Diagnosis of severe hepatitis C recurrence is based on analytical and histological criteria but there is little information about their correlation.
AimTo assess the accuracy of laboratory criteria for the diagnosis of fibrosing cholestatic hepatitis (FCH).
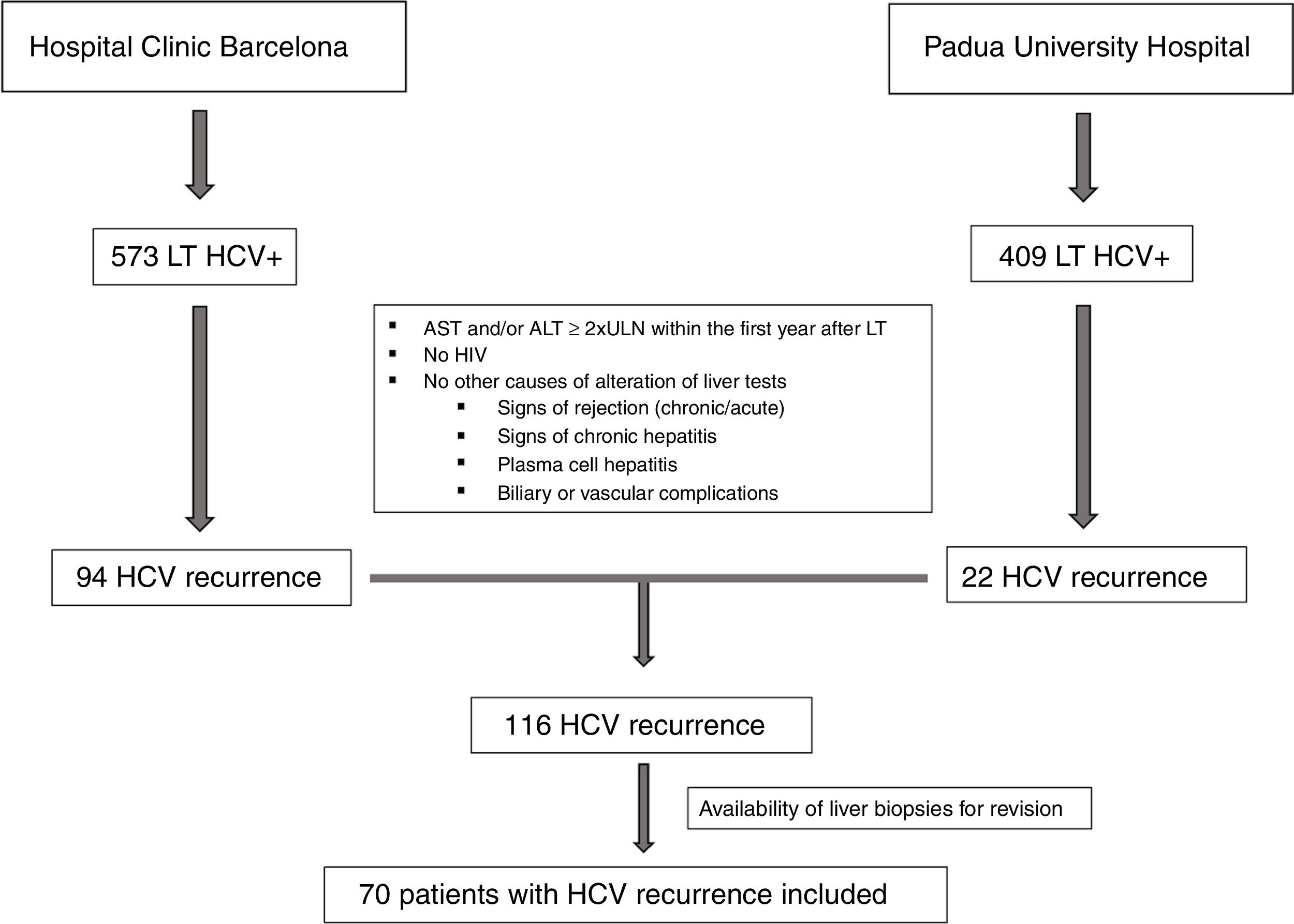
Patients and methodsRetrospective analysis of prospectively collected data form HCV positive patients who underwent liver transplantation (LT) between 2000 and 2014 in two European university hospitals. Patients were classified according to laboratory criteria such as FCH, cholestatic hepatitis (CH) and non-cholestatic acute hepatitis (NCAH). Histological characteristics were also evaluated.
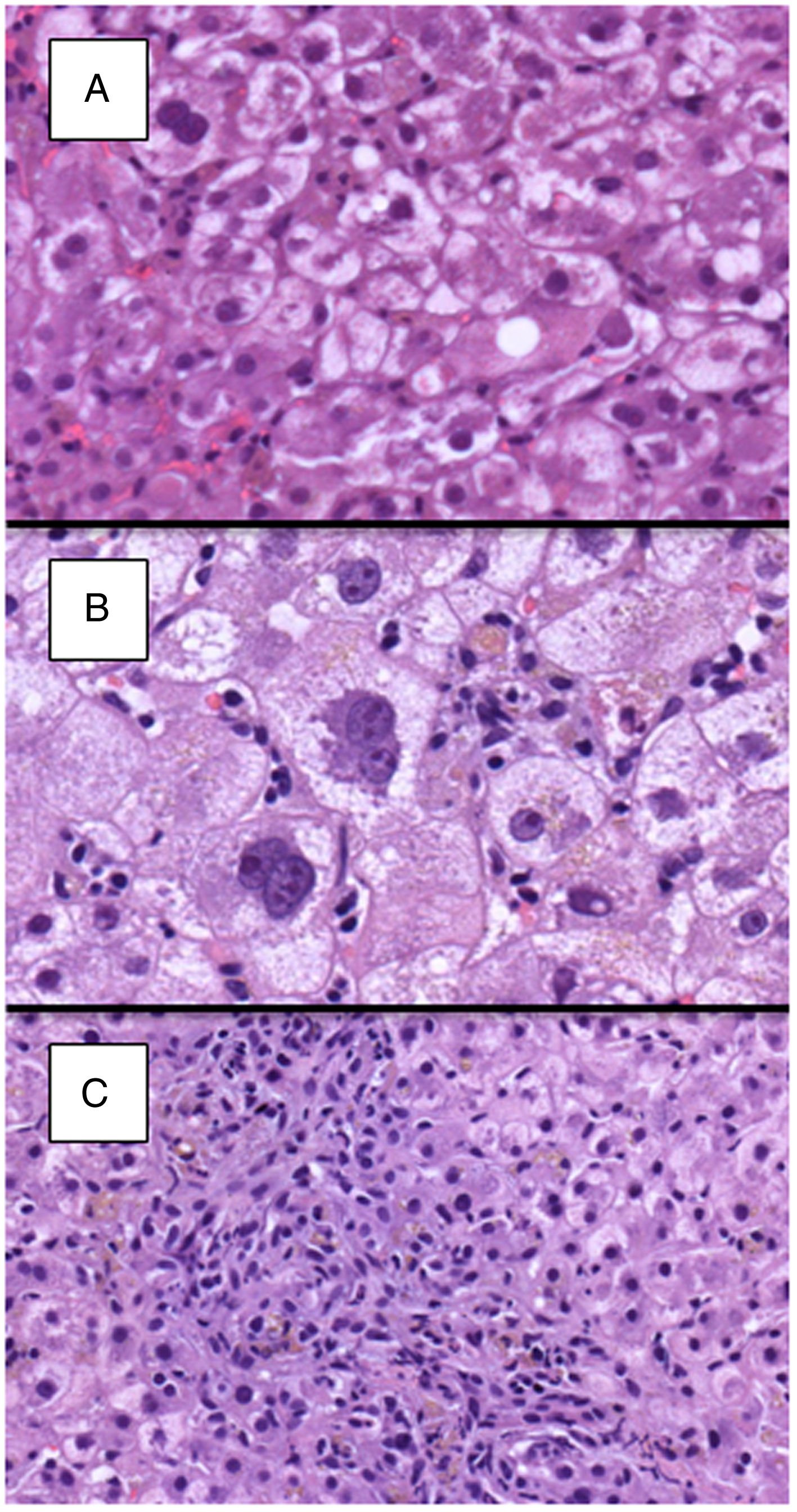
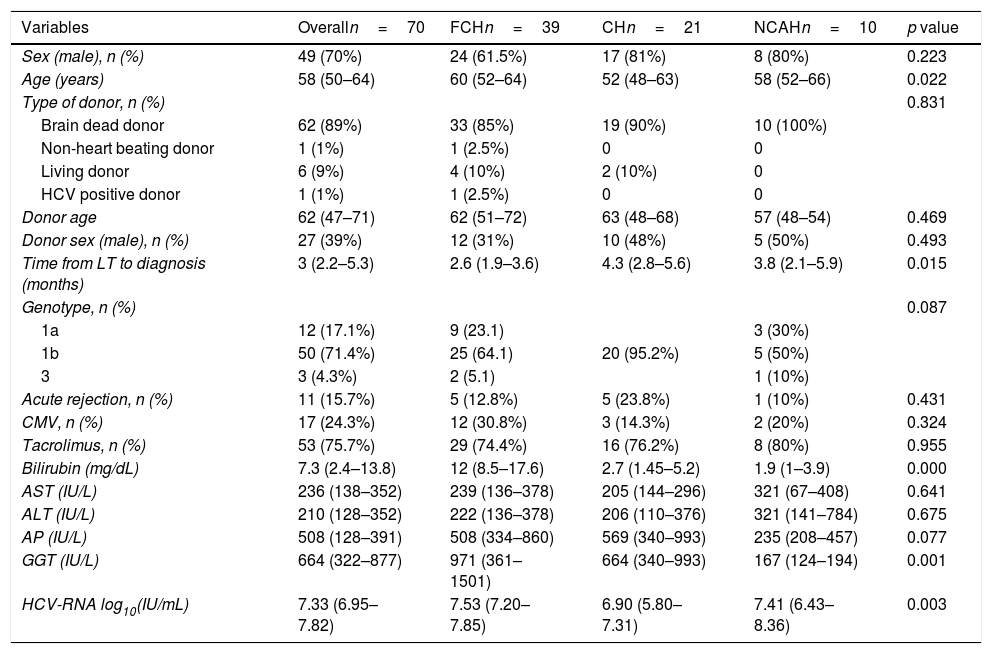
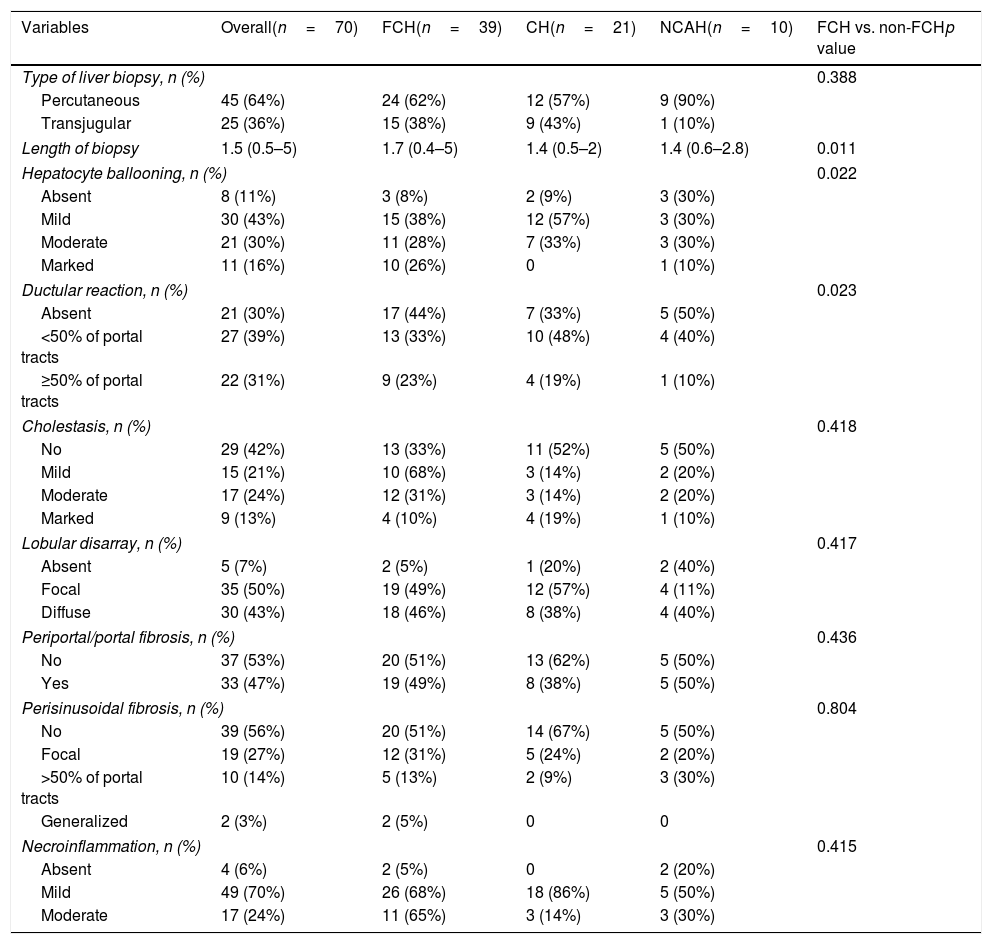
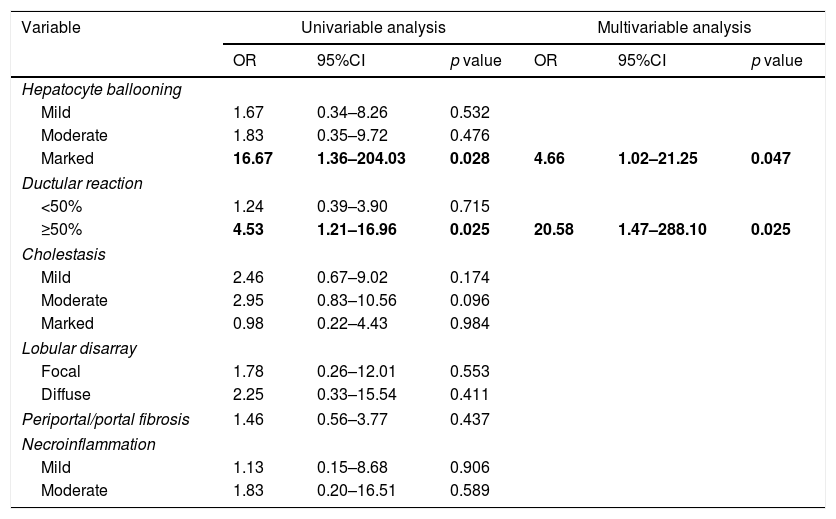
ResultsSeventy patients with acute HCV recurrence within the first year after LT with an available liver biopsy were included in the study. Most patients were male (70%) with a median age of 58 years (50–64) and infected with genotype 1b (71.4%). Median time from LT to diagnosis of recurrence was 2.96 months (2.1–5.3). Thirty-nine patients were classified as FCH, 21 as CH and 10 as NCAH. Marked hepatocyte ballooning and ductular reaction were associated with the presence of FCH with an OR of 4.66 (p=0.047) and 20.58 (p=0.025), respectively. Considering liver biopsy as the gold standard, the sensitivity, specificity, positive and negative predictive values of the analytical criteria were 0.8, 0.5, 0.3 and 0.9, respectively. However, correlation between histological and analytical criteria was poor (k=0.033).
DiscussionAnalytical criteria may be used to rule out the presence of FCH, but a biopsy is mandatory to confirm the diagnosis. Ductular reaction and hepatocyte ballooning were independent predictors of FCH.
El diagnóstico de la recurrencia grave de la hepatitis C se basa en criterios histológicos y analíticos. Sin embargo, existe poca información respecto su correlación.
ObjetivoEvaluar la precisión de los criterios analíticos el diagnóstico de la hepatitis colestásica fibrosante (HCF).
Pacientes y métodosAnálisis retrospectivo de pacientes con una recidiva grave precoz del virus de la hepatitis C (VHC) tras el trasplante hepático (TH) en 2 hospitales universitarios europeos entre 2000-2014. Los pacientes se clasificaron según criterios analíticos en HCF, hepatitis colestásica (HC) y hepatitis aguda no colestásica (HANC). Las características histológicas también fueron evaluadas.
ResultadosSe incluyeron 70 pacientes que desarrollaron una recurrencia grave del VHC en el primer año tras TH con una biopsia hepática disponible. La mayoría eran varones (70%) con mediana de edad de 58 años (50-64) y genotipo 1b (71,4%). La mediana de tiempo desde el TH hasta el diagnóstico de la recurrencia fue de 2,96 meses (2,1-5,3). Treinta y nueve pacientes fueron clasificados como HCF, 21 como HC y 10 como HANC. La balonización intensa y reacción ductular se asociaron con HCF con una OR de 4,66 (p=0,047) y 20,58 (p=0,025), respectivamente. Considerando la biopsia hepática como gold standard, la sensibilidad, especificidad y valores predictivos positivo y negativo de los criterios analíticos fueron 0,8, 0,5, 0,3 y 0,9, respectivamente. Sin embargo, la correlación entre ambos fue escasa (k=0,033).
DiscusiónLos criterios analíticos podrían utilizarse para descartar la presencia de HCF, pero la biopsia sigue siendo obligatoria para el diagnóstico. La reacción ductular y la balonización son predictores de HCF.
Artículo
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora