To evaluate the effectiveness of the multidisciplinary respiratory rehabilitation (RR) programme in patients with severe or very severe chronic obstructive pulmonary disease pre the RR programme, at the end of the programme and one year after the RR, measuring changes in ability to exercise (walking test), effort tolerance (forced expiratory volume (FEV1)) and health-related quality of life.
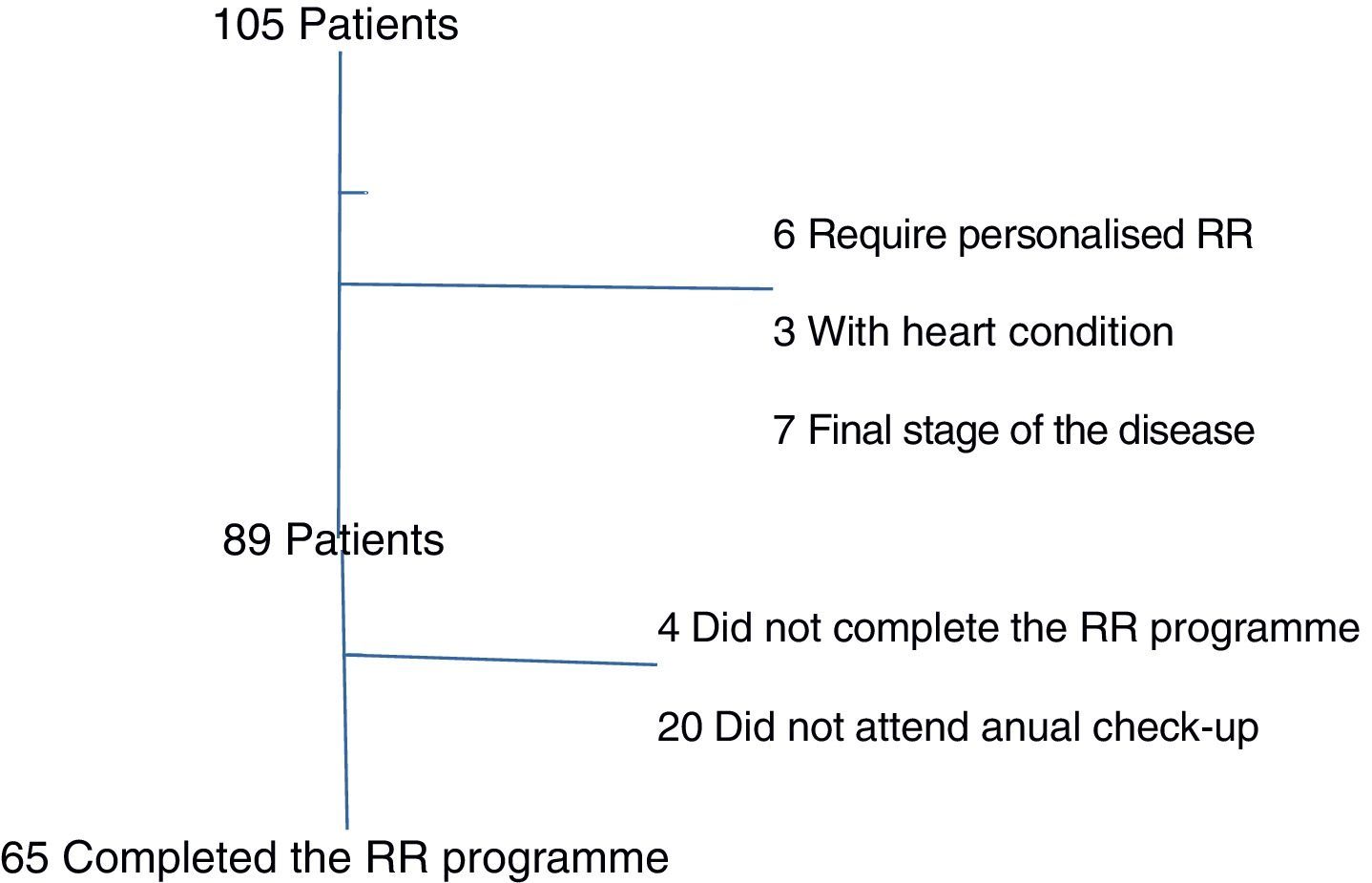
MethodQuasi-experimental single group design. We included patients diagnosed with severe or very severe chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (stages III and IV of the GOLD classification) who entered the rehabilitation programme for the years 2011 and 2012. Demographic data, questionnaires on general health-related quality of life (SF-36) and specific to respiratory patients (St George's Respiratory Questionnaire), FEV1% and exercise capacity test (running test 6min) were collected. Data were collected before the RR programme, at the end of the RR programme and a year after completing the programme.
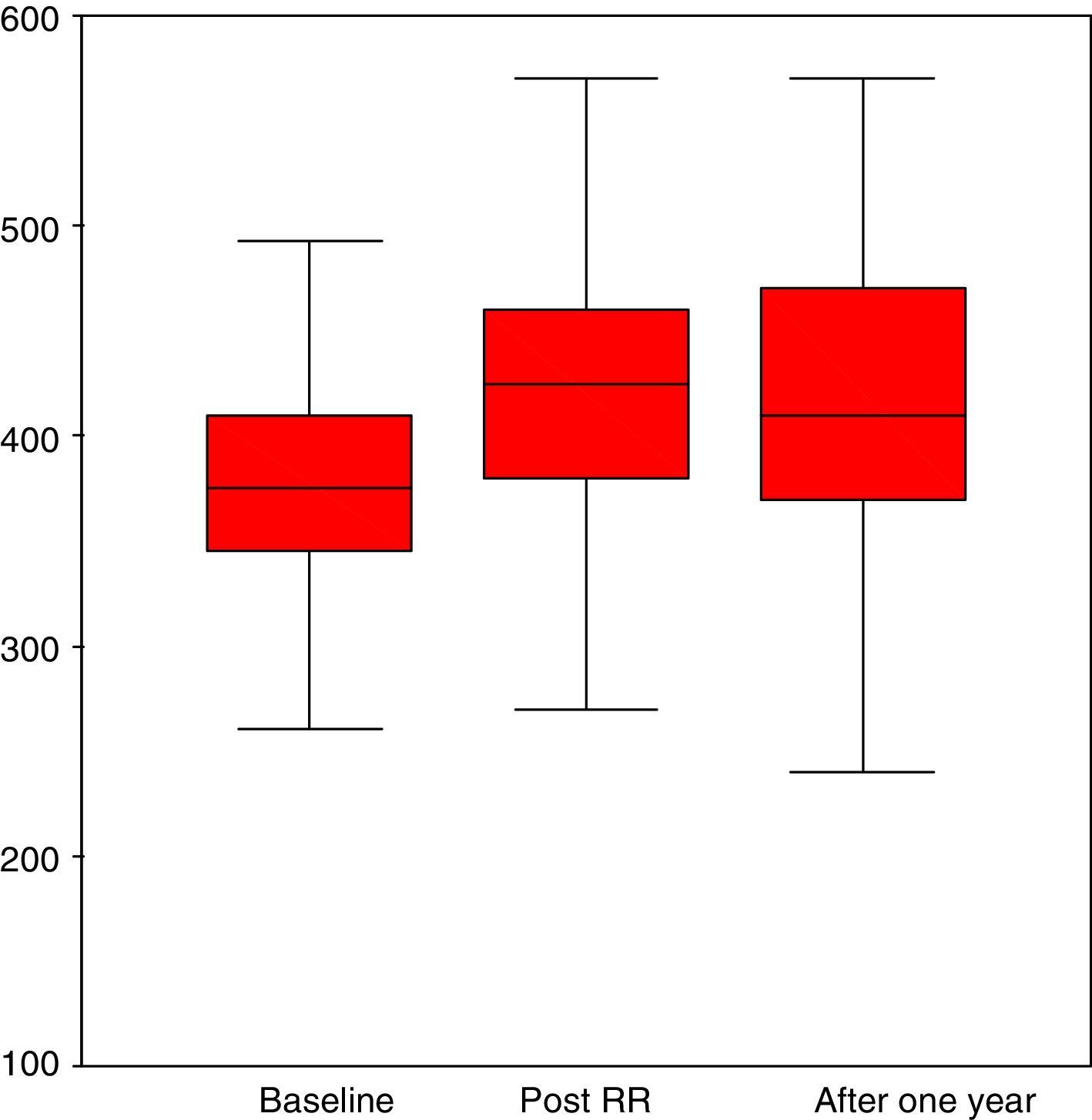
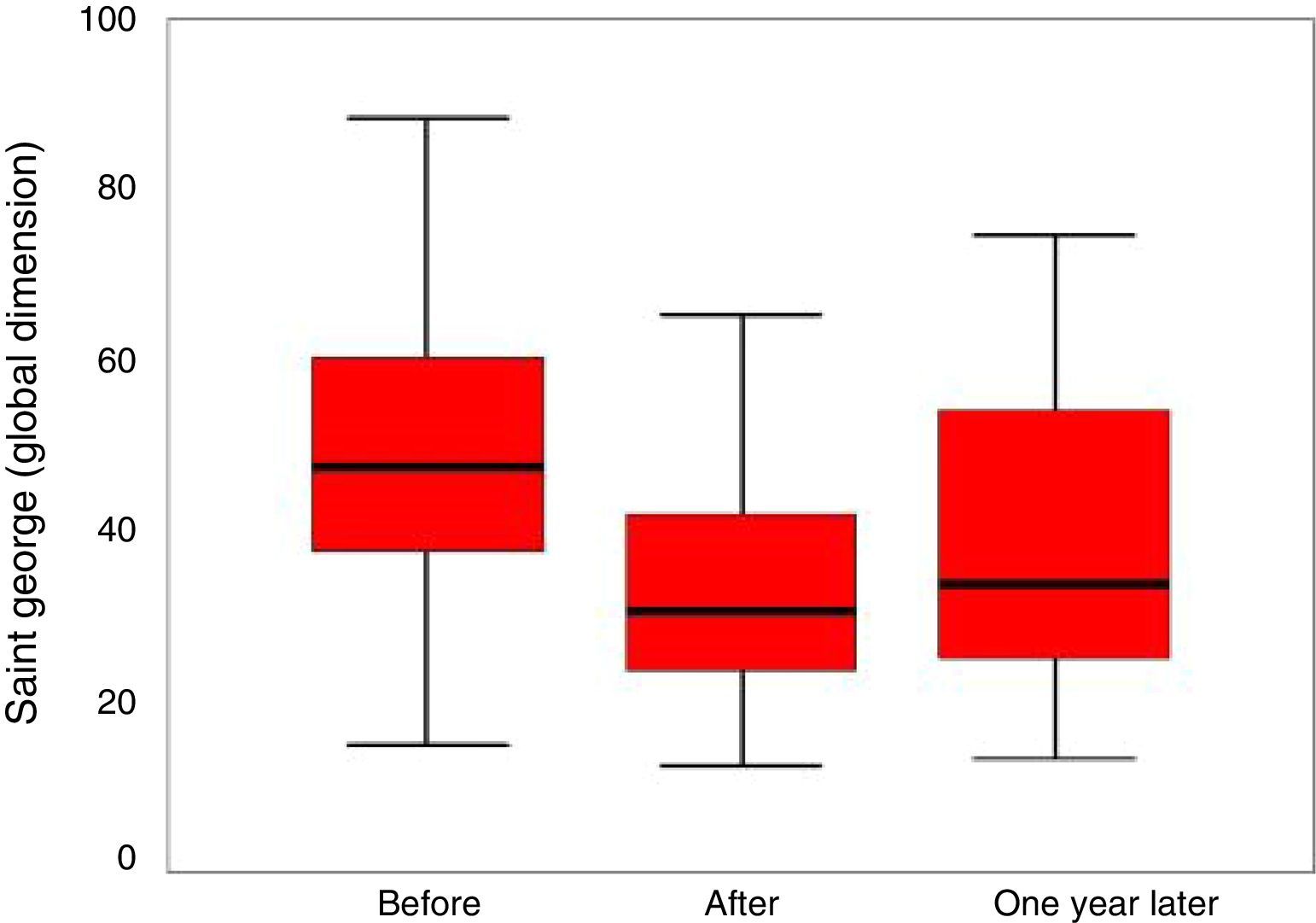
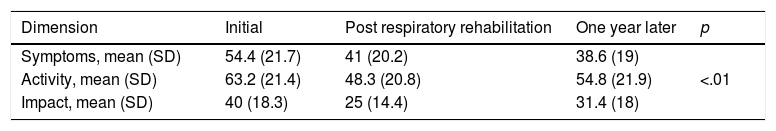
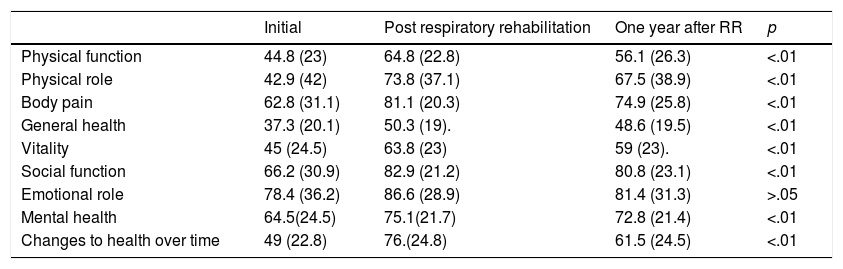
ResultsNo significant differences in FEV1% values were observed. Regarding exercise capacity, an increase in distance walked in the walking test was noted, which changed significantly after training, 377±59.7–415±79m after one year (p<.01). A statistically significant improvement in mean scores of HRQoL was observed, except for the emotional role dimension of the SF-36 questionnaire.
ConclusionA pulmonary rehabilitation programme for 8 weeks improved the exercise capacity, dyspnoea and quality of life of patients with severe and very severe chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.
Evaluar la efectividad de un programa de rehabilitación respiratoria (RR) multidisciplinar en pacientes con enfermedad pulmonar obstructiva crónica grave o muy grave preprograma RR, al terminar el programa y al año de haber realizado la RR midiendo los cambios producidos en: la capacidad de ejercicio (test de marcha), mejoría en la tolerancia al esfuerzo (volumen espiratorio forzado [FEV1]) y en la calidad de vida relacionada con la salud.
MétodoDiseño cuasiexperimental con un solo grupo. Se incluyeron a pacientes con diagnóstico de enfermedad pulmonar obstructiva crónica grave o muy grave (estadios iii y iv de la clasificación GOLD) que entraron en el programa de RR entre 2011 y 2012. Se recogieron datos demográficos, calidad de vida relacionada con la salud general (SF-36) y específica para enfermos respiratorios (Cuestionario Respiratorio St. George), FEV1% y test de capacidad de ejercicio (prueba de la marcha de 6min). La recogida de datos se realizó preprograma RR, al terminar el programa de RR y al año de haber acabado el programa.
ResultadosNo se observaron diferencias significativas en los valores de FEV1%. Respecto a la capacidad de ejercicio se observó un aumento de la distancia recorrida en el test de marcha, que se modificó significativamente después del entrenamiento, de 377±59,7 a 415±79m al año (p<0,01). Se observó una mejoría estadísticamente significativa en las 3 dimensiones del Cuestionario Respiratorio St. George. Las medias de las puntuaciones obtenidas de la calidad de vida relacionada con la salud mejoraron significativamente en todas las dimensiones excepto en la dimensión rol emocional del cuestionario SF-36.
ConclusiónUn programa de RR de 8 semanas de duración mejora la capacidad de realizar ejercicio, la disnea y la calidad de vida en pacientes con enfermedad pulmonar obstructiva crónica grave y muy grave.