO perceptions questionnaire and an incentive to the service/unit with better compliance, adding to the training a modality of practical workshops. The compliance percentages for 2017 and 2018 were compared.
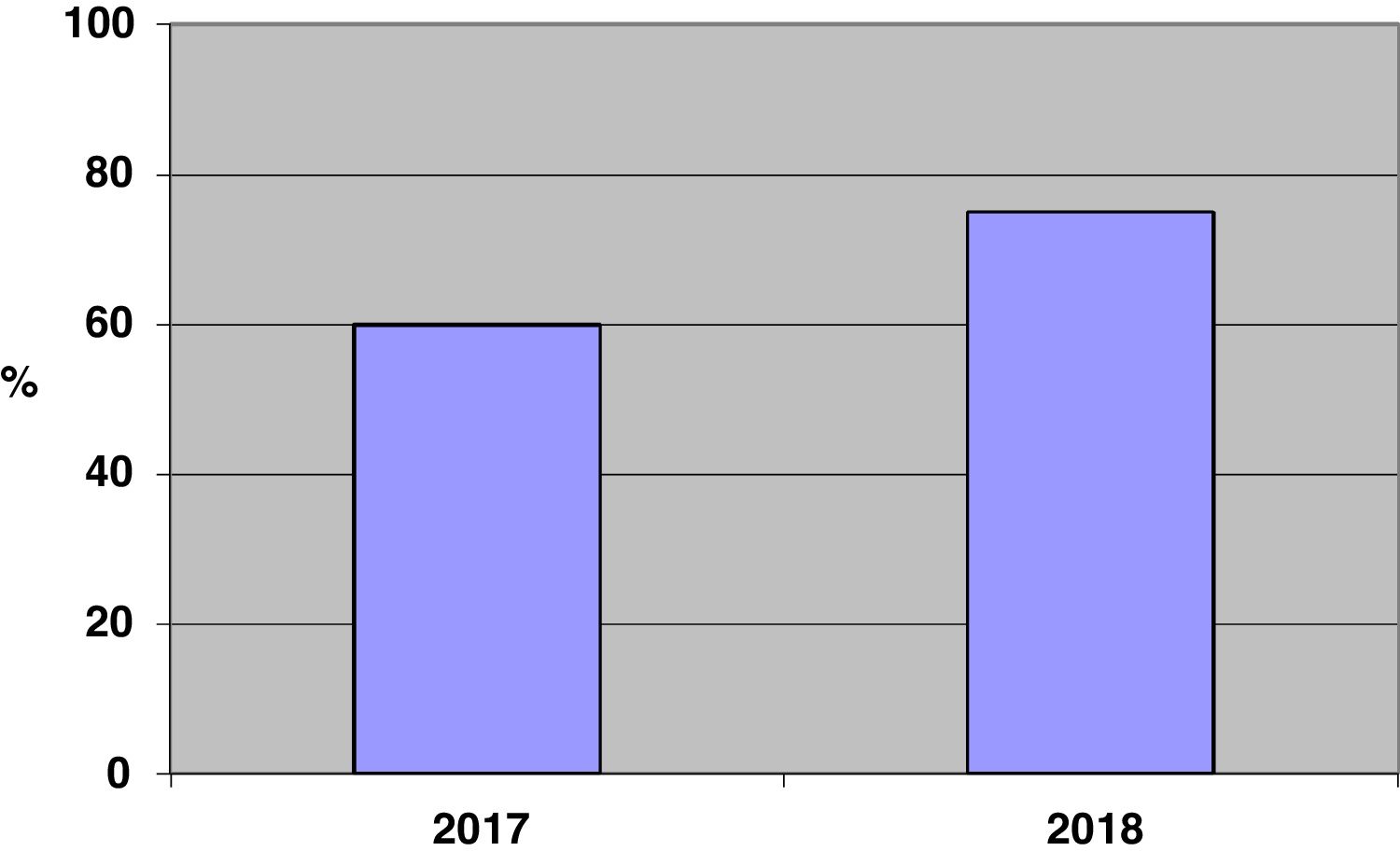
ResultsIn 2017, 1056 opportunities were observed, registering 631 HH actions, with global compliance of 60% (95% CI of 56.7–62.7). In 2018, with 1481 opportunities observed and 1111 HH actions, compliance was 75% (95% CI of 72.7–77.2) (P < .001). This compliance increased in all professional categories and in all indications.
ConclusionsThe application of an expanded multimodal strategy has a positive impact on HH compliance. Strategies should be directed to the categories with the worst compliance and continuously over time.
La Higiene de manos (HM) es la medida más sencilla y eficaz para la prevención de la infección relacionada con la asistencia sanitaria. A pesar de ello, el cumplimiento en los profesionales sanitarios continúa siendo subóptimo. El objetivo de este estudio es evaluar el impacto de una estrategia multimodal de la OMS ampliada en el cumplimiento de la higiene de manos en el personal sanitario.
Material y métodosSe diseñó un estudio cuasiexperimental pretest-posttest, llevando a cabo durante 2018 la estrategia multimodal de la OMS ampliada y dirigida a los profesionales de un hospital de tercer nivel. En esta estrategia, aparte de aplicar los 5 pilares de la OMS, se realizó un video, la administración del cuestionario de percepciones de la OMS y un incentivo al servicio/unidad con mejor cumplimiento, añadiendo a la formación una modalidad de talleres prácticos. Se compararon los porcentajes de cumplimiento del año 2017 y 2018.
ResultadosEn el año 2017 se observaron 1056 oportunidades registrándose 631 acciones de HM siendo el cumplimiento global del 60% (IC 95% de 56,7–62,7). En el año 2018, con 1481 oportunidades observadas y 1111 acciones de HM, el cumplimiento fue del 75% (IC del 95% de 72,7–77,2) (P < ,001). Este cumplimiento se incrementó en todos los estamentos y en todas las indicaciones.
ConclusionesLa aplicación de una estrategia multimodal ampliada tiene un impacto positivo en el cumplimiento de HM. Se deben dirigir estrategias a los estamentos con peor cumplimiento y de forma continuada en el tiempo.