To assess the oncologic outcomes and the safety profile of a reduced-dose versus full-dose BCG regimen in patients with non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer (NMIBC).
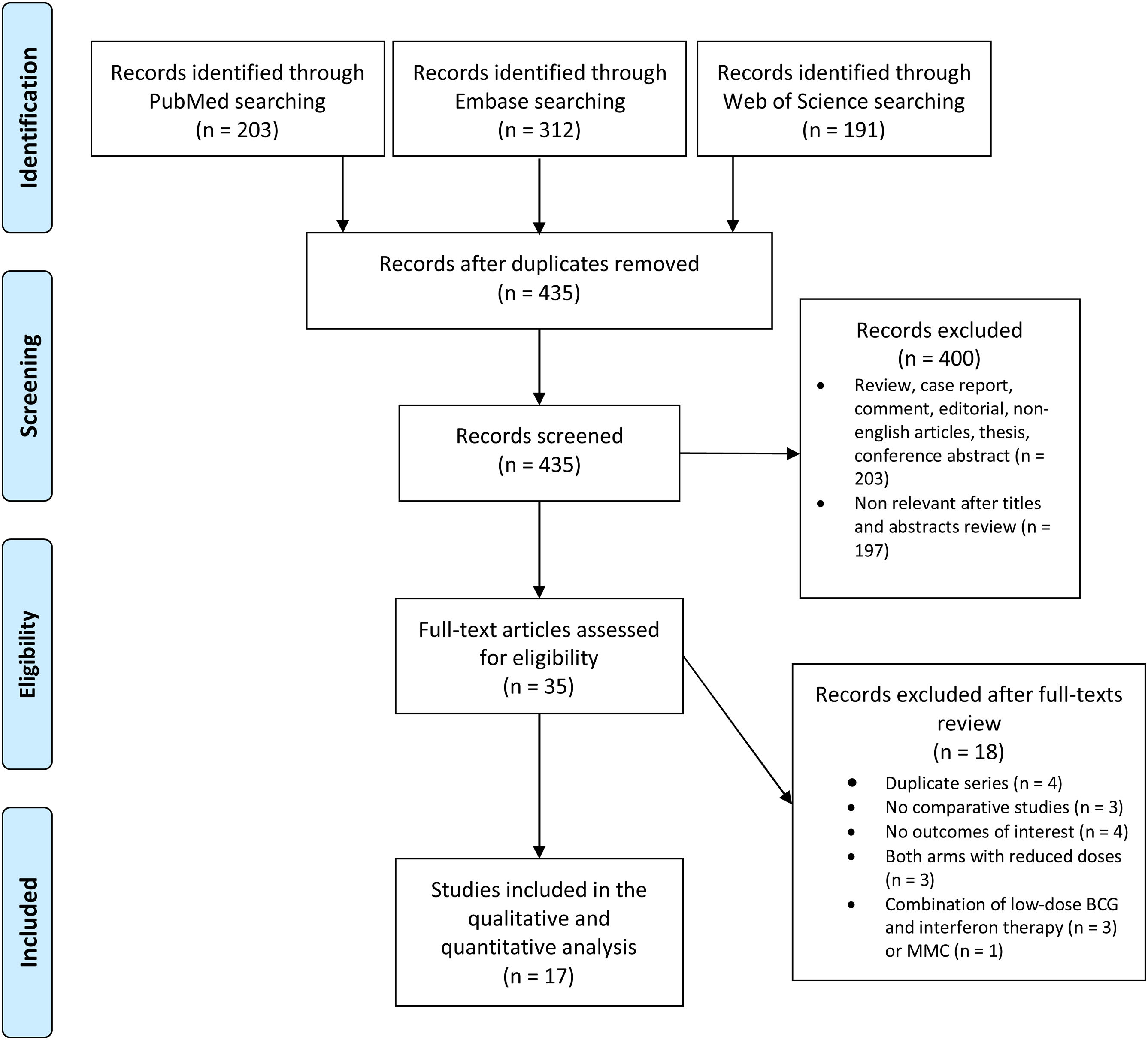
Material and methodsWe performed a systematic review according to Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA). The PubMed, Embase, and Web of Science databases were searched in January 2022 for studies that analyzed oncological outcomes and compared between reduced- and full-dose BCG regimens.
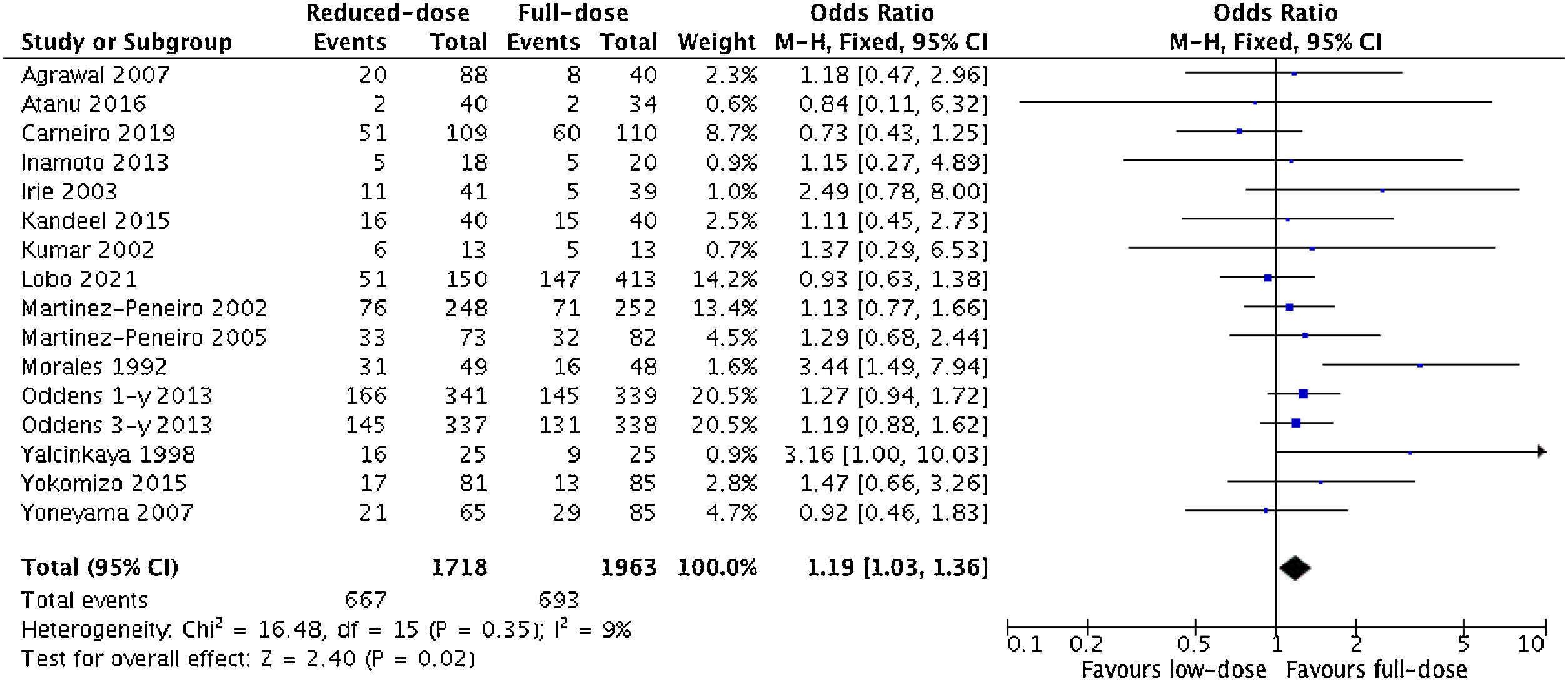
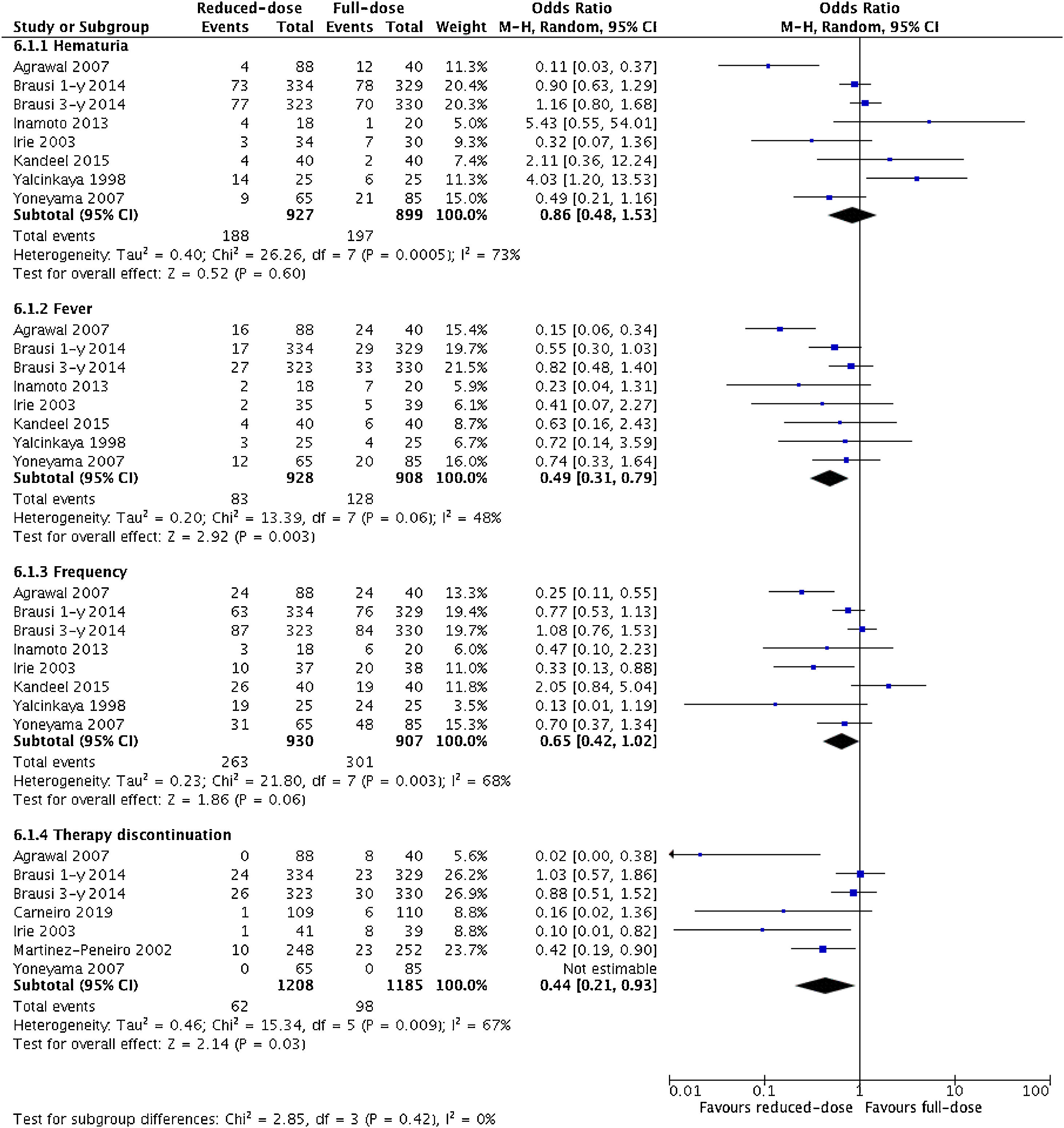
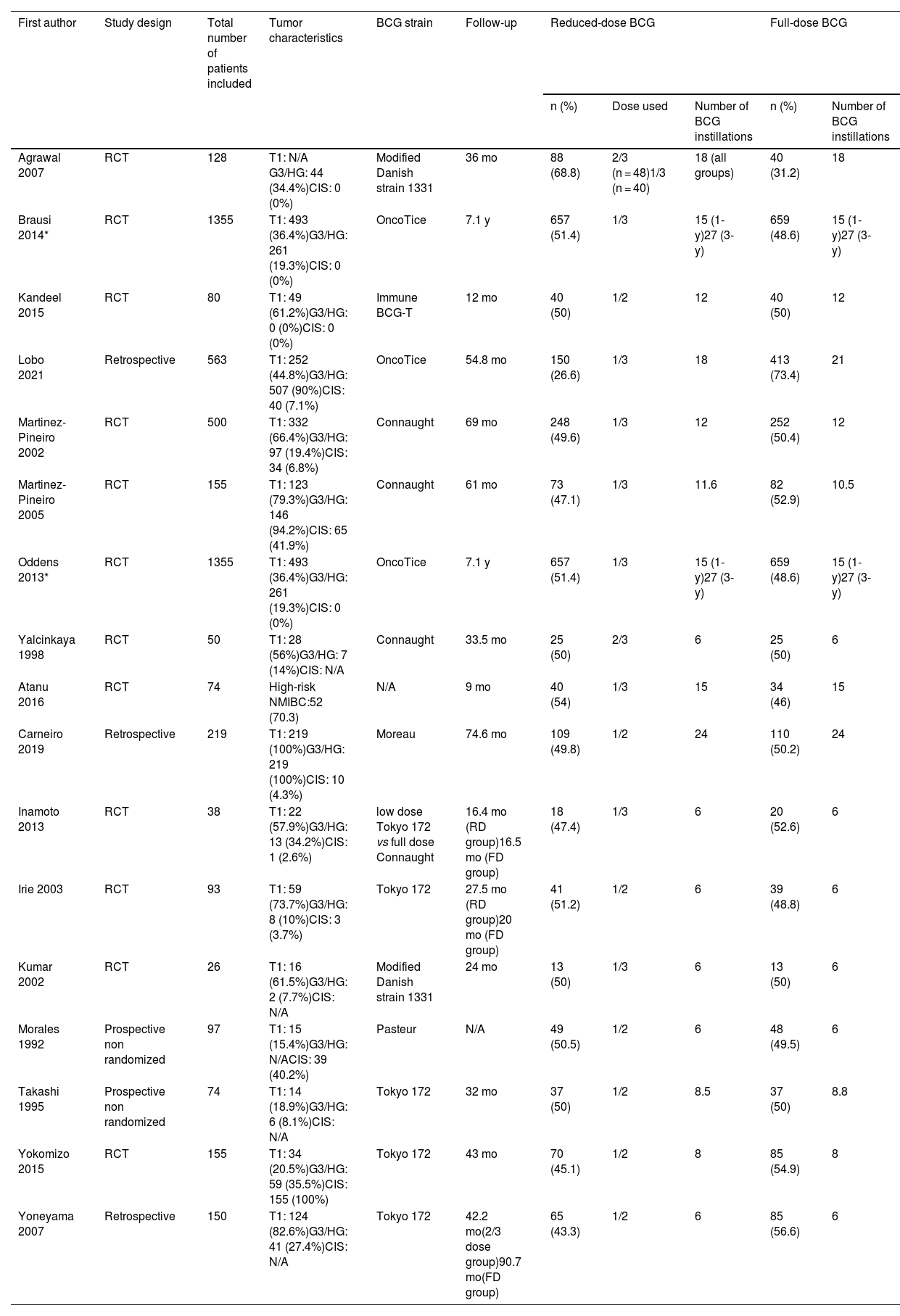
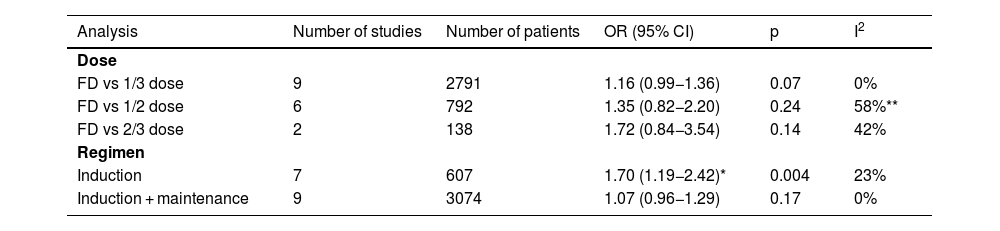
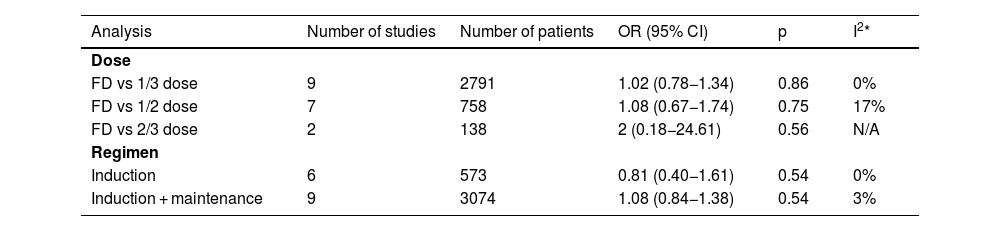
ResultsSeventeen studies including 3757 patients met our inclusion criteria. Patients who received reduced-dose BCG had significantly higher recurrence rates (OR 1.19; 95%CI, 1.03–1.36; p = 0.02). The risks of progression to muscle-invasive BC (OR 1.04; 95%CI, 0.83–1.32; p = 0.71), metastasis (OR 0.82; 95%CI, 0.55–1.22; p = 0.32), death from BC (OR 0.80; 95%CI, 0.57–1.14; p = 0.22), and all-cause death (OR 0.82; 95%CI, 0.53–1.27; p = 0.37) were not statistically different. When restricting the analyses to randomized controlled trials, we found similar results. In subgroup analysis, reduced dose was associated with a higher rate of BC recurrence in studies that used only an induction regimen (OR 1.70; 95%CI, 1.19−2.42; p = 0.004), but not when a maintenance regimen was used (OR 1.07; 95%CI, 0.96−1.29; p = 0.17). Regarding side effects, the reduced-dose BCG regimen was associated with fewer episodes of fever (p = 0.003), and therapy discontinuation (p = 0.03).
ConclusionThis review found no association between BCG dose and BC progression, metastasis, and mortality. There was an association between reduced dose and BC recurrence, which was no longer significant when a maintenance regimen was used. In times of BCG shortage, reduced-dose regimens could be offered to BC patients.
Evaluar los resultados oncológicos y el perfil de seguridad de un régimen de BCG de dosis reducida frente a uno de dosis completa en pacientes con cáncer de vejiga no músculo infiltrante (CVNMI).
Material y métodosSe realizó una revisión sistemática de acuerdo con la declaración PRISMA (Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses). Se realizaron búsquedas de estudios que analizaran los resultados oncológicos entre los regímenes de BCG con reducción de dosis y dosis completa en las bases de datos PubMed, Embase y Web of Science en enero del 2022.
ResultadosDiecisiete estudios que incluían a 3.757 pacientes cumplieron los criterios de inclusión. Los pacientes que recibieron reducción de dosis de BCG tuvieron tasas de recidiva significativamente mayores (OR 1,19; IC del 95%, 1,03–1,36; p = 0,02). Los riesgos de progresión a un CV músculo infiltrante (OR 1,04; IC 95%, 0,83–1,32; p = 0,71), de metástasis (OR 0,82; IC 95%, 0,55–1,22; p = 0,32), de muerte por CV (OR 0,80; IC 95%, 0,57–1,14; p = 0,22) y de muerte por cualquier causa (OR 0,82; IC 95%, 0,53–1,27; p = 0,37) no fueron estadísticamente diferentes. Al restringir los análisis a ensayos controlados aleatorizados, se encontraron resultados similares. En el análisis de subgrupos, la reducción de dosis se asoció con una mayor tasa de recidiva de CV en los estudios que utilizaron sólo un régimen de inducción (OR 1,70; IC 95%, 1,19–2,42; p = 0,004), lo cual no se observó cuando se utilizó un régimen de mantenimiento (OR 1,07; IC 95%, 0,96–1,29; p = 0,17). En cuanto a los efectos secundarios, el esquema reducido de BCG se asoció con menos episodios de fiebre (p = 0,003) y de interrupción del tratamiento (p = 0,03).
ConclusiónEsta revisión no encontró ninguna asociación entre la dosis de BCG y la progresión, la metástasis y la mortalidad del CV. Hubo una asociación entre la reducción de dosis y la recidiva del CV, que dejó de ser significativa cuando se utilizó un régimen de mantenimiento. En períodos de escasez de BCG, podrían ofrecerse esquemas de dosis reducidas a los pacientes con CV.