A 54-year-old Spanish woman sought medical advice at the outpatient clinic of our institution for diarrhoea and abdominal pain that began on her return from Cambodia and Laos ten days earlier. On examination, she had neither fever nor skin lesions. Laboratory tests showed haemoglobin, hepatic enzymes and a leucocyte count within normal range. No eosinophilia was detected. The patient was diagnosed of traveller's diarrhoea. No antibiotic treatment was prescribed given the absence of fever. She was asked to bring three stool samples for microbiological studies over the following days.
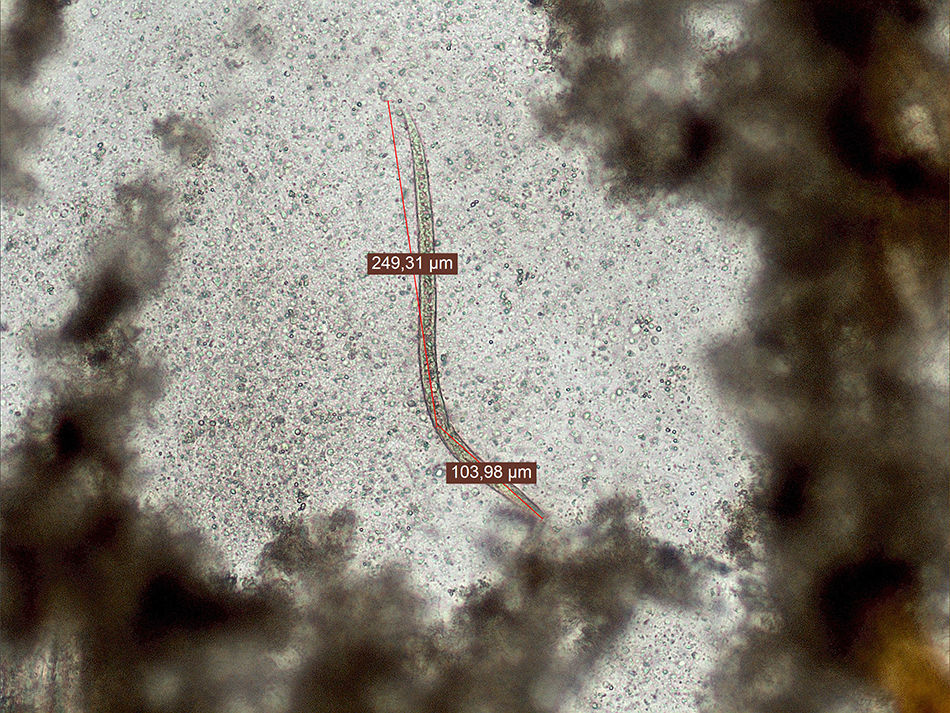
Diagnosis and follow-upThe first stool sample revealed larvae of 350μm in length after concentration in sodium acetate–acetic acid–formalin fixative (SAF) (Fig. 1). No culture for Strongyloides stercoralis was performed due to lack of further fresh sample. In the other two stool samples, larvae were not detected either after concentration or after culture of the stool on blood agar plates. No eggs were observed in any of the samples. No bacterial enteropathogens were detected.
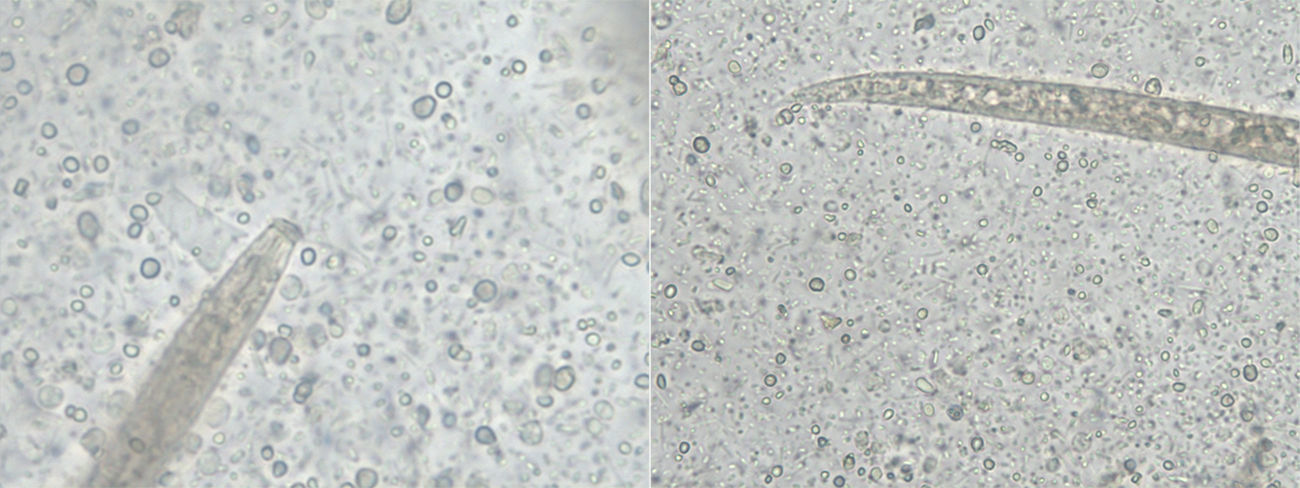
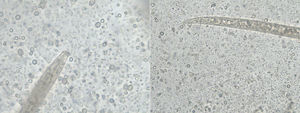
The larvae had tapered ends with long buccal cavities (Fig. 2). No genital primordium was seen. Eggs were not observed. As faeces were properly fixed when collected, hookworms and Trichostrongylus were ruled out because their larvae would not have developed. As none of the features matched S. stercoralis, spurious passage of free-living or plant nematodes was suspected.1 Final confirmation of spurious passage of a free-living or plant nematode came from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC, Atlanta, USA). At follow-up twelve days later, the patient was completely asymptomatic. The cause of the diarrhoea remained undetermined.
DiscussionMicroscopic observation is the basis of parasitological diagnosis. However, many artefacts resembling parasite structures and even non-human parasites may be confused as aetiological agents of human parasitoses.2
In faeces the presence of larvae may not always be clinically meaningful. Larvae of non-human or free-living nematodes may go through the alimentary canal without causing infection. Occasionally spurious nematode infections have been described in humans due to accidental intake of eggs, insects or other animals that could behave as intermediate hosts.1,2 Some larvae may even survive the acidic gastrointestinal passage as in the case of free living nematodes such as Turbatrix aceti (also know as the vinegar eel) and some plant nematodes such as Heterodera.1
When some features of larvae do not match those expected, spurious passage should be taken into consideration, especially when the patient becomes asymptomatic without treatment as in the present case. As in spurious passages parasites will not be maintained in time, further stool samples should be negative to confirm this suspicion.
The authors would like to thank the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) for confirmation of spurious passage.