Advanced parental age (APA) has been associated with an increased risk for autism in the offspring. One explanatory model includes delayed fatherhood in parents with autistic traits.
Material and methodsWe investigated (1) whether autistic traits in parents, evaluated with the Autism-spectrum Quotient (AQ), correlate with APA in 128 families, (2) in 83 trios with genetic data available, whether AQ correlated with polygenic vulnerability calculated by Polygenic Risk Scores (PRS). We stratified the analyses by as per DSM-IV autism subtypes and by parental sex.
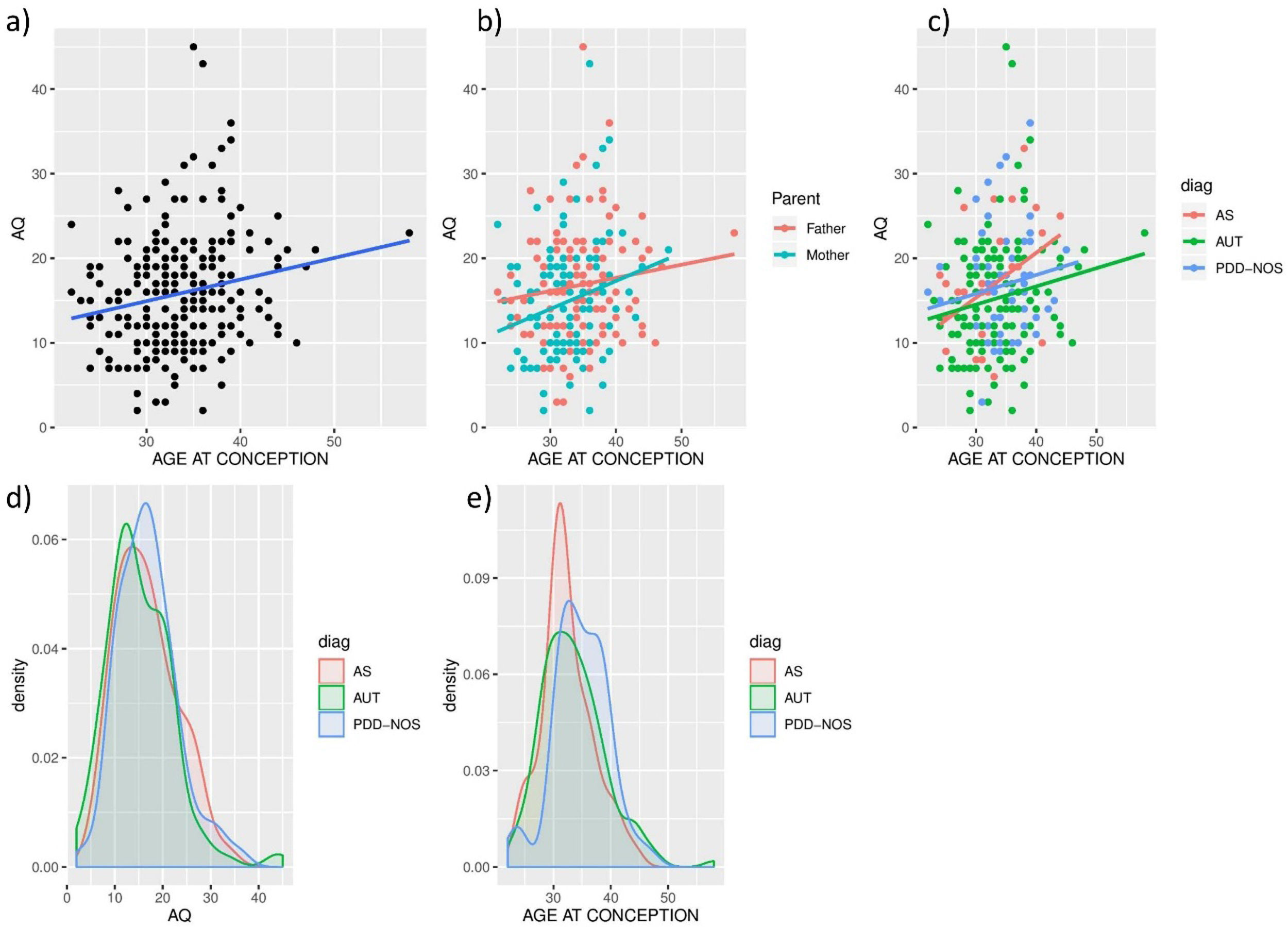
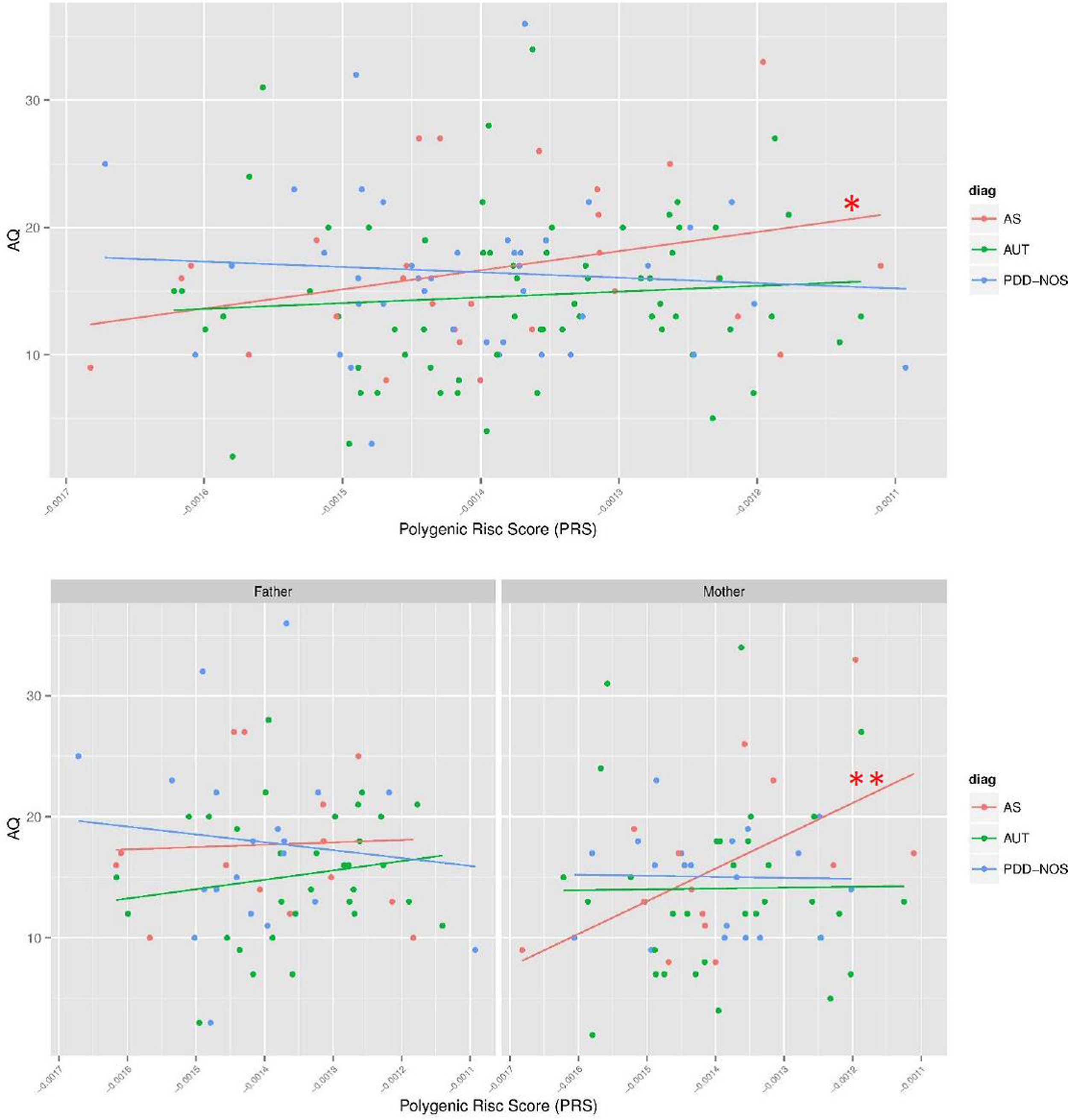
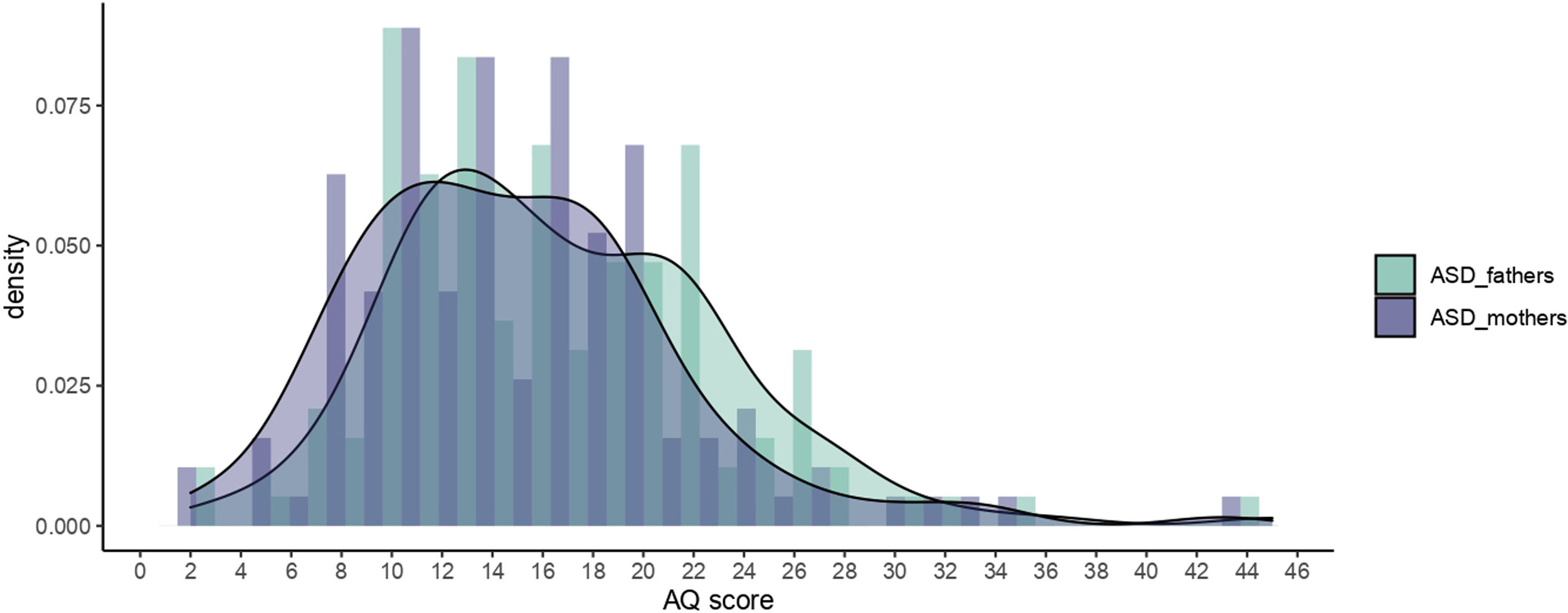
ResultsWe found a statistically significant relation between AQ and APA (r=0.207, p=8.39×10−4, n=256), significantly only in mothers (r=0.233, p=8.23×10−3, n=128) and in Asperger Syndrome (AS) (r=0.319, p=0.034, n=44). There was a significant association between PRS and AQ in the mothers of the participants with AS (β (95%CI)=3.28 (0.03–6.59); p=0.047).
ConclusionsThese results show that, in this sample, older mothers present more autistic traits, and APA seems to relate to an AS profile. Furthermore, PRS is significantly associated with maternal AQ of AS subjects. Consequently, a higher polygenic maternal contribution (both by AQ and PRS) seems to contribute to an AS profile.