Tenofovir disoproxil fumarate (TDF) is recommended for the prevention of perinatal transmission of the hepatitis B virus (HBV). This study aimed to systematically assess the efficacy and safety of TDF in pregnant women with chronic HBV and their infants.
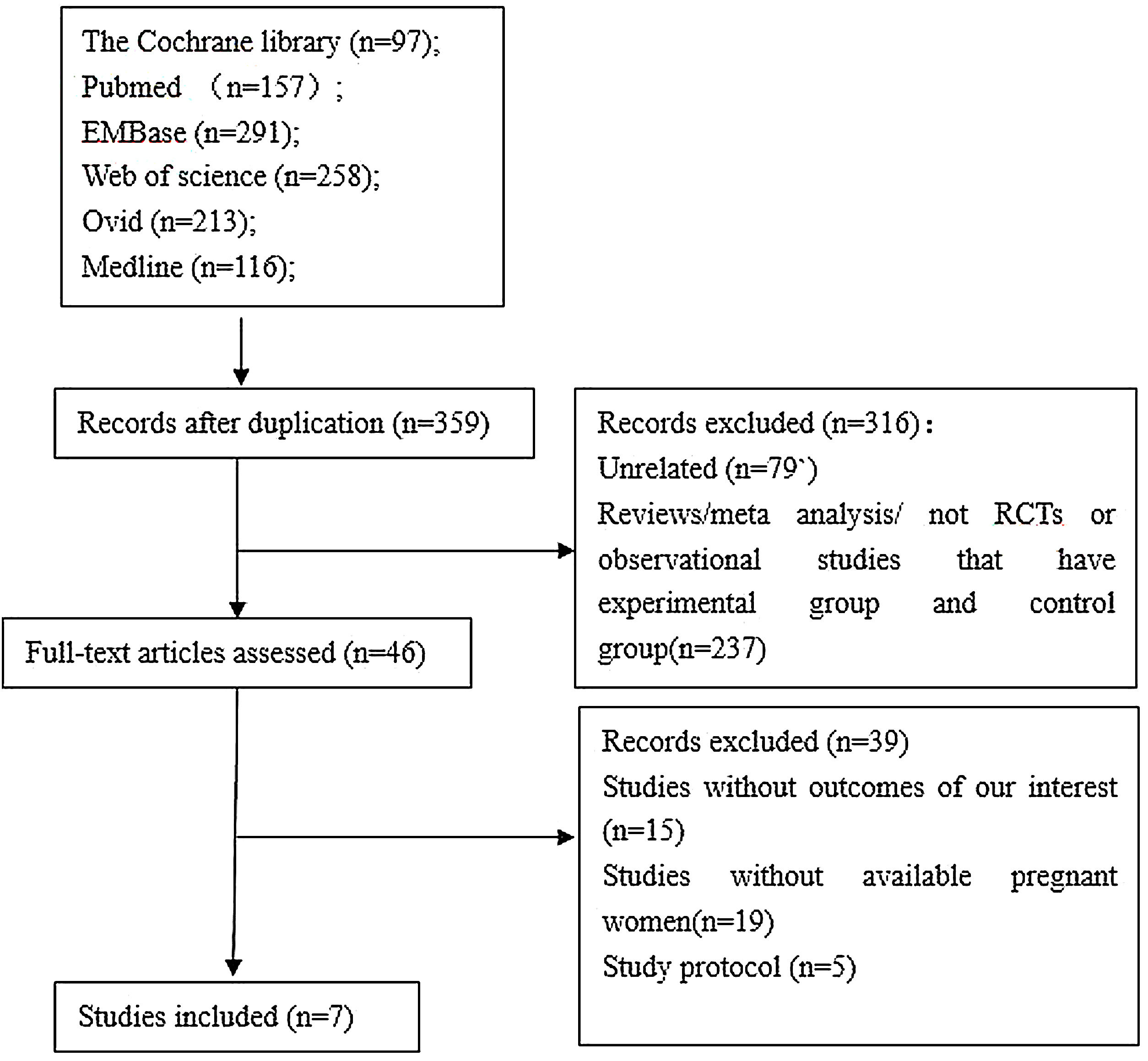
Material and methodsDatabase searches were performed to identify studies blocking the mother-to-child transmission of the hepatitis B virus with tenofovir. The search included pregnant women with chronic HBV infection administered with TDF compared to the no treatment controls, and data from individual studies were pooled using RevMan v5.3 for meta-analysis.
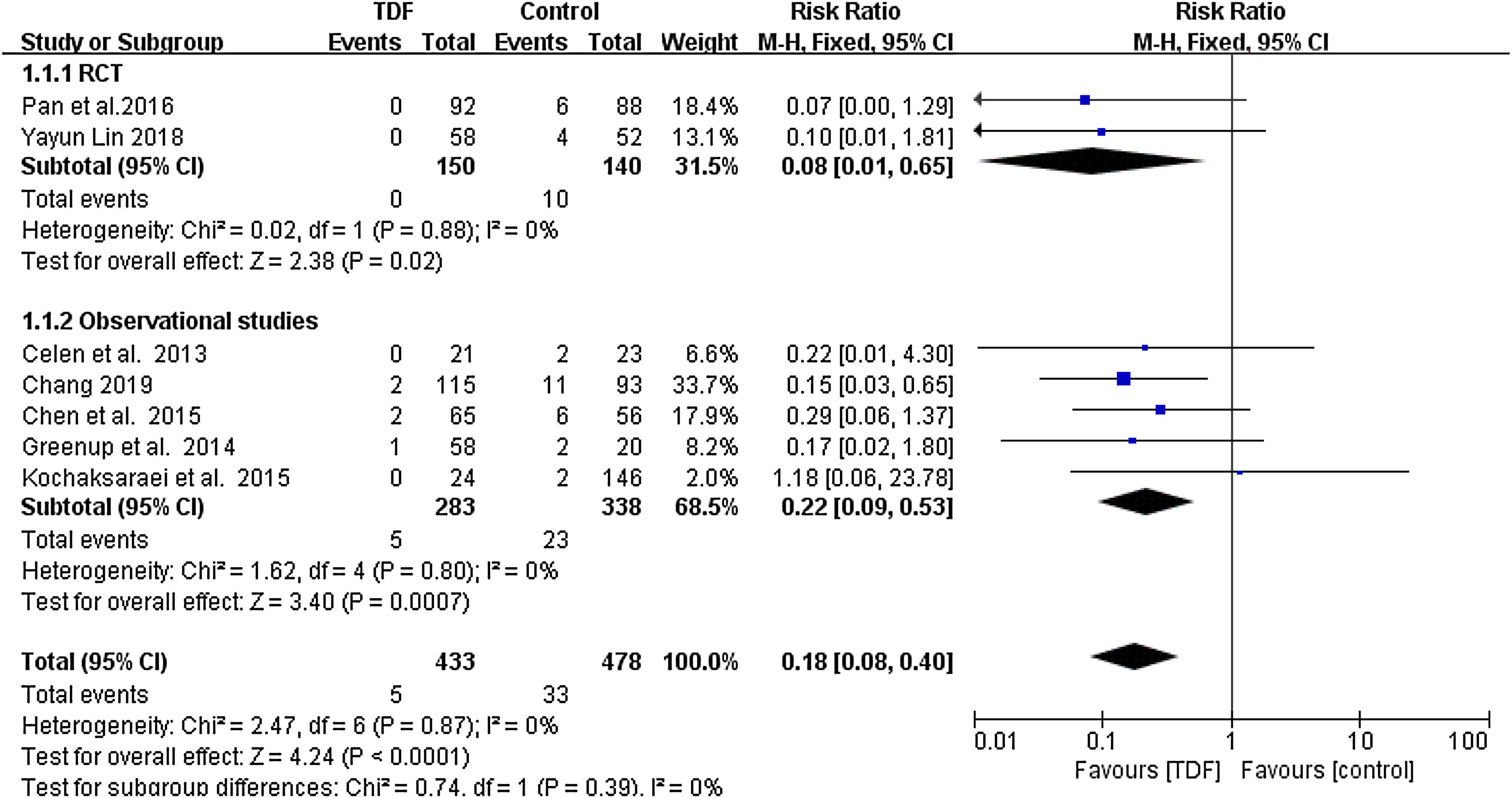
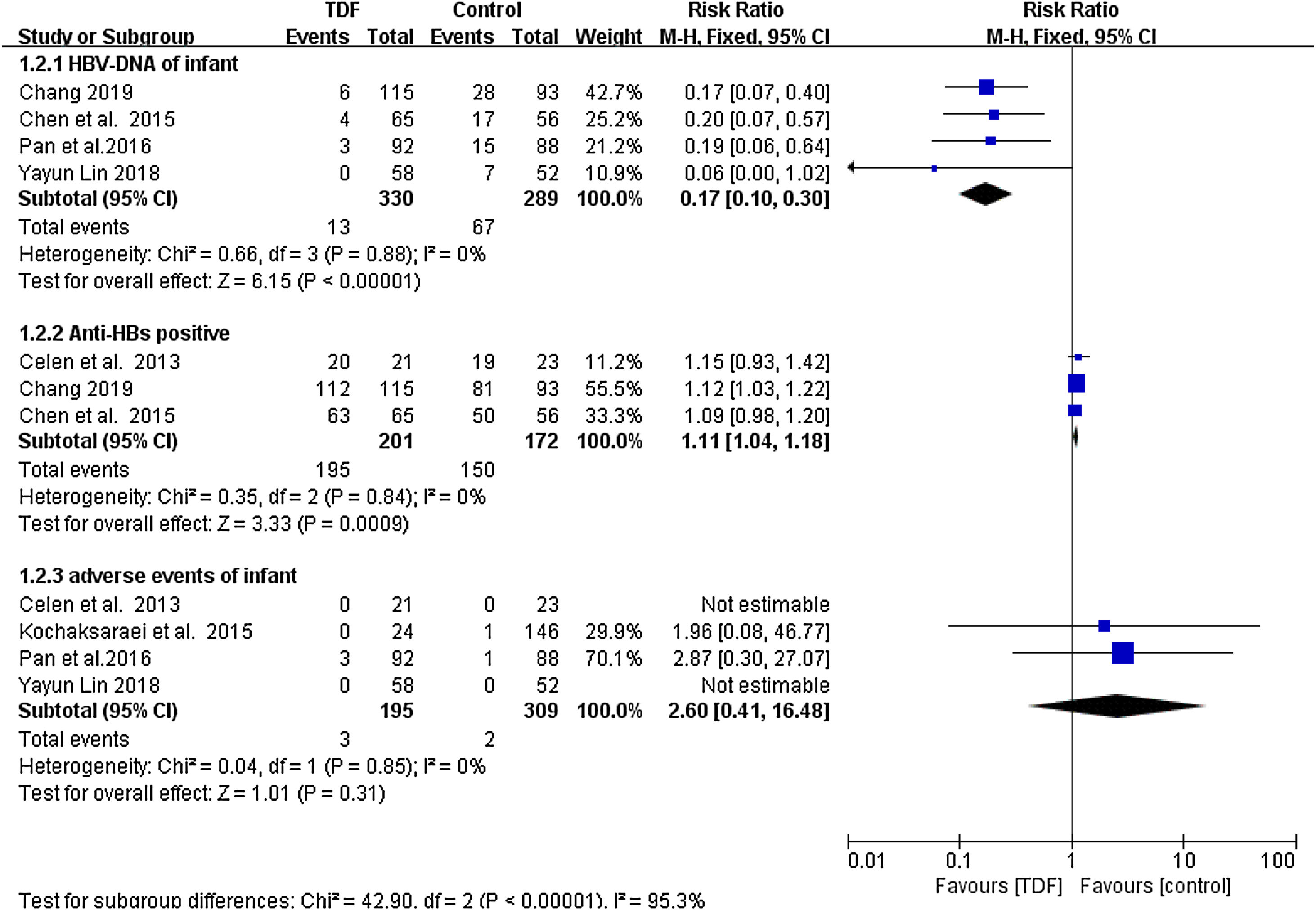
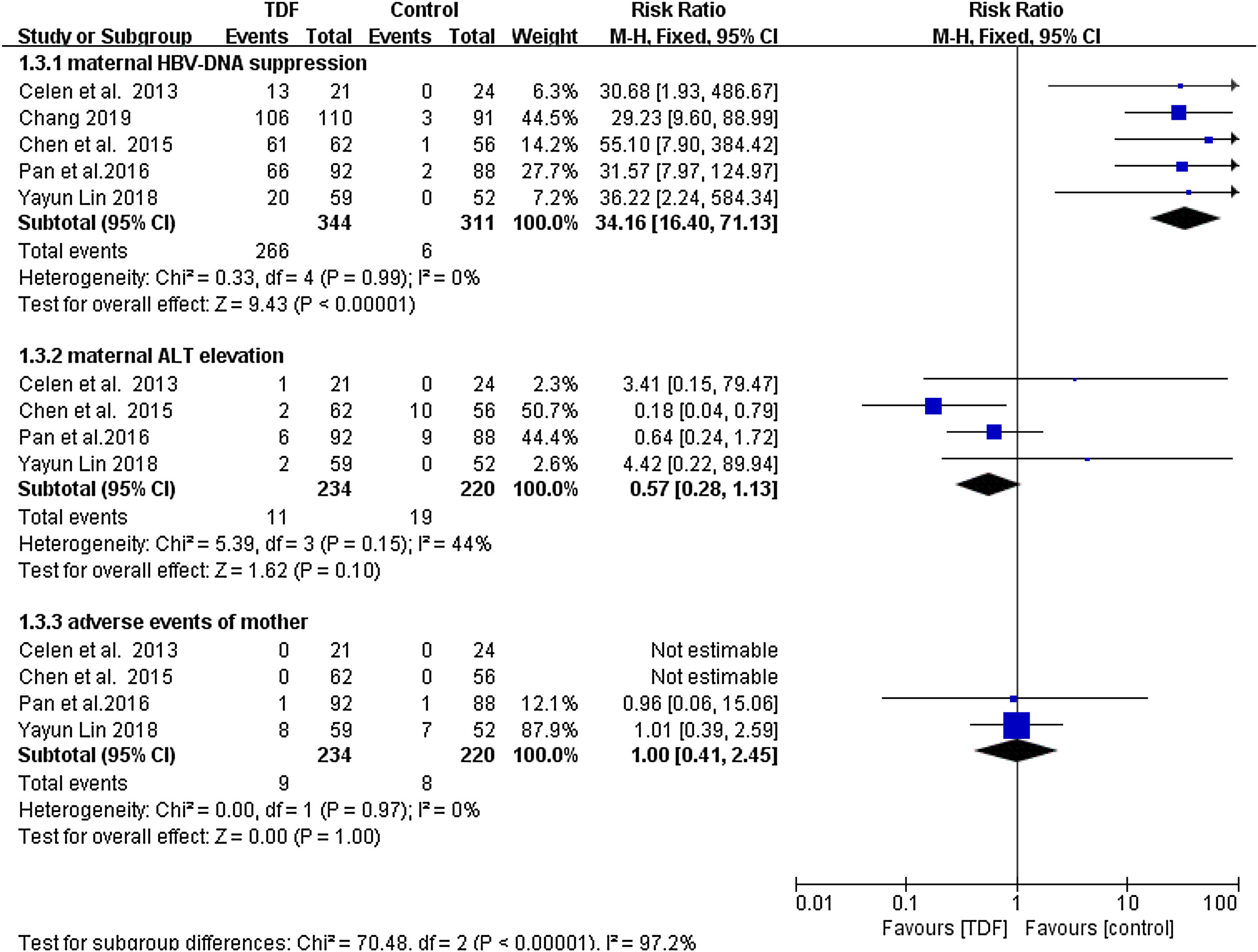
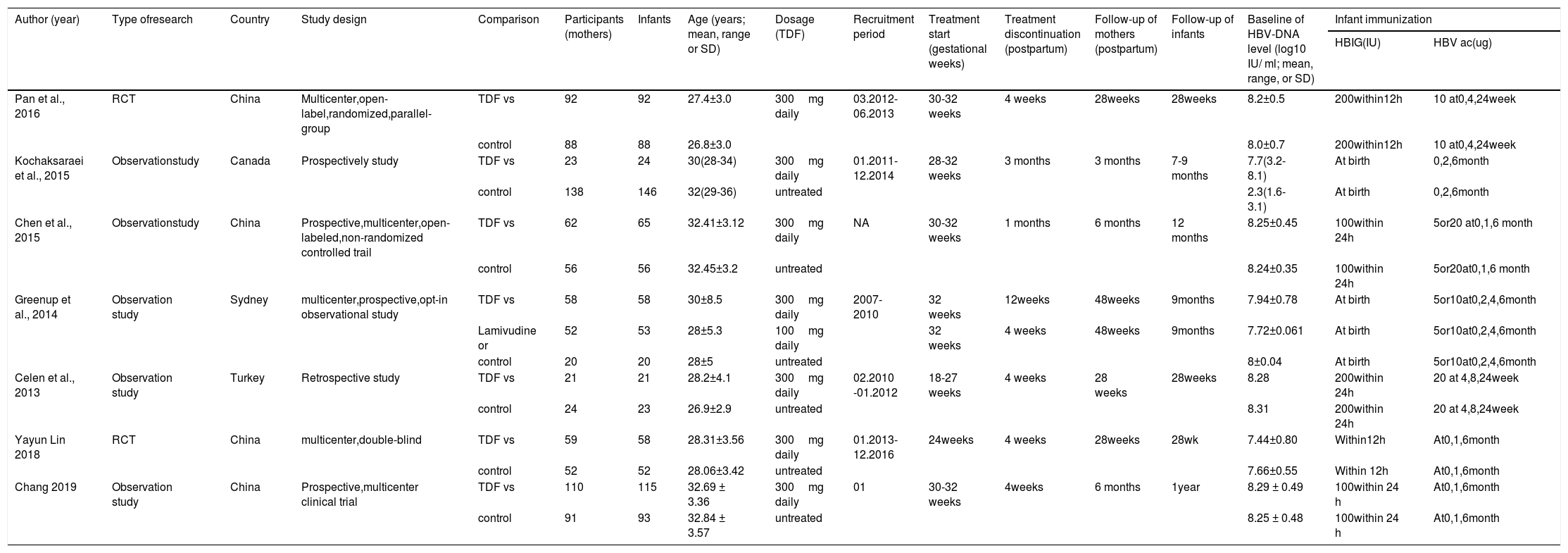
ResultsSeven studies with a total of 911 patients met the inclusion criteria: 433 patients in the TDF group and 478 patients in the non-TDF group. The HBV mother-to-child transmission rate in the tenofovir group was effectively reduced compared to the control group (RR: 0.18, 95% CI: 0.08-0.40). HBV-DNA positivity was also significantly low in infants from TDF group (RR: 0.17, 95% CI: 0.10-0.30) and the TDF treatment resulted in significantly higher anti-HBs production (RR: 1.11, 95% CI: 1.04-1.18). Similarly, maternal HBV-DNA was suppression was significantly high in the TDF group (RR: 34.16, 95% CI: 16.40-71.13). Women treated with TDF and their infants did not result in serious adverse events that are statistically different as compared to the women who did not receive any treatment.
ConclusionTreatment of HBV infected pregnant women with TDF can effectively and safely prevent the perinatal transmission of chronic hepatitis B.
El fumarato de disoproxilo de tenofovir (FDT) se recomienda para la prevención de la transmisión perinatal del virus de la hepatitis B (VHB). El objetivo de este estudio fue evaluar de manera sistemática la eficacia y la seguridad del FDT en las mujeres embarazadas con VHB crónico y en sus hijos lactantes.
Material y métodosSe realizaron búsquedas en las bases de datos para identificar los estudios sobre el bloqueo de la transmisión del virus de la hepatitis B de madre a hijo con el tenofovir. La búsqueda incluyó a mujeres embarazadas con infección crónica por el VHB que recibieron FDT en comparación con controles sin tratamiento, y los datos de los estudios individuales se agruparon mediante el uso de RevMan v5.3 para el metaanálisis.
ResultadosLos criterios de inclusión se cumplieron en siete estudios con un total de 911 pacientes: 433 pacientes en el grupo de FDT y 478 pacientes en el grupo sin FDT. La tasa de transmisión de madre a hijo del VHB en el grupo de tenofovir se redujo efectivamente en comparación con el grupo de control (RR: 0,18, IC del 95 %: 0,08-0,40). Los resultados positivos del ADN del VHB también fueron significativamente bajos en los infantes del grupo de FDT (RR: 0,17, IC del 95 %: 0,10-0,30) y el tratamiento con FDT dio como resultado una producción significativamente mayor de anti-HB (RR: 1,11, IC del 95 %: 1,04-1,18). Del mismo modo, la supresión del ADN del VHB materno fue significativamente alta en el grupo del FDT (RR: 34,16, IC del 95 %: 16,40-71,13). El tratamiento de las mujeres con FDT y sus hijos lactantes no provocó acontecimientos adversos graves en ellas ni en sus hijos que fueran estadísticamente diferentes de los de las mujeres que no recibieron ningún tratamiento.
ConclusiónEl tratamiento con FDT de las mujeres embarazadas infectadas por el VHB puede prevenir de manera eficaz y segura la transmisión perinatal de la hepatitis B crónica.
Artículo
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora