To identify factors associated with the presence of fatigue in patients with inflammatory bowel disease.
Patients and methodProspective cross-sectional descriptive study conducted in a multidisciplinary centre for the treatment of EIMI. Participants were patients diagnosed with IBD under follow-up in an advanced practice nurse (APN) consultation. Sociodemographic and clinical variables, biochemical parameters, disease activity, quality of life, severity of fatigue, anxiety and depression were collected. A multivariate analysis was performed with logistic regression adjusted for sex and years of disease progression.
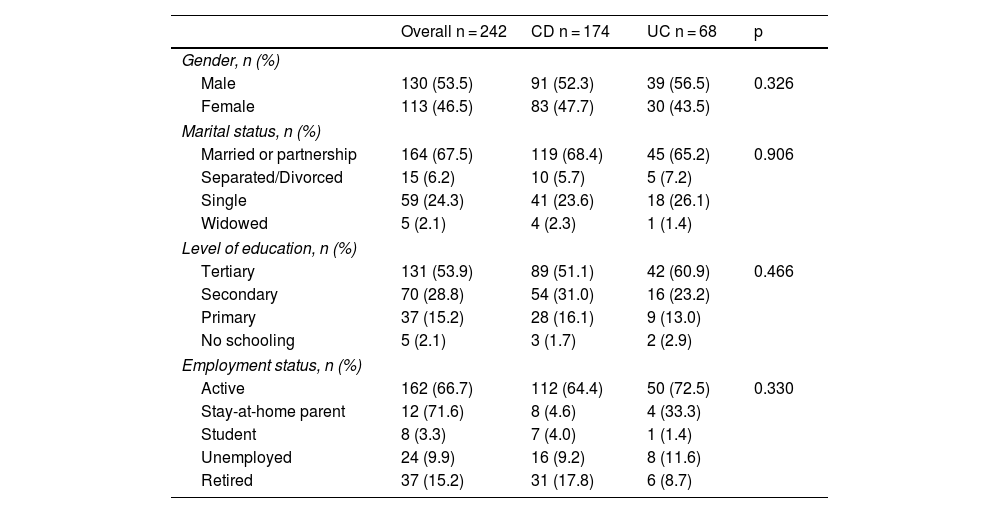
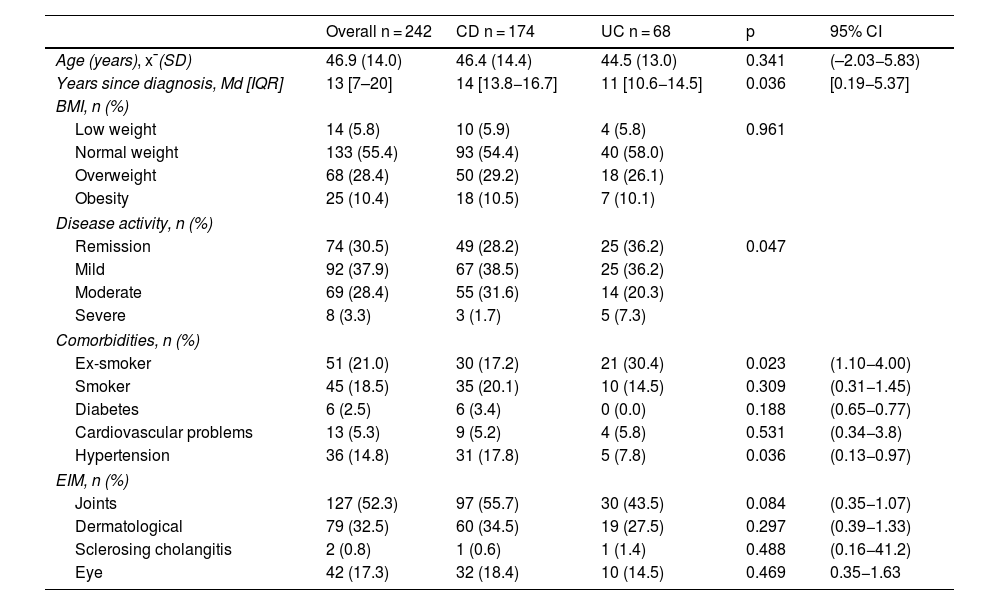
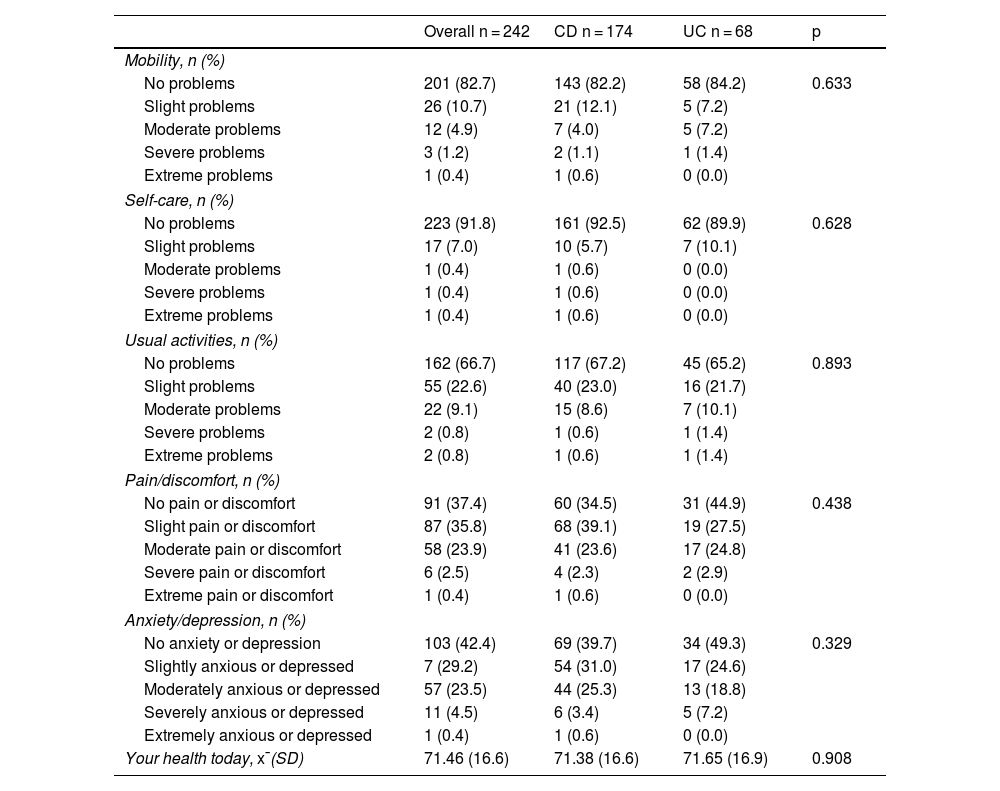
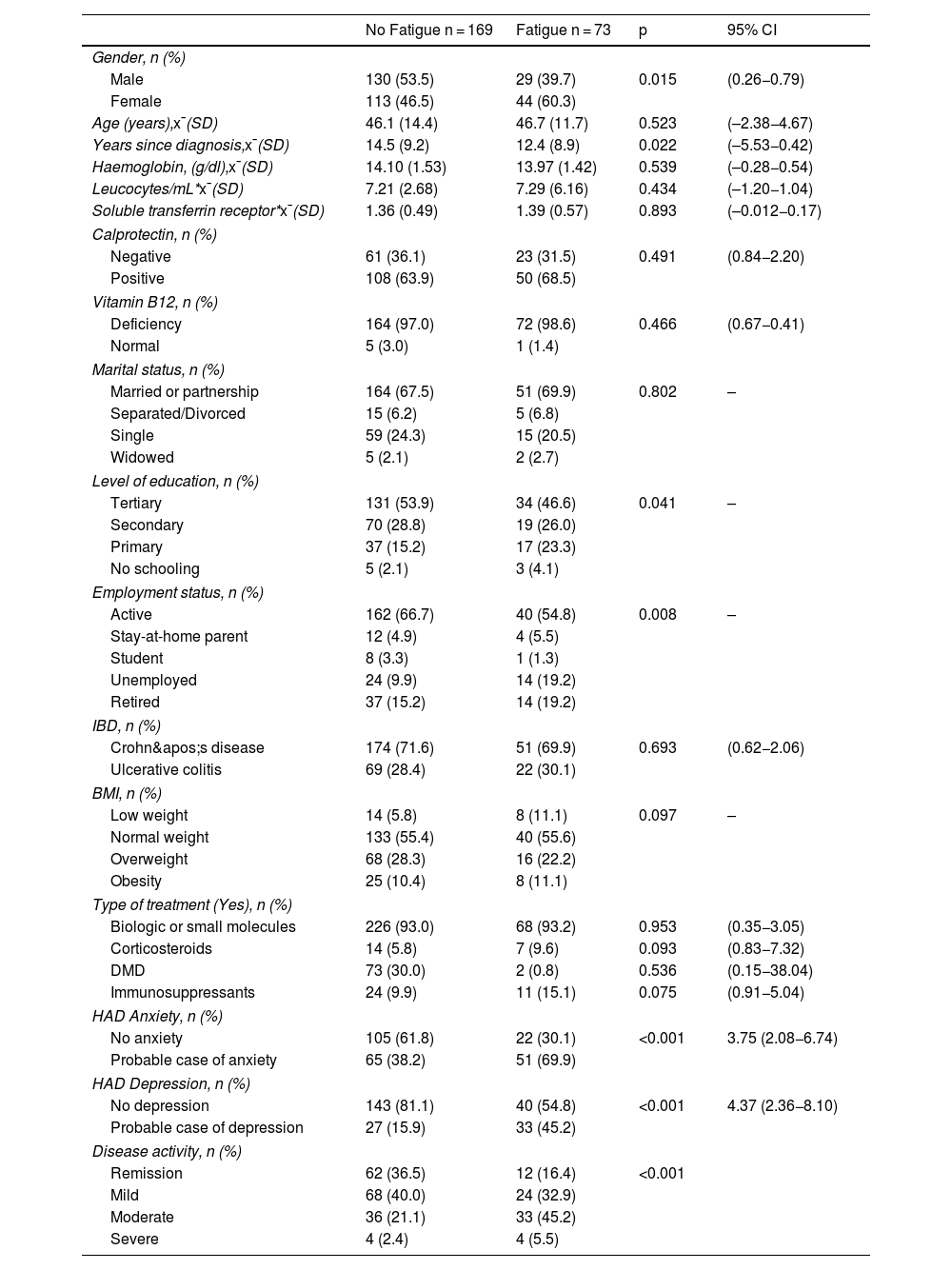
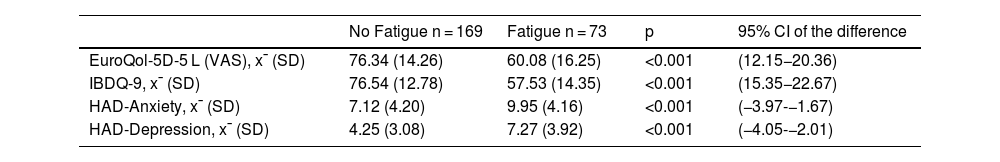
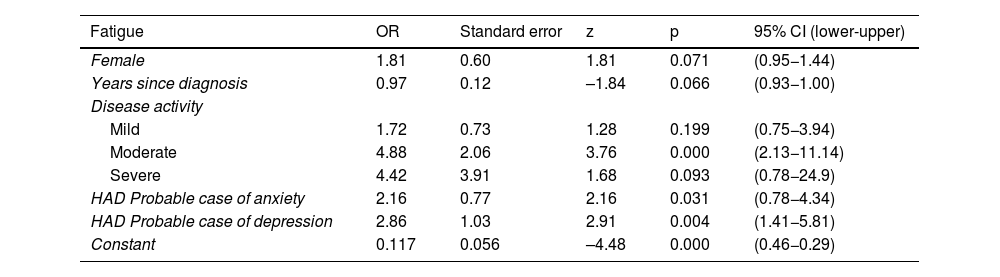
ResultsA total of 243 patients were included, 174 (71.6%) with Crohn’s disease and 69 (28.4%) with ulcerative colitis; 73 (30.2%) reported fatigue. Patients with fatigue had a significantly lower quality of life EuroQol-5D-5L: 60.08 vs. 76.34, (p < 0.001, 95%CI: 12.15–20.36) and IBDQ-9 57.53 vs. 76.54, (p < 0.001, 95%CI:15.35–22.67). The regression model adjusted for sex and years of disease included moderate disease activity (OR: 4.88, p < 0.001, 95%CI: 2.13–11. 14), probable case of anxiety (OR: 2.16, p = 0.031, 95% CI: 0.78−4.34), probable case of depression (OR: 2.86, p = 0.004, 95%CI: 1.41−5.81).
ConclusionsFatigue was significantly associated with poorer health-related quality of life in patients with moderate disease activity and those experiencing anxiety or depression. These findings highlight the necessity of a comprehensive approach that includes early detection of fatigue and associated psychosocial factors.
Identificar los factores asociados a la presencia de fatiga en pacientes con enfermedad inflamatoria intestinal.
Pacientes y métodoEstudio descriptivo transversal prospectivo realizado en un centro multidisciplinar para el tratamiento de EIMI. Los participantes fueron pacientes diagnosticados de EII en seguimiento en consulta de enfermería de práctica avanza. Se recogieron variables sociodemográficas, clínicas, parámetros bioquímicos, actividad de la enfermedad, calidad de vida, gravedad de la fatiga, ansiedad y depresión. Se realizó un análisis multivalente con regresión logística ajustado por sexo y años de evolución de la enfermedad.
ResultadosSe estudiaron 243 pacientes, 174(71.6%) con EC y 69(28.4%) con CU, presentaban fatiga 73(30.2%). Los pacientes con fatiga presentaron una calidad de vida significativamente más baja EuroQol-5D-5L: 60.08 vs.76.34, (p < 0.001, IC95%:12.15–20.36) e IBDQ-9 57.53 vs. 76.54, (p < 0.001, IC95%:15.35–22.67). El modelo de regresión ajustado por sexo y años de enfermedad incluyó la actividad de la enfermedad en estadio moderado (OR:4.88, p < 0.001, IC95%: 2.13−11.14), probable caso de ansiedad (OR:2.16, p = 0.031, IC95%: 0.78−4.34), probable caso de depresión (OR:2.86, p = 0.004, IC95%: 1.41−5.81).
ConclusionesLa fatiga mostró una asociación con una peor calidad de vida relacionada con la salud en pacientes con actividad clínica moderada y presencia de ansiedad o depresión. Estos resultados refuerzan la importancia de adoptar un enfoque integral que contemple la detección precoz tanto de la fatiga como de los factores psicosociales implicados.