Delirium, in addition to causing suffering to patients, relatives and caregivers, is associated with increases in morbidity, mortality and hospital complications, which leads to high costs for the health system.
ObjectiveTo determine the incidence of delirium and related factors in patients admitted to an intensive care unit of a health institution in the city of Monteria, Colombia.
MethodsA descriptive, longitudinal study with a quantitative approach that includes the correlation of variables of interest with the incidence of delirium. For the collection of information and subsequent analysis, the CAM-ICU scale –which allowed the identification of the presence of delirium– and the APACHE II severity scale were used. Likewise, a data card was prepared based on clinical and epidemiological variables of interest.
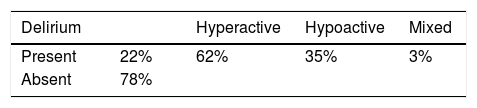
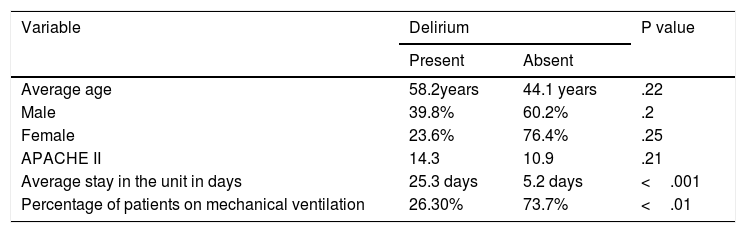
ResultsThe patients were mostly men (50.5%) with an average age of 60 years. The incidence of delirium was 22% with hyperactive presentation in 62% of cases. There was no relationship between the presence of delirium and the variables of age, sex and APACHE II, although correlation was observed with the use of mechanical ventilation and with the days of stay in the health centre.
ConclusionsPatients who developed delirium, the hyperactive form being the most common, were characterised either by having spent several days in the ICU or having undergone mechanical ventilation.
El delirium, además de causar sufrimiento a pacientes, familiares y cuidadores, está asociado a incrementos en la morbilidad, mortalidad y complicaciones hospitalarias, lo que deriva en altos costos para el sistema de salud.
ObjetivoDeterminar la incidencia de delirium y los factores relacionados en los pacientes ingresados en una unidad de cuidados intensivos de una institución de salud en la ciudad de Montería, Colombia.
MétodoEstudio de tipo descriptivo, longitudinal con enfoque cuantitativo, que incluye la correlación de variables de interés con la incidencia de delirium. Para la recolección de información y posterior análisis, se utilizó la escala CAM-ICU –que permitió identificar la presencia de delirium– y la escala de severidad APACHE II. Así mismo, se elaboró una cédula de datos a partir de variables clínicas y epidemiológicas de interés.
ResultadosLos pacientes en su mayoría fueron hombres (50,5%) con edad promedio de 60 años. La incidencia de delirium fue de 22% con presentación hiperactiva en el 62% de los casos. No se documentó relación entre la presencia de delirium y las variables de edad, sexo y APACHE II, aunque sí se observó correlación con el uso de ventilación mecánica y con los días de estancia en el centro de salud.
ConclusionesLos pacientes que presentaron delirium, siendo la forma hiperactiva la más común, se caracterizaron ya sea por haber estado varios días de estancia en la Unidad de Cuidados Intensivos o por haber estado sometidos a ventilación mecánica.
Article
Diríjase al área privada de socios de la web de la SEDENE, (https://sedene.com/revista-de-sedene/ ) y autentifíquese.