To investigate the frequency of hypogonadism and its relationship to inflammation and carotid intima-media thickness (CIMT) in male patients with predialysis chronic kidney disease (CKD).
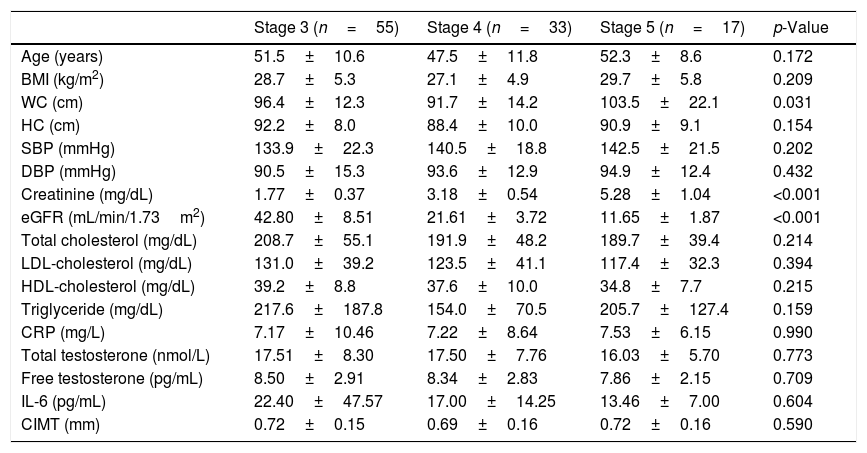
MethodsA total of 105 patients with CKD, 55 (52.4%) as stage 3, 33 (31.4%) as stage 4 and 17 (16.2%) as stage 5, were enrolled into the study. Total testosterone (TT) and free testosterone (FT), interleukin 6 (IL-6), C-reactive protein (CRP) levels, and CIMT were measured.
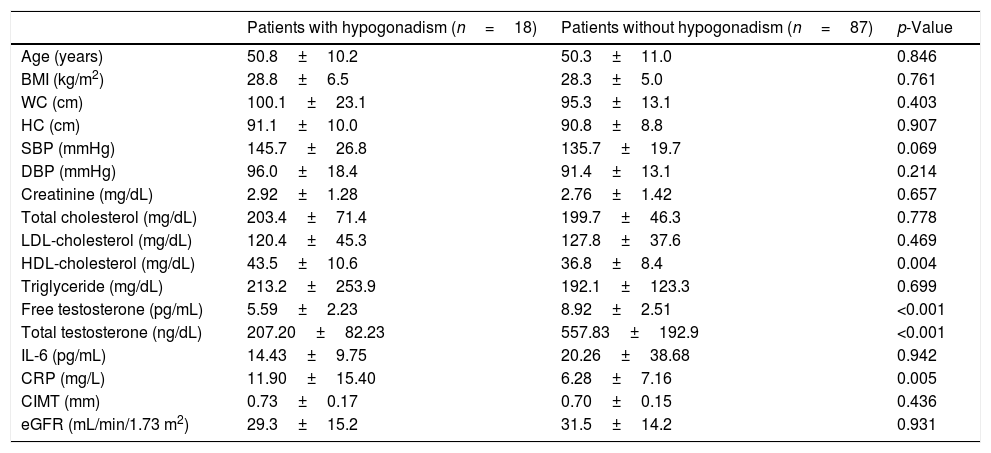
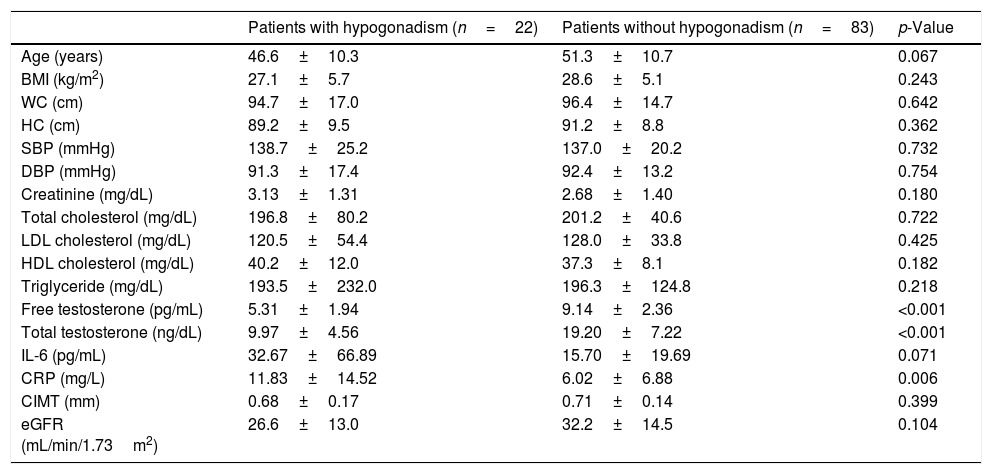
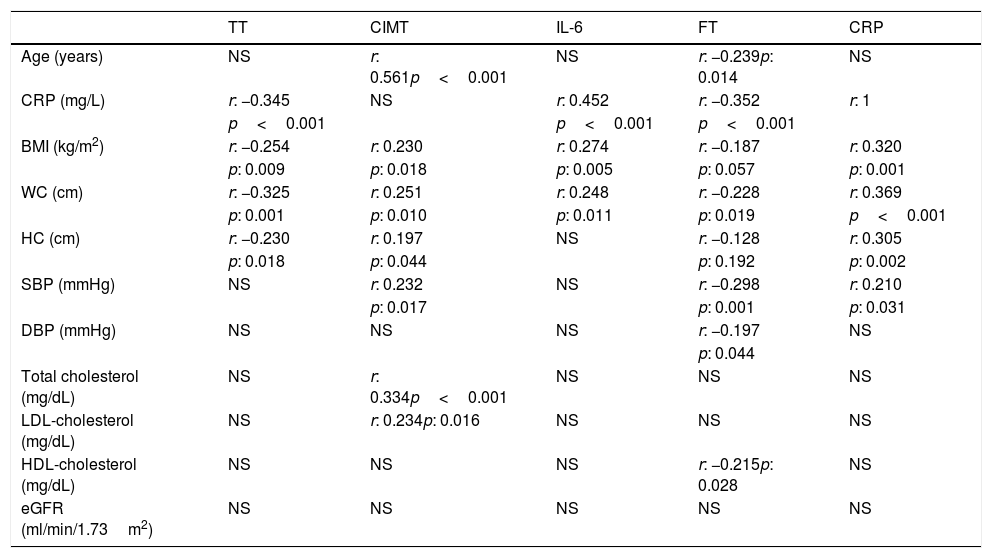
ResultsAccording to TT and FT, hypogonadism was detected in 18 (17.1%) and 22 (20.9%) patients, respectively. There was no difference in terms of TT and FT, CIMT, CRP and IL-6 between the stages of CKD. According to TT, the patients with hypogonadism had significantly higher CRP and high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-cholesterol) levels (p=0.004 and p=0.005, respectively). There was no significant difference in other parameters. According to FT, the patients with hypogonadism had significantly higher CRP (p=0.017), and TT were negatively correlated with body mass index (BMI), waist circumference (WC), hip circumference, and CRP levels. FT was negatively correlated with age, waist circumference, systolic blood pressure, diastolic blood pressure (DBP) and CRP.
ConclusionsThe frequency of hypogonadism was found around 17–21% among the patients with CKD. Despite similar IL-6 and CIMT levels, CRP was found to be higher in the patients with hypogonadism. We consider that further studies with larger populations are needed to elucidate the entity.
Investigar la frecuencia de hipogonadismo y su relación con la inflamación y grosor de la íntima-media carotídea (CIMT) en varones con insuficiencia renal crónica (IRC) prediálisis.
MétodosSe incluyó en el estudio a un total de 105 pacientes con IRC, 55 (52,4%) en estadio 3, 33 (31,4%) en estadio 4, y 17 (16,2%) en estadio 5. Se midieron testosterona total (TT) y testosterona libre (TL), interleucina 6 (IL-6), niveles de proteína C reactiva (PCR), y CIMT.
ResultadosCon respecto a TT y TL, se detectó hipogonadismo en 18 (17,1%) y 22 (20,9%) pacientes, respectivamente. No se encontraron diferencias en términos de TT y TL, CIMT, PCR e IL-6 entre los diferentes estadios de IRC. Con respecto a TT, los pacientes con hipogonadismo tenían valores significativamente más altos de PCR y colesterol de lipoproteínas de alta densidad (HDL-colesterol) (p=0,004 y p=0,005, respectivamente). No se encontraron diferencias significativas en cuanto a otros parámetros. Con respecto a TL, los pacientes con hipogonadismo tenían valores significativamente más altos de PCR (p=0,017), y TT guardó una correlación negativa con el índice de masa corporal (IMC), perímetro de la cintura, perímetro de la cadera, y niveles de PCR. TL se correlacionó negativamente con la edad, perímetro de cintura, presión arterial sistólica (PAS), presión arterial diastólica (PAD) y PCR.
ConclusionesSe encontró frecuencia de hipogonadismo en cerca del 17-21% de los pacientes con IRC. A pesar de encontrar niveles similares de IL-6 y CIMT, los niveles de PCR fueron más altos en los pacientes con hipogonadismo. Consideramos que son necesarios más estudios, con poblaciones de mayor tamaño, para explicar esta entidad.
Artículo
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora