We aimed to investigate the correlation between serum lipoprotein-associated phospholipase A2 (Lp-PLA2) level and acute ischemic stroke (AIS) severity and recurrence, which could indicate the diagnostic and prognostic values of Lp-PLA2.
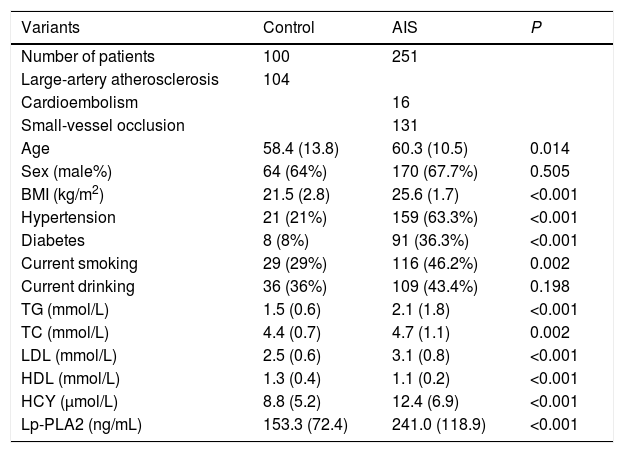
MethodsTwo hundred and fifty-one AIS patients who were diagnosed in the department of neurology, China-Japan Union Hospital, from April 2018 to June 2019 and 100 non-cerebrovascular disease patients were included in this study. Demographic data and clinical materials including age, sex, BMI, medical history, bad habits, imaging data, blood tests, etc., were collected. Stroke severity and risk were evaluated, respectively. AIS patients were followed up for 6 months for stroke recurrence monitoring.
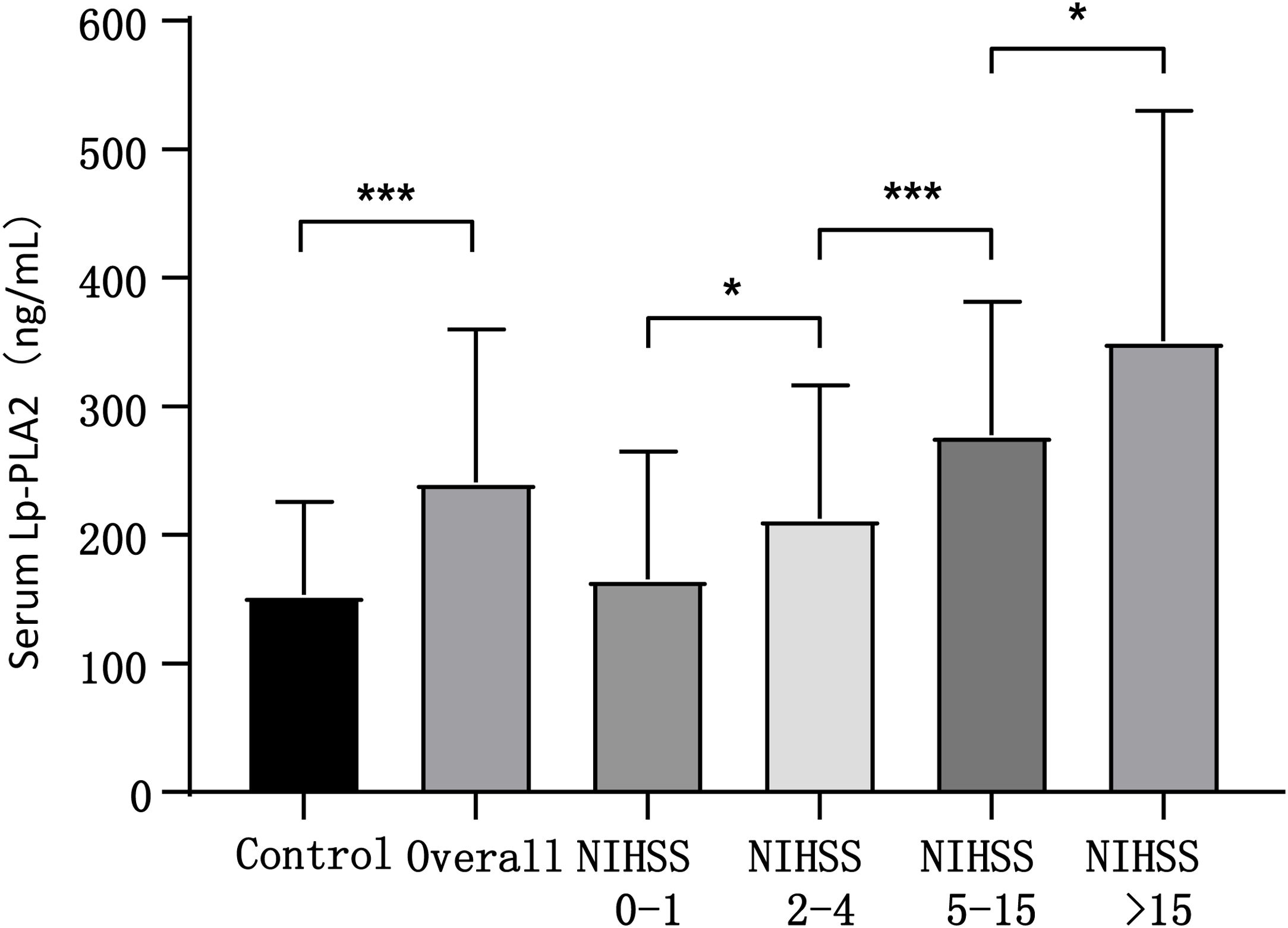
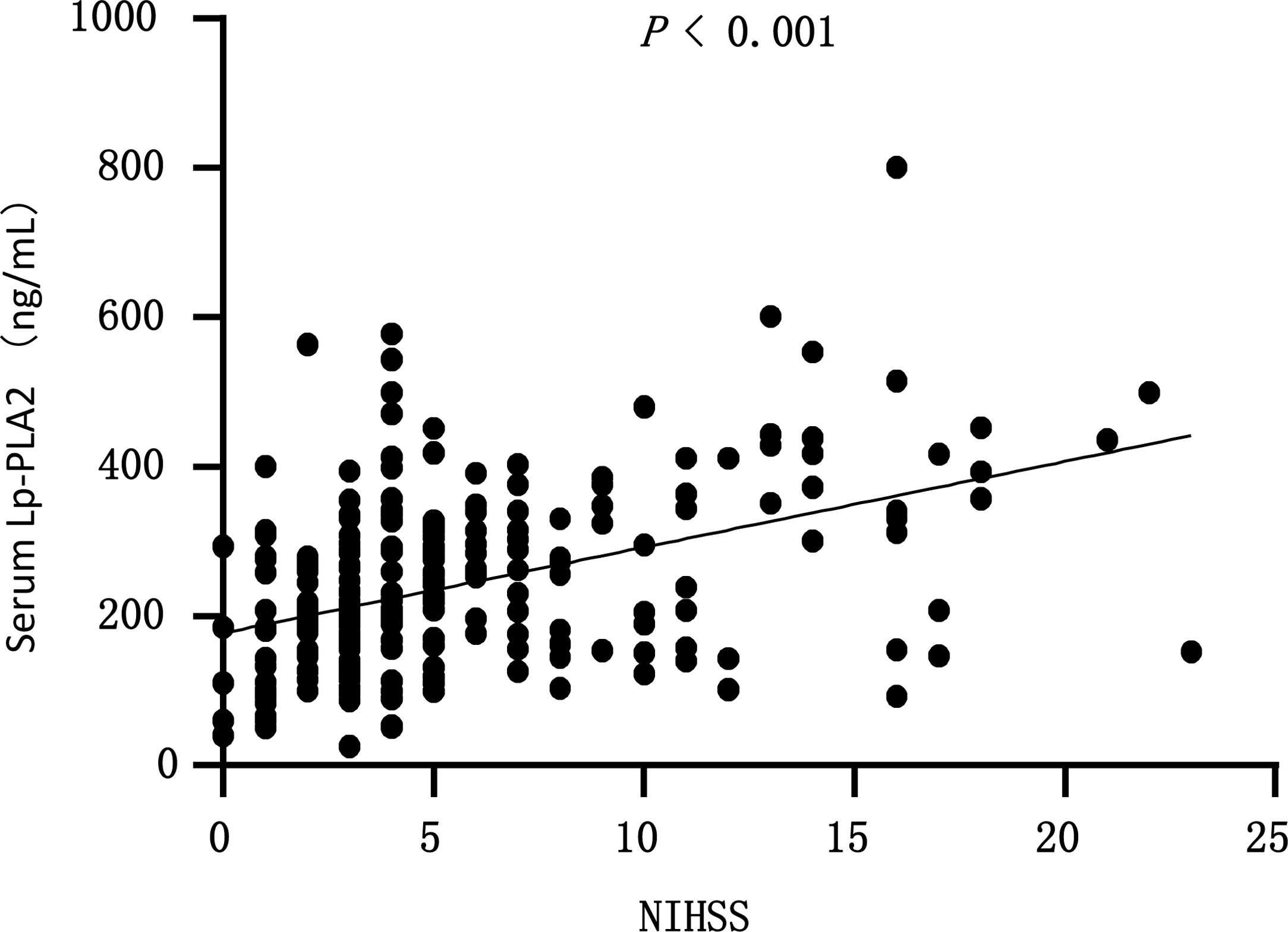
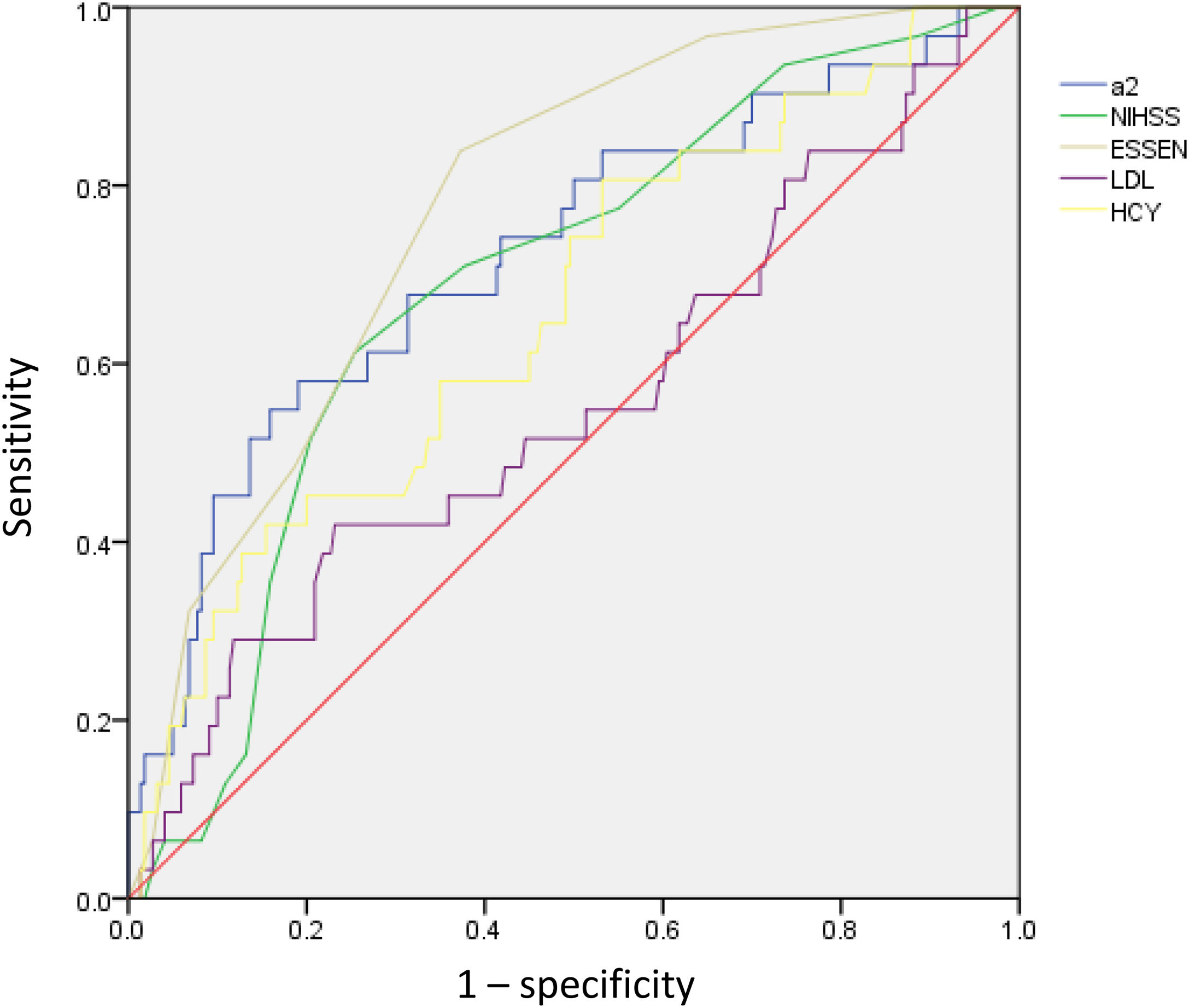
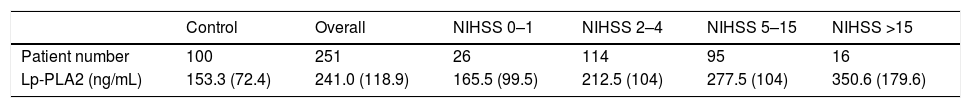
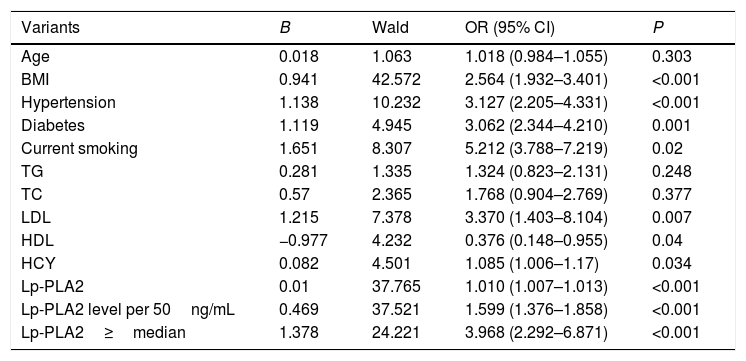
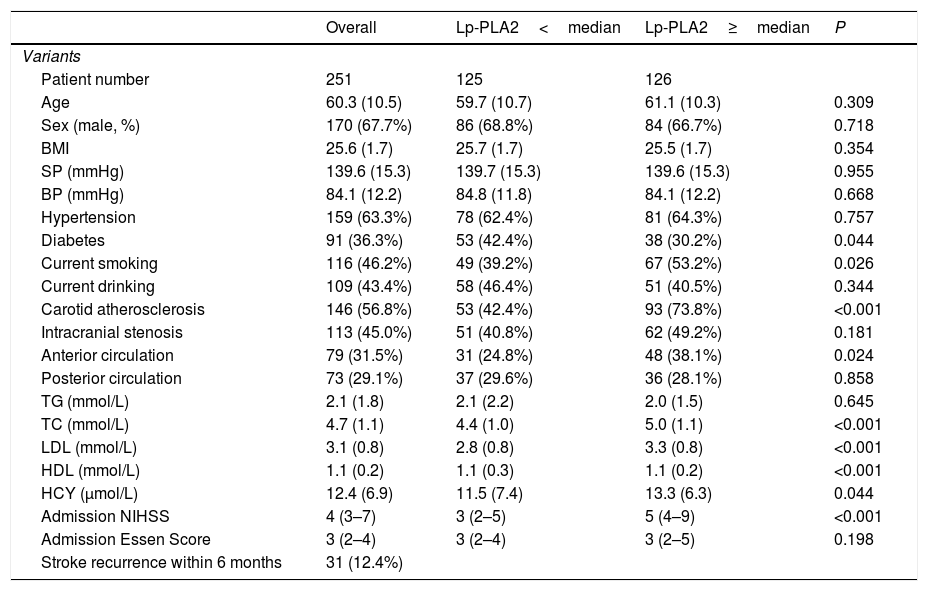
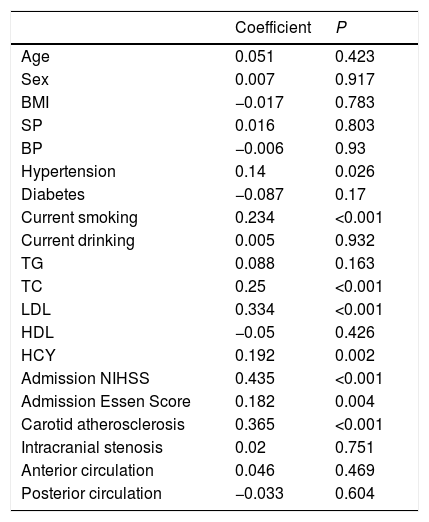
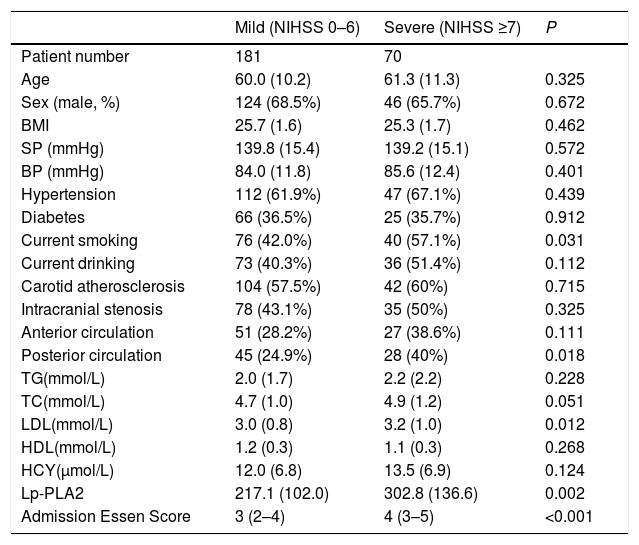
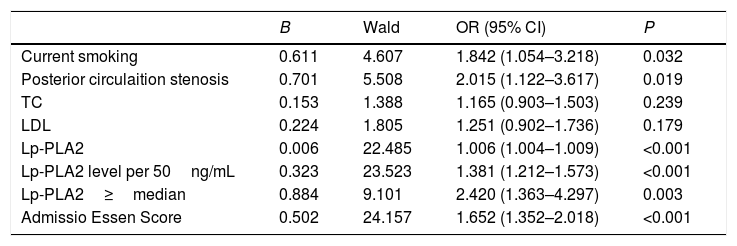
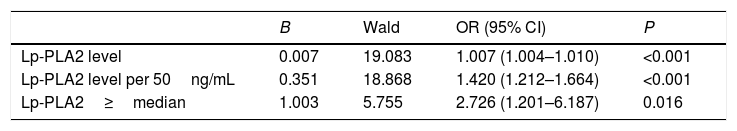
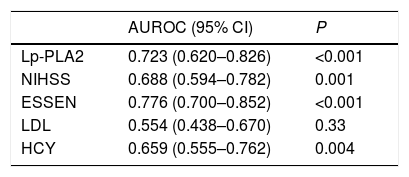
ResultsThe AIS group had significantly higher Lp-PLA2 level than the control group. High Lp-PLA2 level was the independent risk factor of AIS (OR 1.010; 95% CI 1.007–1.013, P<0.001). Admission NIHSS was compared between Lp-PLA2 categories dichotomized by median. Serum Lp-PLA2 level was positively correlated with NIHSS (r=0.268, P<0.001). Mild stroke group and severe stroke group were defined based on NIHSS. Compared with the mild stroke group, the severe stroke group had higher smoking ratio, posterior circulation stenosis incidence, LDL level, Lp-PLA2 level and admission Essen score. Logistic regression showed Lp-PLA2 levels per 50ng/mL (OR 1.381, 95% CI 1.212–1.573, P<0.001) and Lp-PLA2 category (OR 2.420, 95% CI 1.363–4.297, P=0.003) were both independently associated with severe stroke. During the 6-month follow-up of all 251 AIS patients, 31 stroke recurrence cases were observed. Both Lp-PLA2 levels per 50ng/mL (OR 1.420, 95% CI 1.212–1.664, P<0.001) and Lp-PLA2 category (OR 2.726, 95% CI 1.201–6.178, P=0.016) were significantly associated with the stroke recurrence. Under the receiver Operating Characteristic curve, Lp-PLA2 showed significant predicting ability for stroke recurrence (AUC 0.723; 95% CI 0.620–0.826, P<0.001).
ConclusionHigh serum Lp-PLA2 level is correlated with AIS incidence, disease severity and recurrence, which could be utilized to guide clinical practice.
Nuestro objetivo fue investigar la correlación entre el nivel sérico de fosfolipasa A2 asociada a lipoproteína (Lp-PLA2) y la gravedad y recurrencia de los accidentes cerebrovasculares agudos (ACV), lo cual podría ser indicativo de los valores diagnóstico y pronóstico de Lp-PLA2.
MétodosSe incluyó en el estudio a 251 pacientes de ACV diagnosticados en el Departamento de Neurología del Hospital China-Japan Union, desde abril de 2018 a junio de 2019, y a 100 pacientes sin enfermedad cerebrovascular. Se recopilaron los datos demográficos y materiales clínicos incluyendo edad, sexo IMC, historia médica, malos hábitos, estudios por imagen, análisis de sangre, etc. Se evaluaron la gravedad del accidente cerebrovascular y el riesgo, respectivamente, realizándose un seguimiento de supervisión de la recurrencia del accidente, de 6 meses de duración, a los pacientes de ACV.
ResultadosEl grupo ACV tuvo un nivel de Lp-PLA2 significativamente superior al del grupo control. El nivel alto de Lp-PLA2 fue el factor de riesgo independiente de ACV (OR: 1,010; IC 95%: 1,007-1,013; p<0,001). Se comparó el valor de la escala NIHSS durante el ingreso entre las categorías Lp-PLA2, dicotomizadas por mediana. El nivel sérico de Lp-PLA2 se correlacionó positivamente con NIHSS (r=0,268; p<0,001). Se definieron el grupo de accidente leve y el grupo de accidente grave sobre la base de NIHSS. En comparación con el grupo de accidente leve, el grupo de accidente grave tenía un ratio más alto de fumadores, incidencia de estenosis circulatoria posterior, nivel de LDL, nivel de Lp-PLA2 y puntuación Essen durante el ingreso. La regresión logística reflejó que los niveles Lp-PLA2 por 50ng/ml (OR: 1,381; IC 95%: 1,212-1,573; p<0,001) y la categoría Lp-PLA2 (OR: 2,420; IC 95%: 1,363-4,297; p=0,003) estaban independientemente asociados a los accidentes graves. Durante el seguimiento de 6 meses realizado a los 251 pacientes de ACV, se observaron 31 casos de recurrencia de accidentes. Tanto los niveles de Lp-PLA2 por 50ng/ml (OR: 1,420; IC 95%: 1,212-1,664; p<0,001) como la categoría Lp-PLA2 (OR: 2,726; IC 95%: 1,201-6,178; p=0,016) estuvieron significativamente asociados a la recurrencia de accidentes. En la curva ROC, Lp-PLA2 reflejó una capacidad de predicción significativa para la recurrencia de accidentes (AUC: 0,723; IC 95%: 0,620-0,826; p<0,001).
ConclusiónEl alto nivel sérico de Lp-PLA2 está correlacionado con la incidencia de ACV, gravedad de la enfermedad y recurrencia, lo cual podría ser utilizado como guía para la práctica clínica.
Artículo
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora