To identify the relationship and behaviour of the variables of self-control, self-efficacy and locus control in weight regulation of obese, overweight and normal weight adults.
MethodTransversal study undertaken in the Health Centre of El Coto (Gijón) from 1st April to 30th July 2015. Participants: Subjects between 18 and 65 years of age with a body mass index recording within the last two years. Exclusions: serious medical illness, eating disorders or pregnant women. Main measurements: Behavioural variables: self-regulation of body weight (Inventory of self-control of body weight), perceived self-efficacy in weight regulation (Inventory of perceived self-efficacy in weight regulation) and locus control in weight regulation (Inventory of locus control in weight regulation). Anthropometric variables: weight (kg) and height (m), body mass index.
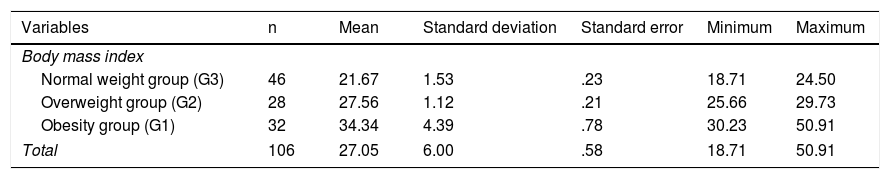
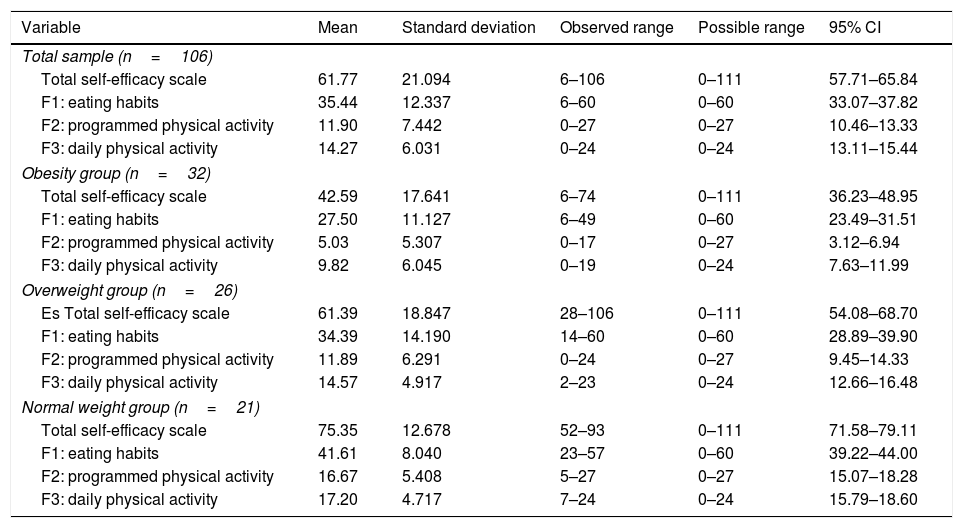
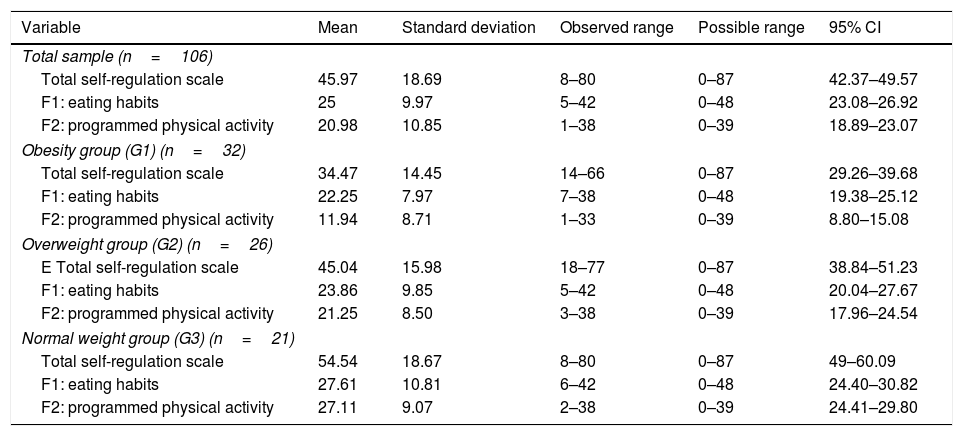
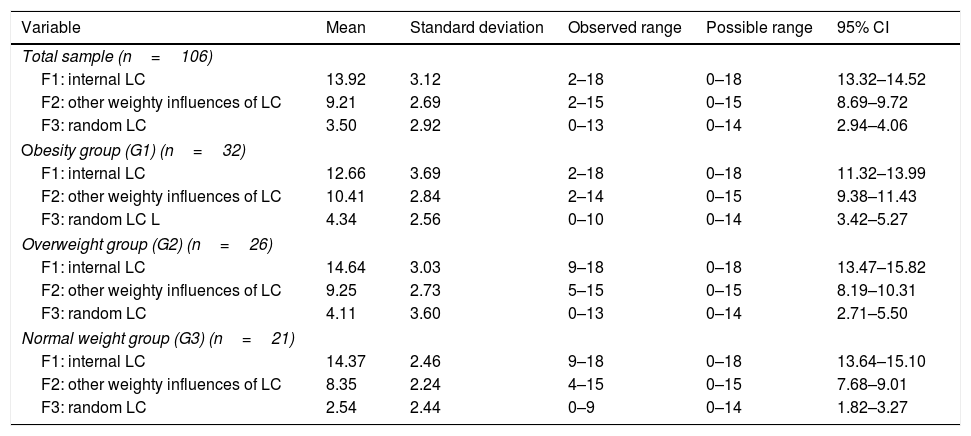
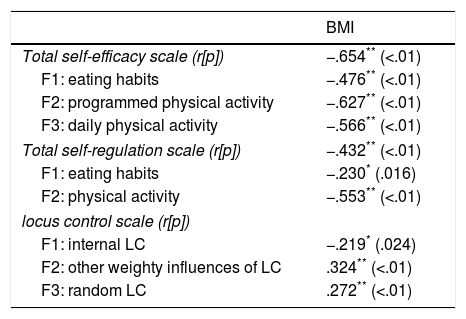
ResultsOne hundred and six participants were included: 32 were obese, 28 overweight and 46 normal weight. Significant differences were found between the 3 study groups for total scale of self-efficacy (F=61.77; p<.01), total scale of self-regulation (F=45.97; p<.01), internal locus control (F=13.92; p=.019), other weighty influences of locus control (F=9.21; p<.01) and random locus control (F=3.50; p=.011).
ConclusionsThe relationship between body mass index and behavioural variables of self-efficacy, self-regulation and locus control, suggests the need for healthcare professionals to include psychological factors of behaviour in any preventive action and intervention directed at weight control.
Identificar la relación y el comportamiento de la autorregulación, autoeficacia y locus control en la regulación del peso, en población adulta con obesidad, sobrepeso y normopeso.
MétodoSe realizó un estudio transversal en el Centro de Salud del Coto (Gijón) entre el 1 de abril al 30 de julio de 2015. La muestra estuvo formada por personas entre 18-65 años que contaran con un registro del índice de masa corporal en los dos últimos años. Los criterios de exclusión fueron: enfermedad médica grave, trastornos de la alimentación o mujeres embarazadas. Se midieron variables conductuales: autorregulación del peso corporal (Inventario de autorregulación del peso corporal), autoeficacia percibida en la regulación del peso (Inventario autoeficacia percibida en la regulación del peso) y locus control en la regulación del peso (Inventario Locus control en la regulación del peso). Variables antropométricas: peso (kg) y talla (m), índice de masa corporal.
ResultadosSe incluyeron 106 participantes: 32 con obesidad, 28 con sobrepeso y 46 con normopeso. Se encontraron diferencias estadísticamente significativas entre los 3 grupos de estudio para las variables escala total de autoeficacia (F=61,77; p<0,01), escala total de autorregulación (F=45,97; p<0,01), locus control interno (F=13,92; p=0,019), locus control otros poderosos (F=9,21; p<0,01) y locus control azar (F=3,50; p=0,011).
ConclusionesLa existencia de una relación entre el índice de masa corporal y las variables conductuales de autoeficacia, autorregulación y locus control, plantea a los profesionales sanitarios la necesidad de incluir los factores psicológicos o conductuales en cualquier actividad preventiva y de intervención dirigida al control del peso.