To evaluate the effect of a physical activity programme in the aquatic environment with immersion up to the neck, of six weeks duration, on haemodynamic constants in pregnant women.
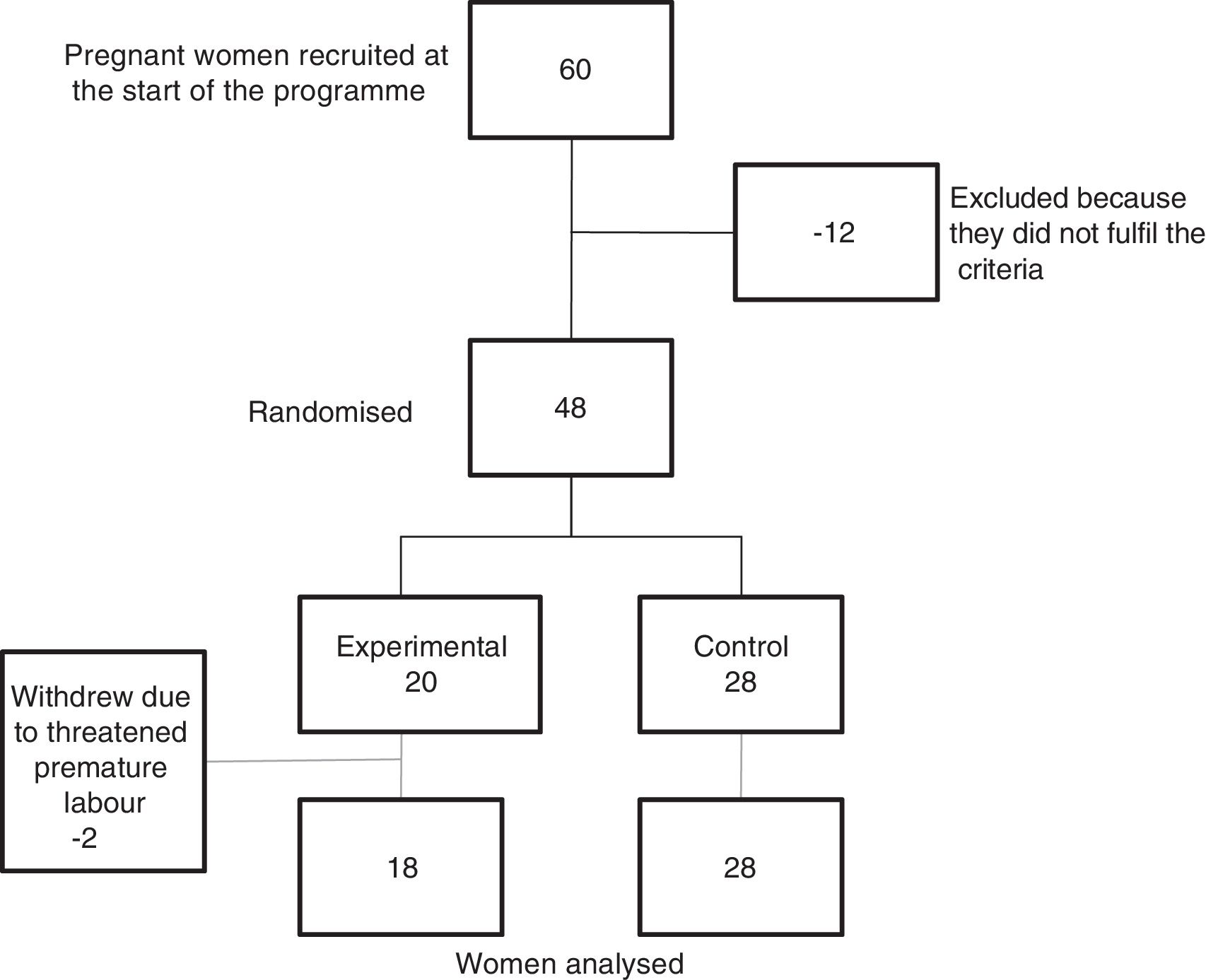
MethodsA six-week physical activity programme in the aquatic environment was carried out with a total of 46 pregnant women, who were distributed into an experimental group (n=18), which participated in the programme, and a control group (n=28), which followed routine care. In both groups different haemodynamic measurements were evaluated before and after the programme.
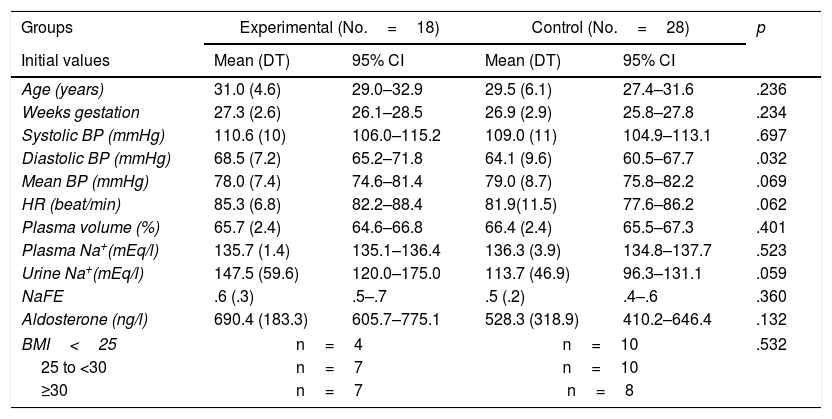
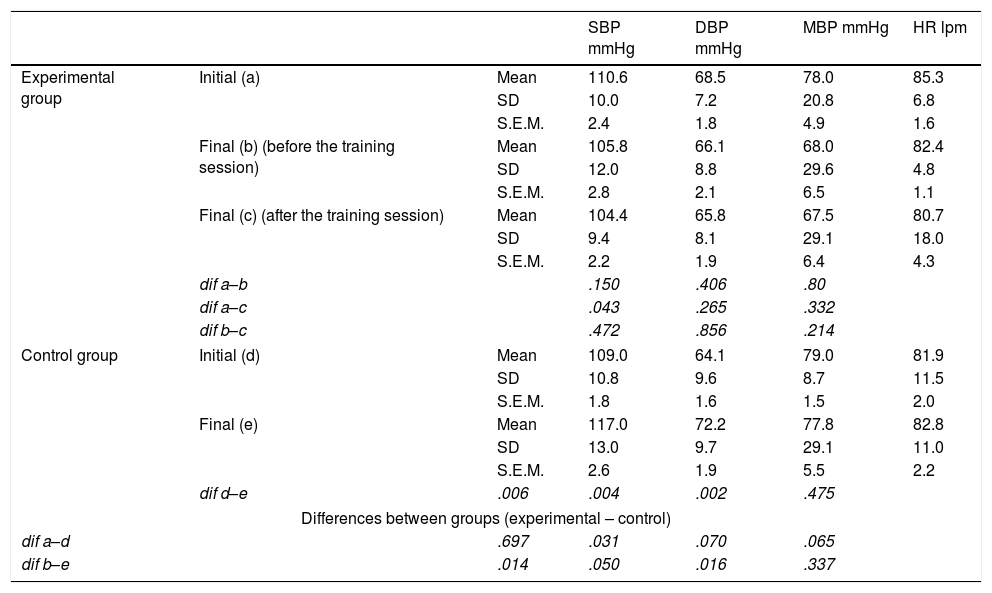
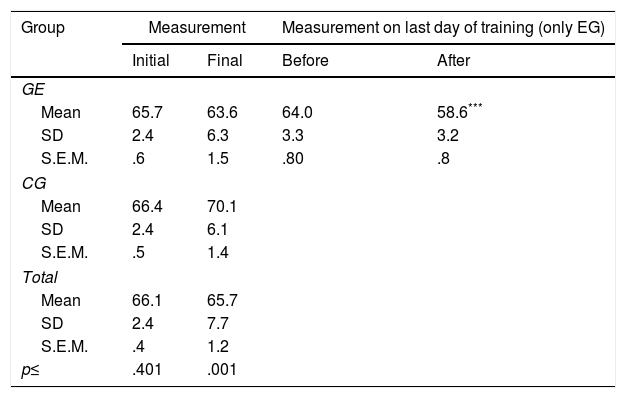
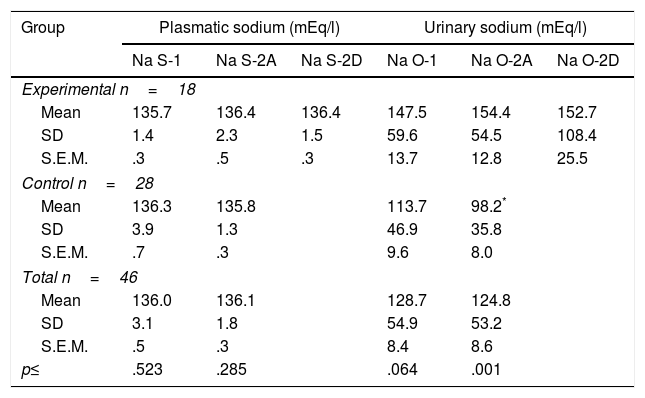
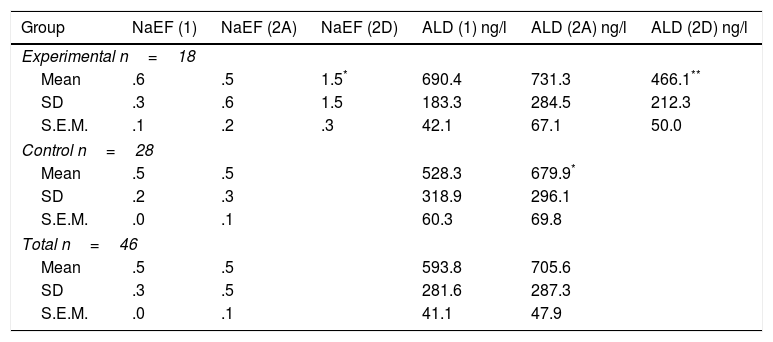
ResultsAt the beginning of the programme the mean systolic blood pressure was similar between groups, but diastolic blood pressure was slightly higher in the experimental group. When the measurements at the last session were compared, arterial pressures (systolic, diastolic and mean) were significantly higher in the control group (p<.050). Similarly, the initial plasma volume values did not differ between groups, but after the intervention, the control group women showed a higher mean (p<.010). The fraction of sodium excretion (FENa) increased significantly in the experimental group, after the programme, with a mean three times higher (p<.050). Aldosterone plasma levels did not show significant differences between the groups in the different measurements.
ConclusionA programme of swimming and immersion exercises in pregnant women contributes to hydrosaline balance, preventing an excessive increase in usual plasma volume during pregnancy and in the activity of the renin-aldosterone axis.
Evaluar el efecto de un programa de actividad física en el medio acuático con inmersión hasta el cuello, de seis semanas de duración, sobre las constantes hemodinámicas en mujeres gestantes.
MétodoSe llevó a cabo un programa de actividad física en el medio acuático, de seis semanas de duración a un total de 46 mujeres embarazadas, que fueron distribuidas en grupo experimental que participó en el programa (n=18) y grupo control (n=28) que desarrolló los cuidados habituales. En los dos grupos se valoraron diferentes medidas hemodinámicas antes y después del programa.
ResultadosAl inicio del programa el promedio de presión arterial sistólica era similar en ambos grupos pero la presión arterial diastólica era ligeramente mayor en el grupo experimental. Cuando se contrastan las medidas en la última sesión, resultan significativamente mayores las presiones arteriales (sistólica, diastólica y media), en el grupo control (p<0,050). De forma similar, los valores iniciales de volumen plasmático no diferían en ambos grupos, pero tras la intervención las mujeres del grupo control evidencian un mayor promedio (p<0,010). La fracción de excreción de sodio (FENa) aumenta significativamente en el grupo experimental, tras la realización del programa, cuyo promedio se triplica (p<0,050). Los niveles plasmáticos de aldosterona no muestran diferencias significativas entre ambos grupos en las distintas mediciones.
ConclusiónUn programa de ejercicios de natación e inmersión, en mujeres gestantes, contribuye al equilibrio hidrosalino, previniendo el aumento excesivo de volumen plasmático habitual en el embarazo, y en la actividad del eje renina-aldosterona.