Different studies have shown the relationship between erectile dysfunction, metabolic syndrome and cardiovascular disease. The objective of this study was to evaluate the presence of arteriopathy performing carotid ultrasound in patients with and without erectile dysfunction.
Material and methodsWe conducted a case–control study on 44 patients consulting for erectile dysfunction and 20 controls. All subjects completed the IIEF-5 test and we studied the criteria for metabolic syndrome, and a carotid ultrasound to study the intima-media thickness and the presence of atherosclerotic plaques was done.
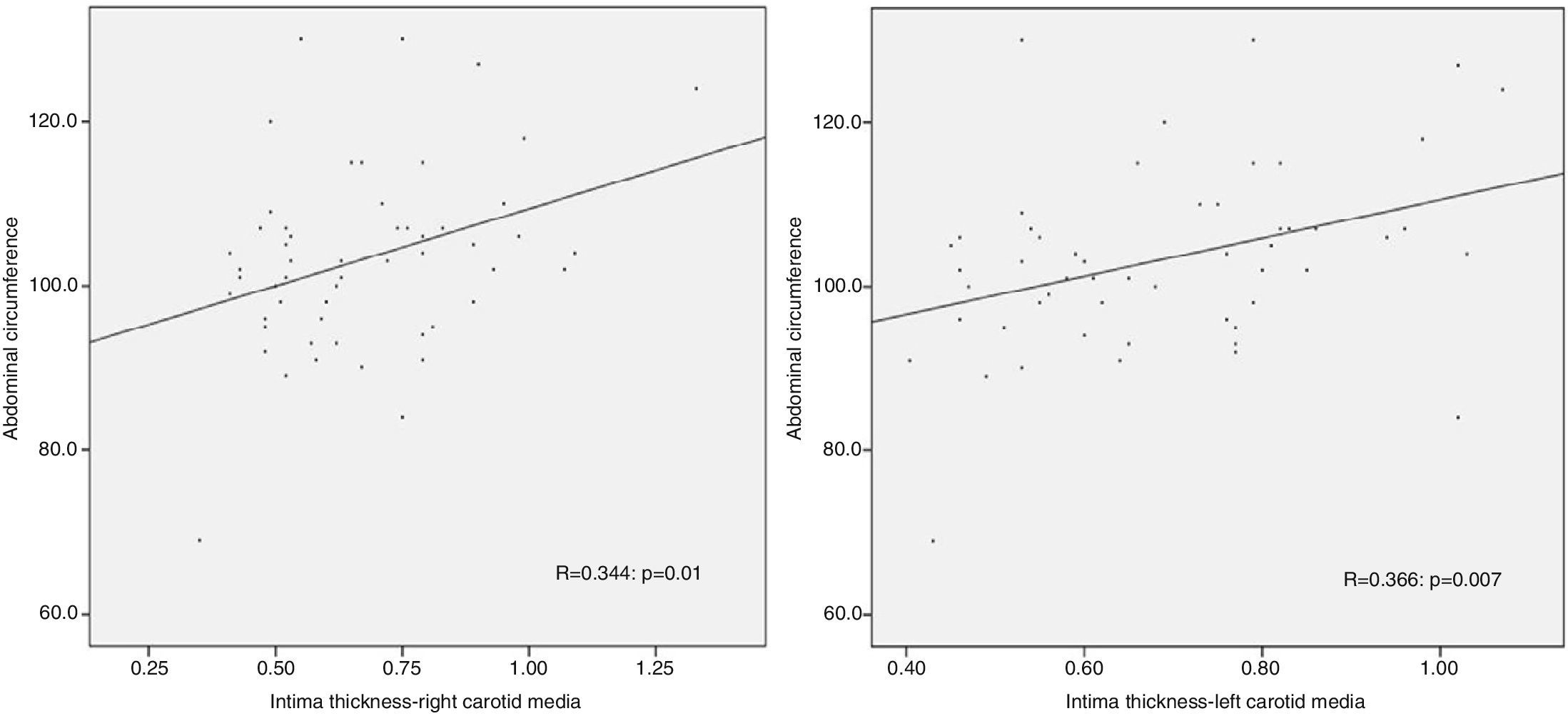
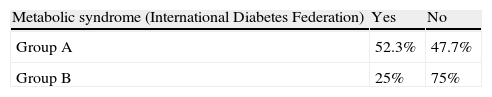
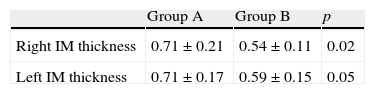
ResultsMean intima-media thickness was 0.71mm±0.21 for the right and of 0.71±0.17 for the left carotid in patients with erectile dysfunction. In the control group, the means were 0.54±0.11 and 0.59±0.15mm respectively, and statistically significant differences were P=0.02 and P=0.05 respectively. No plaque was found in any control, but in 25% of both carotid arteries of patients with erectile dysfunction (P=0.01). As metabolic syndrome, according to the American Heart Association, was diagnosed in 52.8% of patients with erectile dysfunction, and in 16.7% of controls, and according to the International Diabetes Federation, 52.3% of patients with erectile dysfunction and 25% of controls met diagnostic criteria. In both cases there were significant differences (P<0.01 and P=0.02 respectively). We found a positive linear correlation between waist circumference and the intima-media thickness in both carotids (P<0.05).
ConclusionsPatients with erectile dysfunction may be at increased risk of cardiovascular disease, as determined by the presence of arterial disease in the carotid arteries, which indicates that we should make a more thorough and comprehensive study of patients with erectile dysfunction.
Diferentes estudios ponen de manifiesto la relación entre disfunción eréctil, síndrome metabólico y enfermedad cardiovascular. El objetivo de este estudio fue evaluar la presencia de arteriopatía mediante la realización de ecografía de carótidas en pacientes con y sin disfunción eréctil.
Material y métodosHemos realizado un estudio caso-control con 44 pacientes que consultan por disfunción eréctil y 20 controles. Todos los sujetos rellenaron el test IIEF-5 y se estudiaron los criterios de síndrome metabólico, además de una ecografía carotídea, para estudiar el grosor íntima-media y la presencia de placas de ateroma.
ResultadosLa media del grosor íntima-media en milímetros fue de 0,71±0,21 para la derecha y de 0,71±0,17 para la izquierda en los pacientes con disfunción eréctil. En el grupo control las medias fueron de 0,54±0,11 y de 0,59±0,15 respectivamente, existiendo diferencias estadísticamente significativas (p=0,02 y p=0,05 respectivamente). No se encontró placa de ateroma en ningún control, pero sí en el 25% de ambas carótidas de los pacientes con disfunción eréctil (p=0,01). En cuanto al síndrome metabólico, según la American Heart Association, se diagnosticó a un 52,8% de los pacientes con disfunción eréctil y a un 16,7% de los controles, y según la International Diabetes Federation un 52,3% de los pacientes con disfunción eréctil y un 25% de los controles cumplen criterios diagnósticos. En ambos casos existieron diferencias significativas (p<0,01 y p=0,02 respectivamente). Hemos encontrado correlación lineal y positiva entre el perímetro abdominal y el grosor íntima-media en ambas carótidas (p<0,05).
ConclusionesLos pacientes con disfunción eréctil pueden presentar mayor riesgo de enfermedad cardiovascular, determinado por la presencia de arteriopatía en las carótidas, lo cual nos indica que debería realizarse un estudio más detenido y global a los pacientes con disfunción eréctil.