Management of patients diagnosed of acute uncomplicated diverticulitis has evolved lately and according to the latest guidelines, outpatient treatment and management without antibiotherapy may be used in selected patients. The aim of this study is to evaluate the adhesión among national centres to these and others recommendations related to this pathology.
MethodsAn online national survey, that has been broadcast by several applications, was performed. The results obtained were statistically analysed.
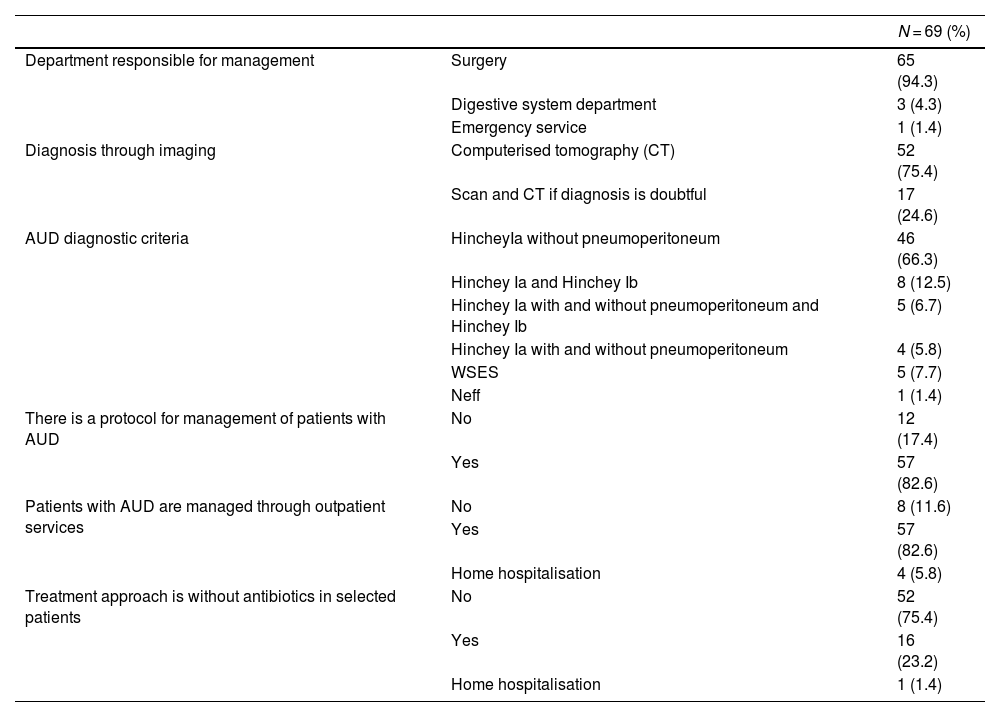
ResultsA total of 104 surgeons participated, representing 69 national hospitals. Of those, in 82.6% of the centres, outpatient management is performed for acute uncomplicated diverticulitis. 23.2% of the hospitals have a protocol stablished for treatment without antibiotherapy in selected patients. Centres that do not follow these protocols allege that the mean reasons are the logistic difficulties to set them up (49.3%) and the lack of current evidence for it (44.8%). Significative statistical differences have been found when comparing the establishment of such protocols between centres with advanced accredited units and those who are not, with higher rates of outpatient management and treatment without antibiotics in accredited units (p ≤ .05).
ConclusionsIn spite that this a very common disease, there is a huge national heterogeneity in its treatment. This is why it would adviseable to unify diagnostic and treatment criteria by the collaboration of scientific societies and the simplification of the development of hospitalary protocols.
El manejo de los pacientes diagnosticados de diverticulitis aguda no complicada ha evolucionado en los últimos años y según diversas guías clínicas internacionales actuales, el tratamiento ambulatorio y sin antibioterapia puede ser utilizado en pacientes seleccionados. El objetivo de este estudio es evaluar la adhesión de los distintos centros nacionales a estas y otras recomendaciones en esta patología.
MétodosSe realizó una encuesta online a nivel nacional que se dio a conocer a través de diversas aplicaciones informáticas y se analizaron estadísticamente los resultados obtenidos.
ResultadosParticiparon 104 cirujanos, representando 69 centros hospitalarios nacionales. En el 82,6% de los centros, se realiza manejo ambulatorio de los pacientes diagnosticados de diverticulitis aguda no complicada. El 23,2% de los centros tiene implantado un protocolo de tratamiento sin antibioterapia en pacientes seleccionados, mientras que en los centros que no siguen estas recomendaciones, las razones principales son las dificultades logísticas para su desarrollo (49,3%) y la ausencia de evidencia actual para ello (44,8%). Se han encontrado diferencias estadísticamente significativas al comparar la implantación de dichos protocolos entre centros con unidades acreditadas avanzadas y aquellas que no, con mayores tasas de manejo ambulatorio y sin antibioterapia en los centros acreditados avanzados (p ≤ 0,05).
ConclusionesA pesar de ser una patología muy frecuente, existe mucha heterogeneidad en su tratamiento a nivel nacional, por lo que sería recomendable la unificación de criterios diagnósticos y de tratamiento mediante la colaboración de las sociedades científicas y la simplificación de la puesta en marcha de protocolos hospitalarios.