The ability to process information depends on the state of cerebral activation, which can be recorded using the electroencephalogram (EEG). In this article, a bioelectrical quantification method is used for the study of attention, based on a frequency exponent.
ObjectivesTo analyse the attention of a selected sample of 36 volunteers from the Armed Forces in a state of rest and during the performance of military simulation tasks. To establish the potential existence of differences between the male and female groups in different EEG types (rest with closed eyes and 2 specific attention tasks).
MethodsThe spectral power was calculated and an exponent obtained that models this magnitude by means of a function of coloured noise type. The third minute of the signals of each subject was used in 3 types of EEG and 12 channels. The data were analysed using a statistical test.
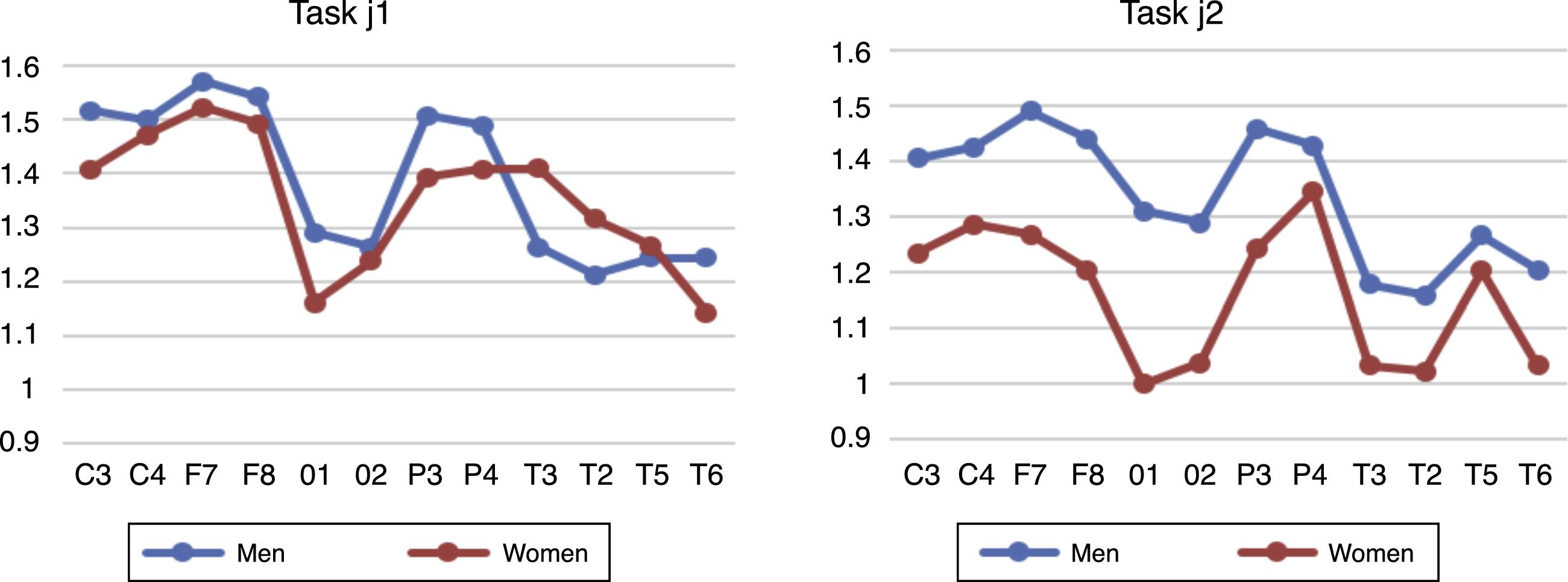
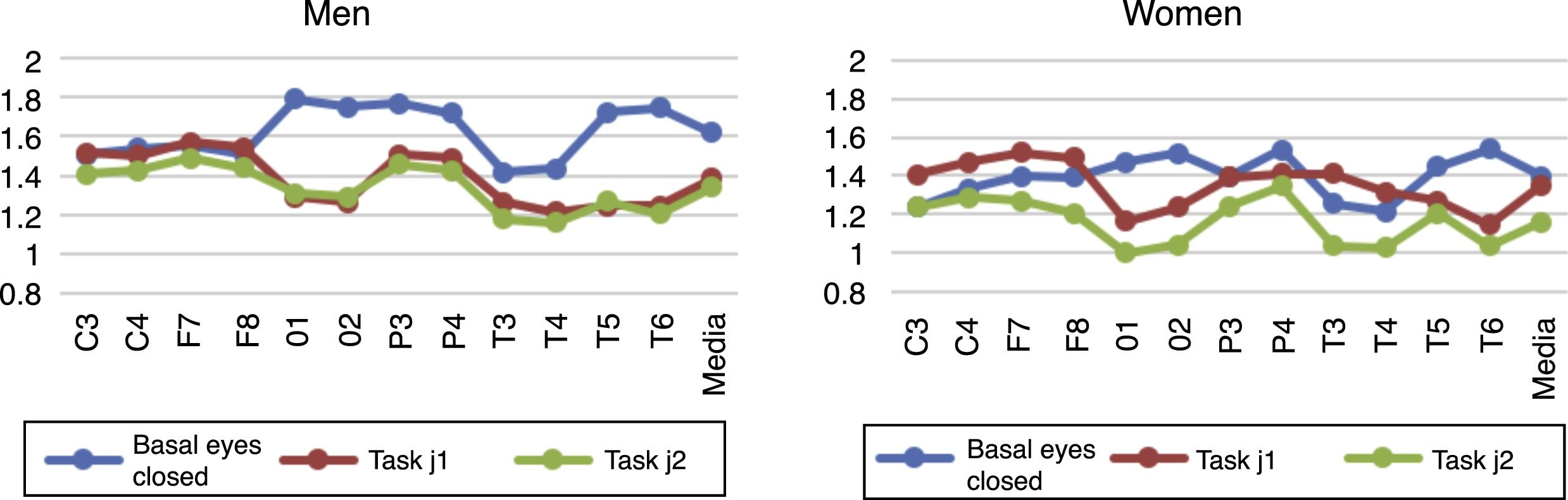
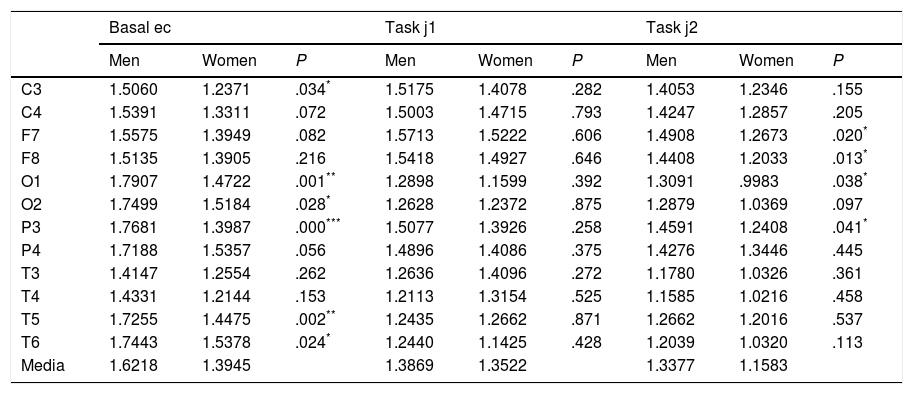
ResultsSignificant differences were observed between males and females in the basal EEG (rest with closed eyes) in the parietal, occipital, temporal, and central regions (1.62 was the value of the male cortical average versus 1.39 for the female), and during the task (j2) in frontal, occipital and parietal regions (1.34 for the male cortical average versus 1.16 in the female).
ConclusionsThe female group shows greater cerebral bioelectrical complexity than that of men in the same type of EEG. The frequency exponent behaves inversely to the difficulty of the task, in both genders.
La capacidad para procesar la información depende del estado de activación cerebral, que puede registrarse por medio del electroencefalograma (EEG). En este artículo se utiliza un método de cuantificación bioeléctrica para el estudio de la atención, basado en un exponente de tipo frecuencial.
ObjetivosAnalizar la atención de una muestra elegida entre 36 voluntarios de las Fuerzas Armadas en estado de reposo y durante el desempeño de tareas de simulación militar. Establecer si existen diferencias entre el grupo de hombres y el de mujeres en distintos tipos de EEG (reposo con ojos cerrados y 2tareas atencionales específicas).
MétodosSe ha calculado la potencia espectral y obtenido un exponente que modeliza esta magnitud por medio de una función del tipo ruido coloreado. Se utilizó el tercer minuto de las señales de cada sujeto en 3 tipos de EEG y 12 canales. Se han analizado los datos con la prueba estadística.
ResultadosSe observan diferencias significativas entre géneros en el registro basal (reposo con ojos cerrados) en regiones parietal, occipital, temporal y central (1,62 es el valur del promedio cortical masculino frente a 1,39 del femenino) y durante la tarea (j2) en regiones frontal, occipital y parietal (1,34 es el promedio cortical masculino frente a 1,16 en el femenino).
ConclusionesEl grupo de mujeres muestra mayor complejidad bioeléctrica cerebral que el de hombres en un mismo tipo de EEG. El exponente frecuencial se comporta de forma inversa a la dificultad de la tarea, en ambos sexos.
Article
Diríjase al área privada de socios de la web de la SEDENE, (https://sedene.com/revista-de-sedene/ ) y autentifíquese.