There is controversy concerning the use of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors (ACEI) or angiotensin II type-I receptor blockers (ARB) for treating hypertensive patients with Covid-19. It has been hypothesized that these drugs might increase the risk of severe Covid-19, but some authors suggested that blocking the renin-angiotensin system might actually decrease this risk.
MethodsRetrospective cohort study of all the consecutive hypertensive patients with confirmed SARS-CoV-2 infection in a health area. The outcome variable was hospitalization because of severe Covid-19.
Results539 subjects were diagnosed of SARS-CoV-2 infection. Of these, 157 (29.1%) had hypertension and were included in the study. Sixty-nine cases (43.9%) were hospitalized because of severe Covid-19. In multivariable analysis older age, diabetes and hypertensive myocadiopathy were related to a higher risk of hospital admission. ARB treatment was associated with a significantly lower risk of hospitalization (HR: 0.29, 95% CI: 0.10 – 0.88). A similar albeit not significant trend was observed for ACEI.
ConclusionARB or ACEI treatment was not associated with a worse clinical outcome in consecutive hypertensive patients infected by SARS-CoV-2.
Existe controversia respecto al uso de los inhibidores de la enzima convertidora de angiotensina (IECA) o los bloqueadores de los receptores tipo I de la angiotensina II (ARA-II) para el tratamiento de la hipertensión arterial en COVID-19. Se ha sugerido que estos fármacos podrían tanto aumentar como reducir el riesgo de COVID-19 grave.
Pacientes y métodoEstudio de cohortes retrospectivo de pacientes consecutivos de un área sanitaria, con hipertensión e infección por SARS-CoV-2. Variable de resultados: ingreso hospitalario por COVID-19 grave.
ResultadosFueron diagnosticados 539 sujetos por infección por SARS-CoV-2. De estos, 157 (29,1%) eran hipertensos y se incluyeron en el estudio. Se ingresaron 69 (43,9%) pacientes por COVID-19 grave. En el análisis multivariante, la edad más elevada, la diabetes y la miocardiopatía hipertensiva se relacionaron con el riesgo de ingreso hospitalario. El tratamiento con ARA-II se asoció con un riesgo significativamente más bajo de ingreso (HR: 0,29, IC 95%: 0,10-0,88). Una tendencia similar, aunque no significativa, se encontró para los IECA.
Conclusiónel tratamiento con ARA-II o IECA no se asoció con una peor evolución clínica en pacientes hipertensos consecutivos infectados por SARS-CoV-2.
Comorbidities negatively impact novel coronavirus disease 2019 (Covid-19) outcome, being hypertension the most prevalent comorbid condition.1 Most of the available information comes from series of hospitalized patients, and there are scarce data on comorbidities of patients initially managed as outpatients and its influence on clinical aggravation. Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) binds to its target cells through angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2).2 Some authors suggested that treatment with angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors (ACEI) or angiotensin II type-I receptor blockers (ARB) might increase the expression of ACE2 and thus, the risk of severe Covid-19.3 Accordingly, it has been suggested to replace these drugs with suitable alternatives.3 In contrast, there is health hazard resulting from withdrawal of these drugs, particularly in patients with underlying cardiovascular diseases (CVD). Moreover, it has been hypothesized that blocking the renin-angiotensin system with ACEI/ARB might actually benefit rather than harm patients with Covid-19.4 The objective of this study was to assess the effect of ACEI and ARB on clinical outcomes of patients infected with SARS-CoV-2.
Patients and MethodsThis retrospective cohort study included all consecutive patients with confirmed SARS-CoV-2 infection in our healthcare area from March 9th to April 1st 2020. Patients were selected from our 823-bed hospital's complete list of positive PCR tests results. Inclusion criteria were follow-up of ≥ 15 days since the confirmation of diagnosis and a prior diagnosis of hypertension. Data were obtained from the electronical medical records. During the Covid-19 emergency, infected patients who were not urgently admitted to the hospital were contacted by phone either by a team of physicians and nurses trained in telehealth programs, by the preventive medicine team or by a primary care physician. All the comorbidities listed in the subject's medical records and those expressed during phone interviews, and chronic therapies were systematically registered, including antihypertensive treatments, common cardiovascular risk factors and associated cardiovascular diseases (CVD). Diagnosis of non-decompensated comorbidities, without evidence of clinical severity, was not an admission criterion per se.
The outcome variable of the present study was hospitalization because of severe Covid-19. Between-groups comparisons for quantitative variables were carried out using Mann-Whitney test. Qualitative data were compared using Chi-squared test. We performed univariable and multivariable logistic regression analysis to evaluate the effect of treatment with ACEI or ARB, adjusted for confounding factors, on the risk of hospital admission because of Covid-19. Multivariable analysis was conducted through the simultaneous introduction of all variables with biological plausibility (i.e. cardiovascular risk factors, antihypertensive therapies and CVD). Age was coded in 1-year increments. The other variables were coded dichotomously (present/absent).
The clinical data for the study were recorded in a registry authorized by our Ethical Committee (Comité de Ética de la Investigación de Santiago-Lugo, Registry: 2019/245) and subsequently de-identified for analysis. Informed consent was waived due to the retrospective, non-interventional design of the study and the use of anonymous clinical data for the analysis
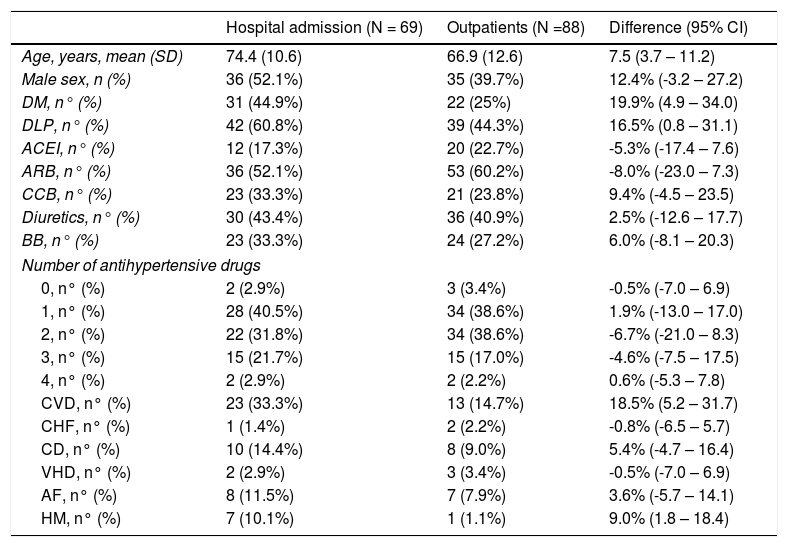
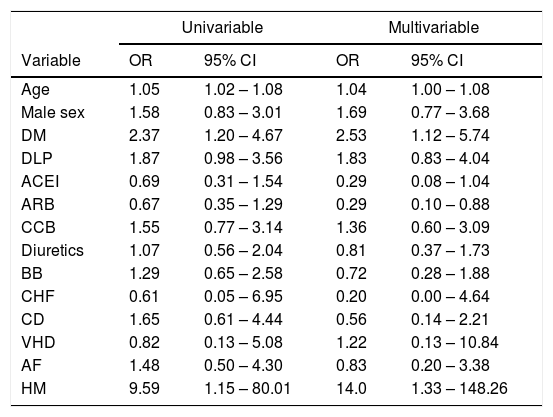
ResultsDuring the recruitment period, 539 subjects were diagnosed of SARS-CoV-2 infection. Of these, 157 (29.1%) had been diagnosed of hypertension and were included in the study. Mean age was 70.4 ± 12.3 years. Seventy-two (45.8%) were males and 85 (54.1%) females. Mean follow-up was 22.0 ± 7.0 days. Sixty-nine cases (43.9%) were hospitalized because of severe Covid-19. The other 88 patients (56.0%) were managed as outpatients. Table 1 reflects the differences between patients who were admitted to the hospital and those managed as outpatients. Table 2 shows the results of the logistic regression analysis. In multivariable analysis older age, diabetes and hypertensive myocadiopathy were related to a higher risk of admission. ARB treatment, on the other hand, was associated with a significantly lower risk of hospitalization (OR: 0.29, 95% CI: 0.10 – 0.88). A similar trend was observed for ACEI, although the results were not significant.
differences between patients admitted to the hospital and those managed as outpatients.
| Hospital admission (N = 69) | Outpatients (N =88) | Difference (95% CI) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age, years, mean (SD) | 74.4 (10.6) | 66.9 (12.6) | 7.5 (3.7 – 11.2) |
| Male sex, n (%) | 36 (52.1%) | 35 (39.7%) | 12.4% (-3.2 – 27.2) |
| DM, n° (%) | 31 (44.9%) | 22 (25%) | 19.9% (4.9 – 34.0) |
| DLP, n° (%) | 42 (60.8%) | 39 (44.3%) | 16.5% (0.8 – 31.1) |
| ACEI, n° (%) | 12 (17.3%) | 20 (22.7%) | -5.3% (-17.4 – 7.6) |
| ARB, n° (%) | 36 (52.1%) | 53 (60.2%) | -8.0% (-23.0 – 7.3) |
| CCB, n° (%) | 23 (33.3%) | 21 (23.8%) | 9.4% (-4.5 – 23.5) |
| Diuretics, n° (%) | 30 (43.4%) | 36 (40.9%) | 2.5% (-12.6 – 17.7) |
| BB, n° (%) | 23 (33.3%) | 24 (27.2%) | 6.0% (-8.1 – 20.3) |
| Number of antihypertensive drugs | |||
| 0, n° (%) | 2 (2.9%) | 3 (3.4%) | -0.5% (-7.0 – 6.9) |
| 1, n° (%) | 28 (40.5%) | 34 (38.6%) | 1.9% (-13.0 – 17.0) |
| 2, n° (%) | 22 (31.8%) | 34 (38.6%) | -6.7% (-21.0 – 8.3) |
| 3, n° (%) | 15 (21.7%) | 15 (17.0%) | -4.6% (-7.5 – 17.5) |
| 4, n° (%) | 2 (2.9%) | 2 (2.2%) | 0.6% (-5.3 – 7.8) |
| CVD, n° (%) | 23 (33.3%) | 13 (14.7%) | 18.5% (5.2 – 31.7) |
| CHF, n° (%) | 1 (1.4%) | 2 (2.2%) | -0.8% (-6.5 – 5.7) |
| CD, n° (%) | 10 (14.4%) | 8 (9.0%) | 5.4% (-4.7 – 16.4) |
| VHD, n° (%) | 2 (2.9%) | 3 (3.4%) | -0.5% (-7.0 – 6.9) |
| AF, n° (%) | 8 (11.5%) | 7 (7.9%) | 3.6% (-5.7 – 14.1) |
| HM, n° (%) | 7 (10.1%) | 1 (1.1%) | 9.0% (1.8 – 18.4) |
CI: confidence interval; DM: diabetes mellitus; DLP: dyslipidemia; ACEI: ACEI: angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors; ARB: angiotensin-II receptor blockers; CCB: calcium channel blockers; BB: beta-blockers; CVD: cardiovascular disease (any); CHF: chronic heart failure; CD: coronary disease; VHD: valvular heart disease; AF: atrial fibrillation; HM: hypertensive myocadiopathy. Some patients were diagnosed with more than one CVD.
Results of the univariable and multivariable logistic regression analysis for the risk of hospital admission.
| Univariable | Multivariable | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variable | OR | 95% CI | OR | 95% CI |
| Age | 1.05 | 1.02 – 1.08 | 1.04 | 1.00 – 1.08 |
| Male sex | 1.58 | 0.83 – 3.01 | 1.69 | 0.77 – 3.68 |
| DM | 2.37 | 1.20 – 4.67 | 2.53 | 1.12 – 5.74 |
| DLP | 1.87 | 0.98 – 3.56 | 1.83 | 0.83 – 4.04 |
| ACEI | 0.69 | 0.31 – 1.54 | 0.29 | 0.08 – 1.04 |
| ARB | 0.67 | 0.35 – 1.29 | 0.29 | 0.10 – 0.88 |
| CCB | 1.55 | 0.77 – 3.14 | 1.36 | 0.60 – 3.09 |
| Diuretics | 1.07 | 0.56 – 2.04 | 0.81 | 0.37 – 1.73 |
| BB | 1.29 | 0.65 – 2.58 | 0.72 | 0.28 – 1.88 |
| CHF | 0.61 | 0.05 – 6.95 | 0.20 | 0.00 – 4.64 |
| CD | 1.65 | 0.61 – 4.44 | 0.56 | 0.14 – 2.21 |
| VHD | 0.82 | 0.13 – 5.08 | 1.22 | 0.13 – 10.84 |
| AF | 1.48 | 0.50 – 4.30 | 0.83 | 0.20 – 3.38 |
| HM | 9.59 | 1.15 – 80.01 | 14.0 | 1.33 – 148.26 |
OR: odds ratio; CI: confidence internal. For further definitions, see legend to Table 1.
According to the results of this study, ARB or ACEI treatment is not associated with a worse clinical outcome in consecutive hypertensive patients infected by SARS-CoV-2. On the contrary, ARB treatment was associated with a lower risk of hospital admission. Continuity of treatment with renin-angiotensin inhibitors during Covid-19 pandemia have been a matter of uncertainty for clinicians. Both the possibility of a harmful as well as a beneficial effect have been suggested on theoretical grounds. Recent statements published by several scientific societies have recommended continuation of these drugs for patients with hypertension and Covid-19 because of the absence of clinical data demonstrating either beneficial or adverse outcomes with this drugs’ use in Covid-19.
Meng et al reported the outcomes of 51 hypertensive chinese patients hospitalized because of Covid-19 infection. They found a trend towards less cases with severe disease, lower peak viral load and lower IL-6 in patients treated with ACEI or ARB,5 suggesting a potential to reduce the risk of a more severe form of Covid-19. Another study carried out in Hubei, China, found lower mortality rates in 1128 hospitalized Covid-19 patients with hypertension and treated in-hospital with ACEI or ARB, compared with patients who did not receive such treatments.6
The present study was carried out in a different geographic area and in other clinical setting to those previously mentioned (consecutive patients across all the spectrum of disease severity instead of subjects hospitalized because of severe disease). The results are congruent with the previous papers, and suggest that treatment with ACEI or ARB in patients with hypertension does not aggravate the clinical evolution of patients infected by SARS-CoV-2, and it might even be associated with a lower risk of suffering severe Covid-19.The proposed mechanism for the protective effect of renin-angiotensin system inhibition would be a reduction in a theoretical overexpression of inflammatory cytokines mediated by angiotensin-II in Covid-19.5
Three new large studies have been published since we performed our analysis.7–9 One of them was carried out in hospitalized patients with confirmed Covid-19,8 and the other 2 included subjects without the disease (either patients with Covid-19 test performed, with negative results8 or matched controls from an administrative database10). Neither ACEI nor ARB were related to a higher risk of suffering Covid-198,9 or with suffering a more severe form of the disease.7,8 Actually, treatment with ACEI was associated with a lower mortality risk in hospitalized Covid-19 cases.7
The present study has some limitations, the most obvious being its relatively small sample size and its retrospective design, that makes it vulnerable to information and recall bias. Actually, the small number of patients with hypertensive myocadiopathy and the corresponding wide confidence intervals found in the analysis raises doubts about the significance of this variable. On the other hand, the study has some strengths: it has been performed in consecutive, unselected patients representing all the spectrum of disease severity, and to our knowledge, it is the first study on this topic carried out in Spain.
In conclusion, the present study agrees with previous reports and supports the current recommendation to maintain the treatment with ACEI or ARB in patients with hypertension irrespective of infection with SARS-CoV2.10 Whether these drugs can actually be used to improve clinical outcomes in Covid-19 beyond their usual clinical indications should be confirmed with adequately designed randomized clinical trials.
FundingNone
Conflicts of interest statementNone of the authors report any conflict of interest related to the manuscript
Authorship contribution: RG: study concept and design, acquisition of data, analysis of data, drafting of the manuscript, had full access to all of the data in the study and takes responsibility for the integrity of the data and the accuracy of the data analysis. LA P-d-LL: Analysis and interpretation of data, drafting of the manuscript. DD, HGS, CPF, BPV, PVV: acquisition of data, critical revision of the manuscript for important intellectual content.