The efficacy of antipsychotic drugs in improving negative symptoms of schizophrenia remains controversial. Psychological interventions, such as Social Skills Training (SST) and Social Cognition and Interaction Training (SCIT), have been developed and applied in clinical practice. The current meta-analysis was therefore conducted to evaluate the efficacy of controlled clinical trials using SST and SCIT on treating negative symptoms.
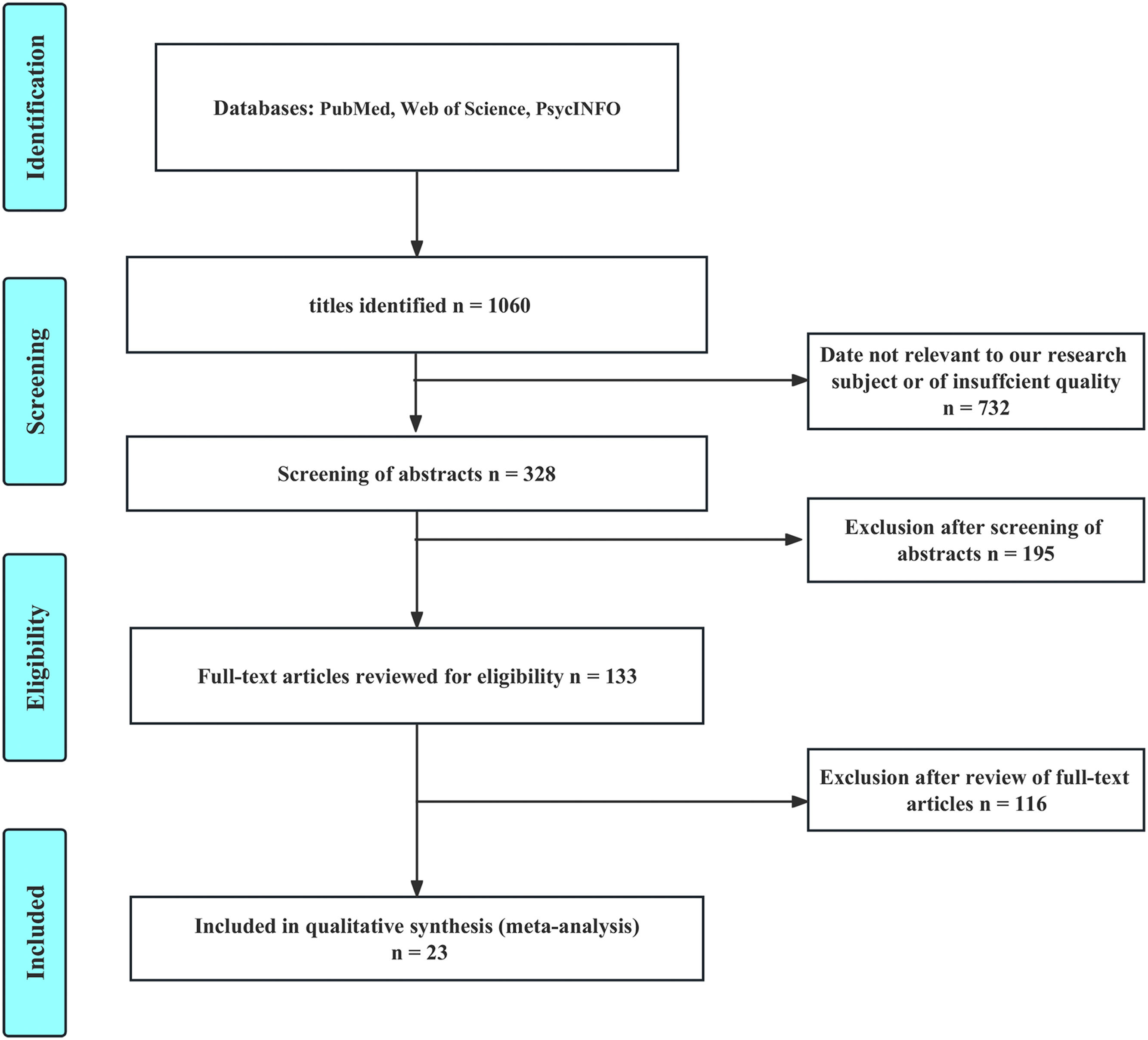
MethodsSystematical searches were carried out on PubMed, Web of Science, and PsycINFO databases. The standardized mean difference (SMD) with 95% confidence intervals (CI) was calculated to assess the effect size of SST/SCIT on negative symptoms. Subgroup and meta-regression analyses were conducted to explore sources of heterogeneity and identify potential factors that may influence their efficacy.
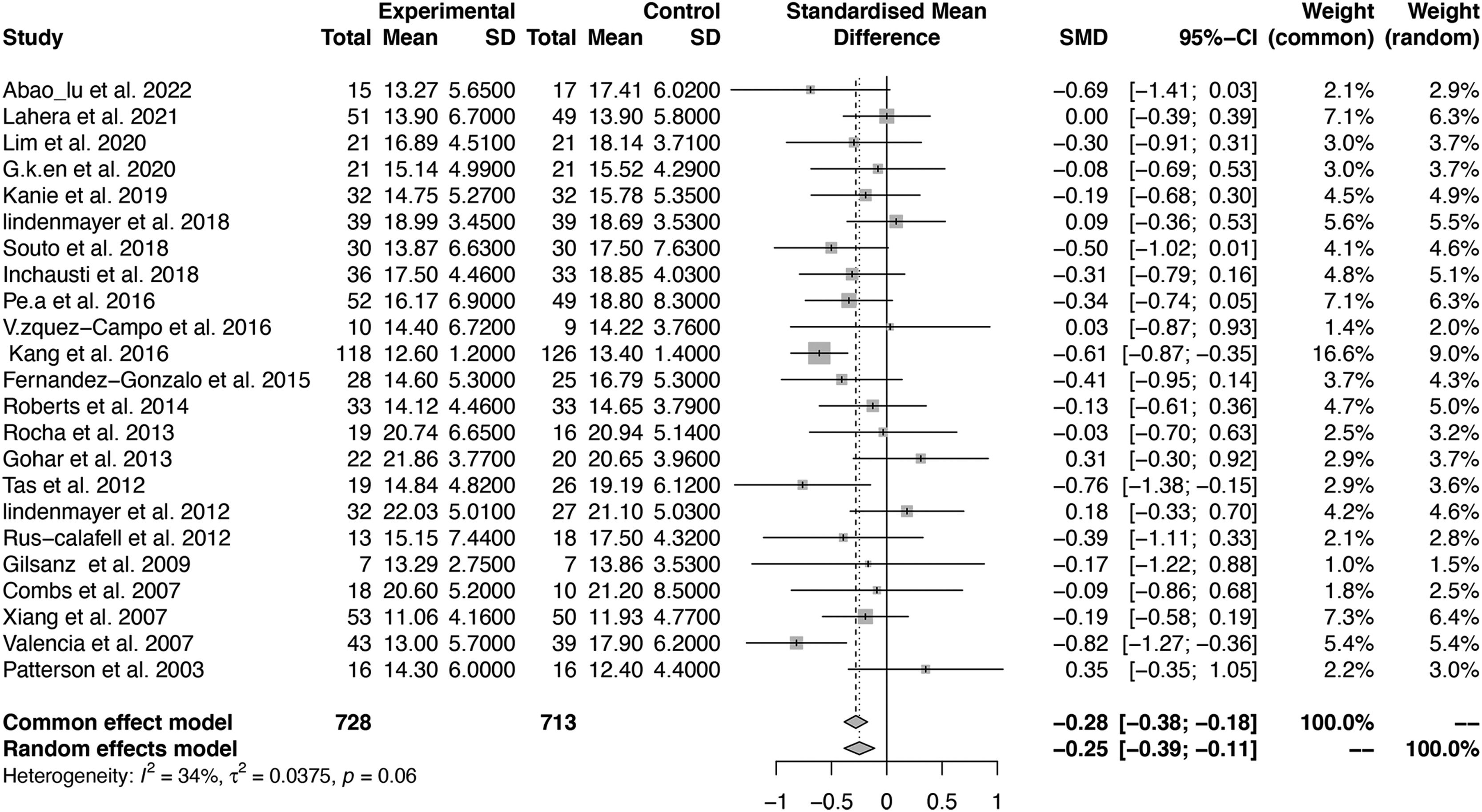
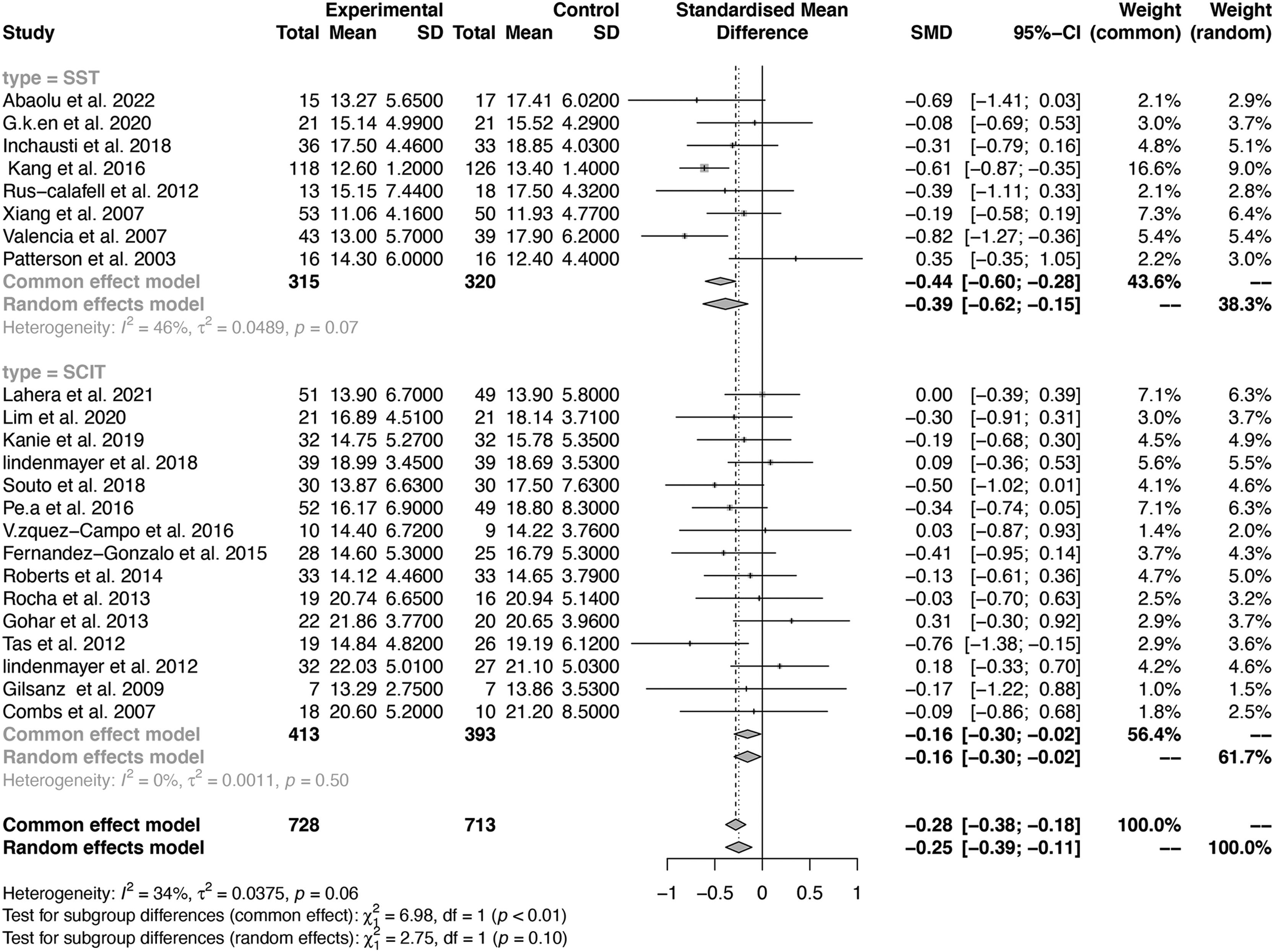
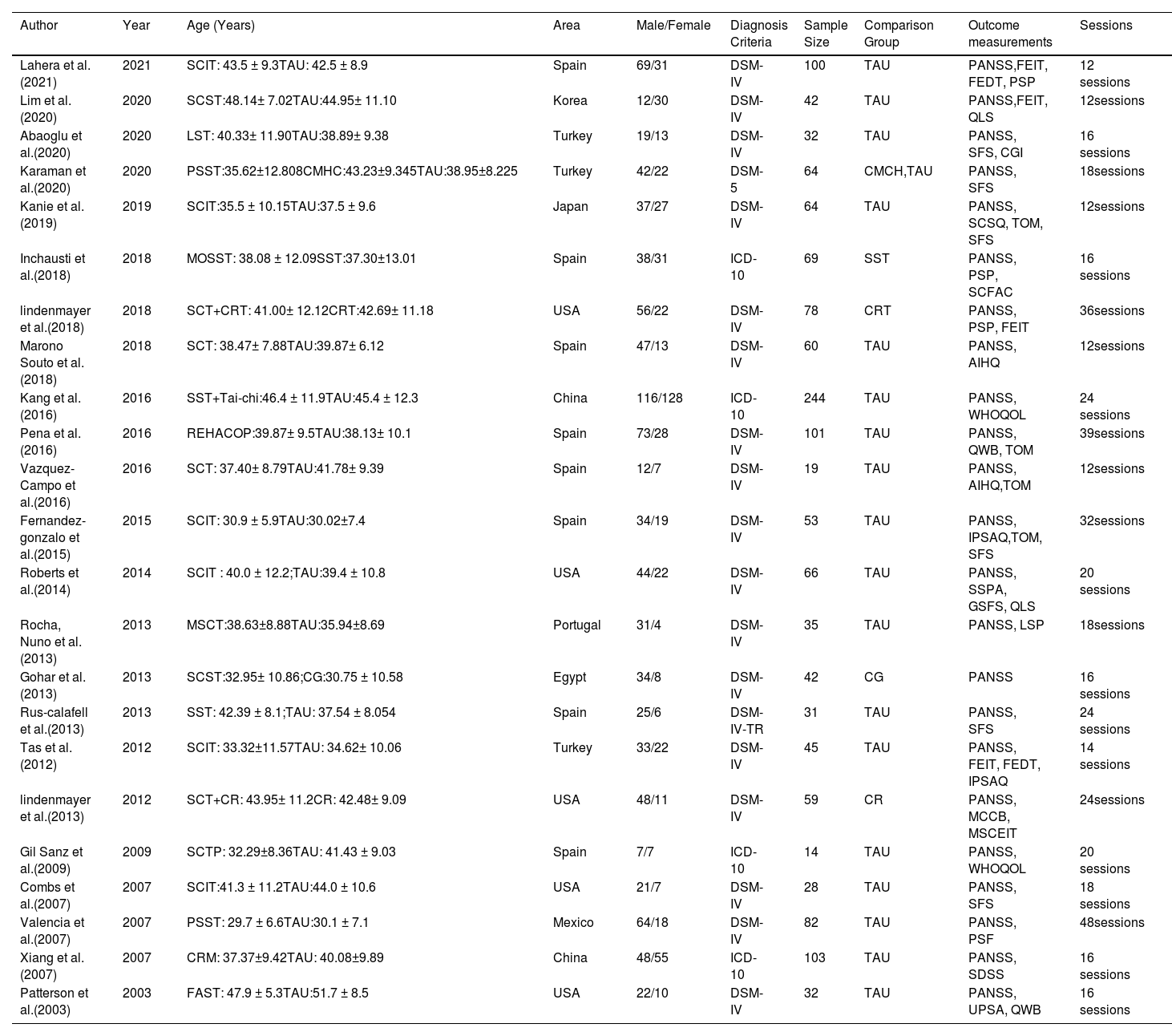
ResultsA total of 23 studies including 1441 individuals with schizophrenia were included. The SST group included 8 studies with 635 individuals, and the SCIT group included 15 studies with 806 individuals. The effect size for the efficacy of SST on negative symptoms was -0.44 (95% CI: -0.60 to -0.28; p < 0.01), while SCIT was -0.16 (95% CI: -0.30 to -0.02; p < 0.01).
ConclusionsOur findings suggest that while both SST and SCIT can alleviate negative symptoms, the former appears to be more effective. Our results provide evidence-based guidance for the application of these interventions in both hospitalized and community individuals and can help inform the treatment and intervention of individuals with schizophrenia.