To determine the prevalence and symptom severity of urinary incontinence (UI) in women who attend primary care gynecological consultations, as well as the proportion of women with UI symptoms who wish to be studied and treated.
Materials and methodsA multicentre, observational, descriptive cross-sectional study was conducted of women who visit the 8 specialized consultations for sexual and reproductive health (SRH) in the 4 Catalan provinces for any reason (except UI, pregnancy and postpartum). We employed the ICQ-UI-SF questionnaire to detect UI symptoms. Women with UI symptoms (ICI-Q-SF>0) were asked whether they wanted specific care for their UI problem. Those who answered “no” were asked why.
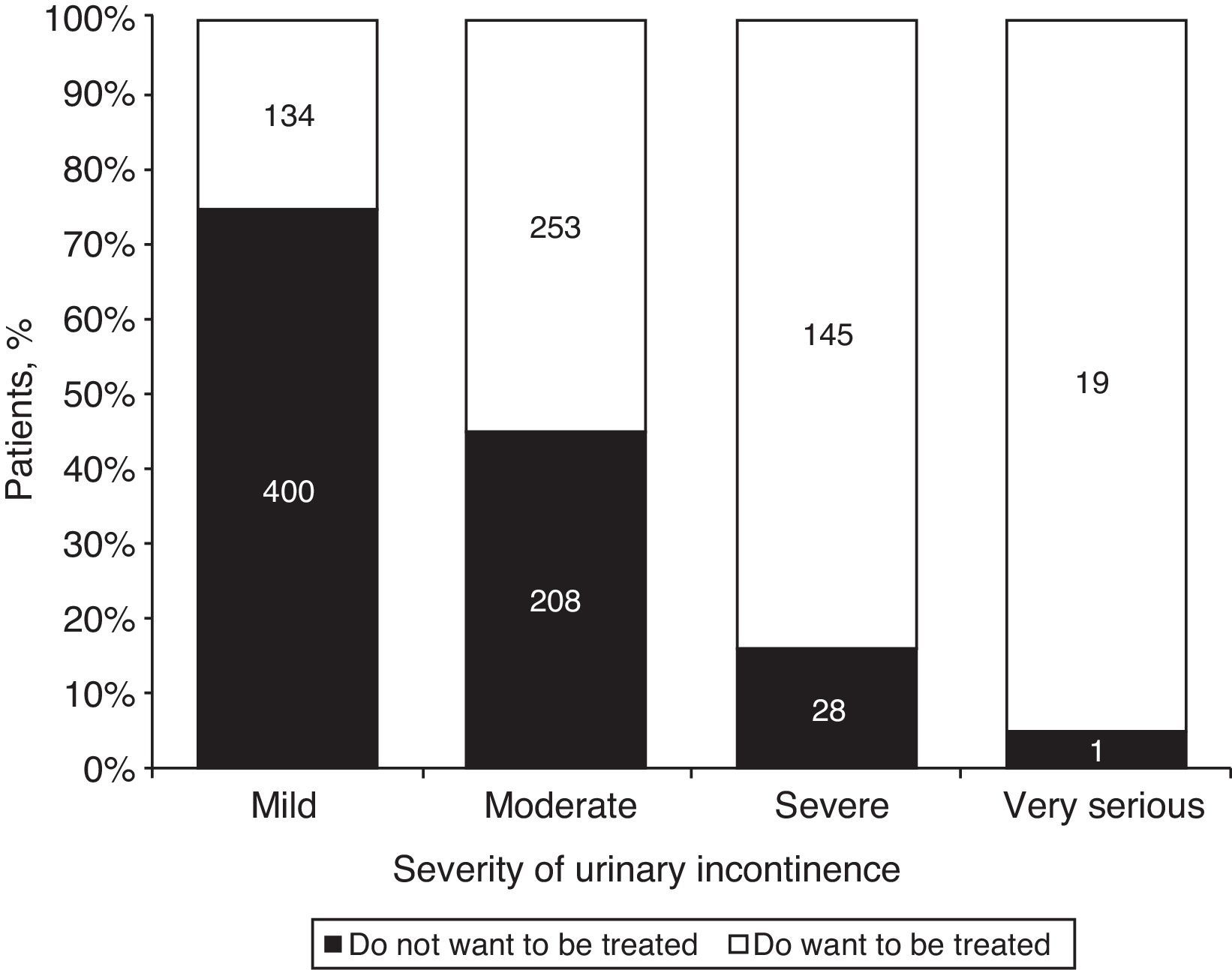
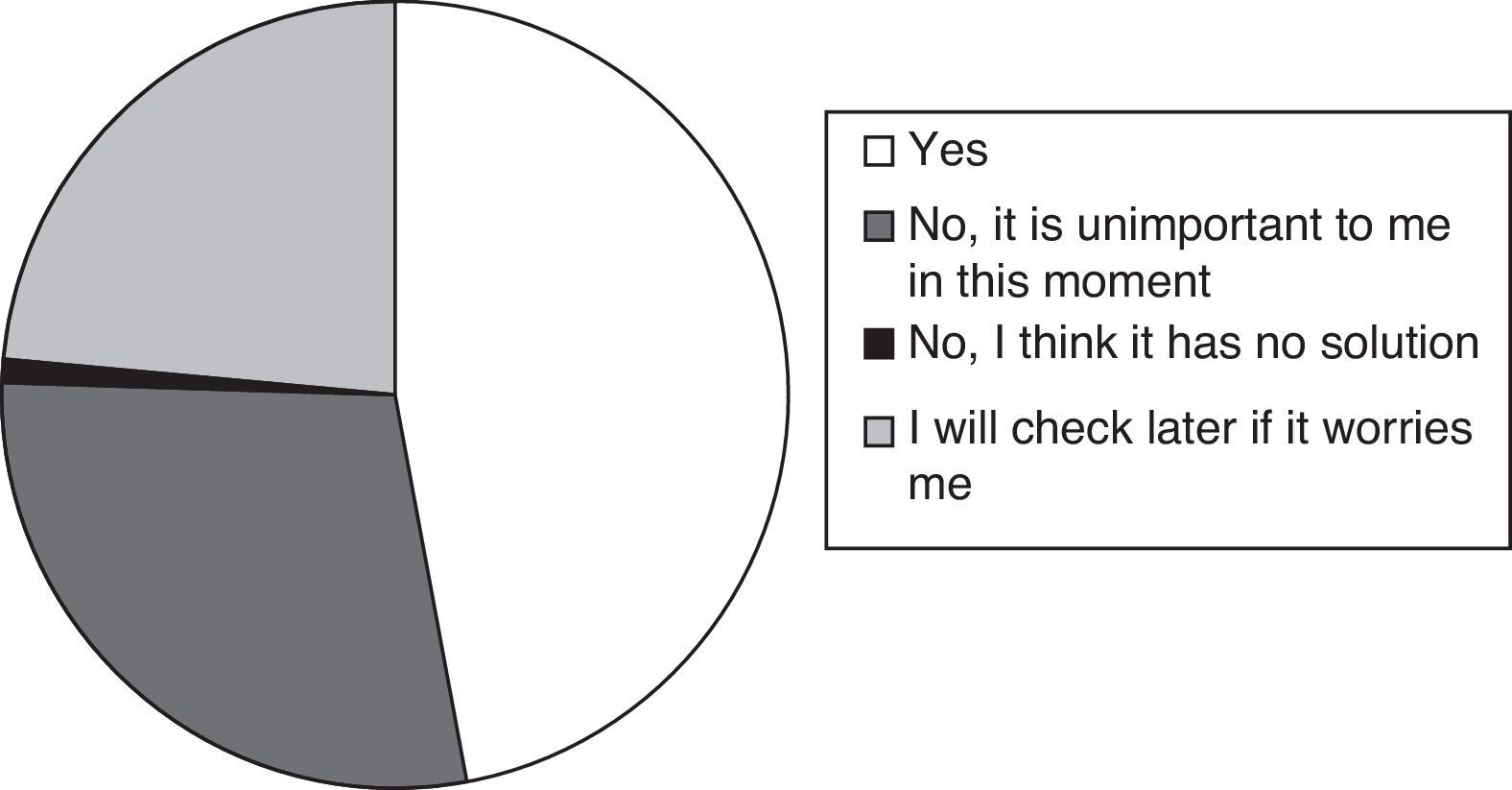
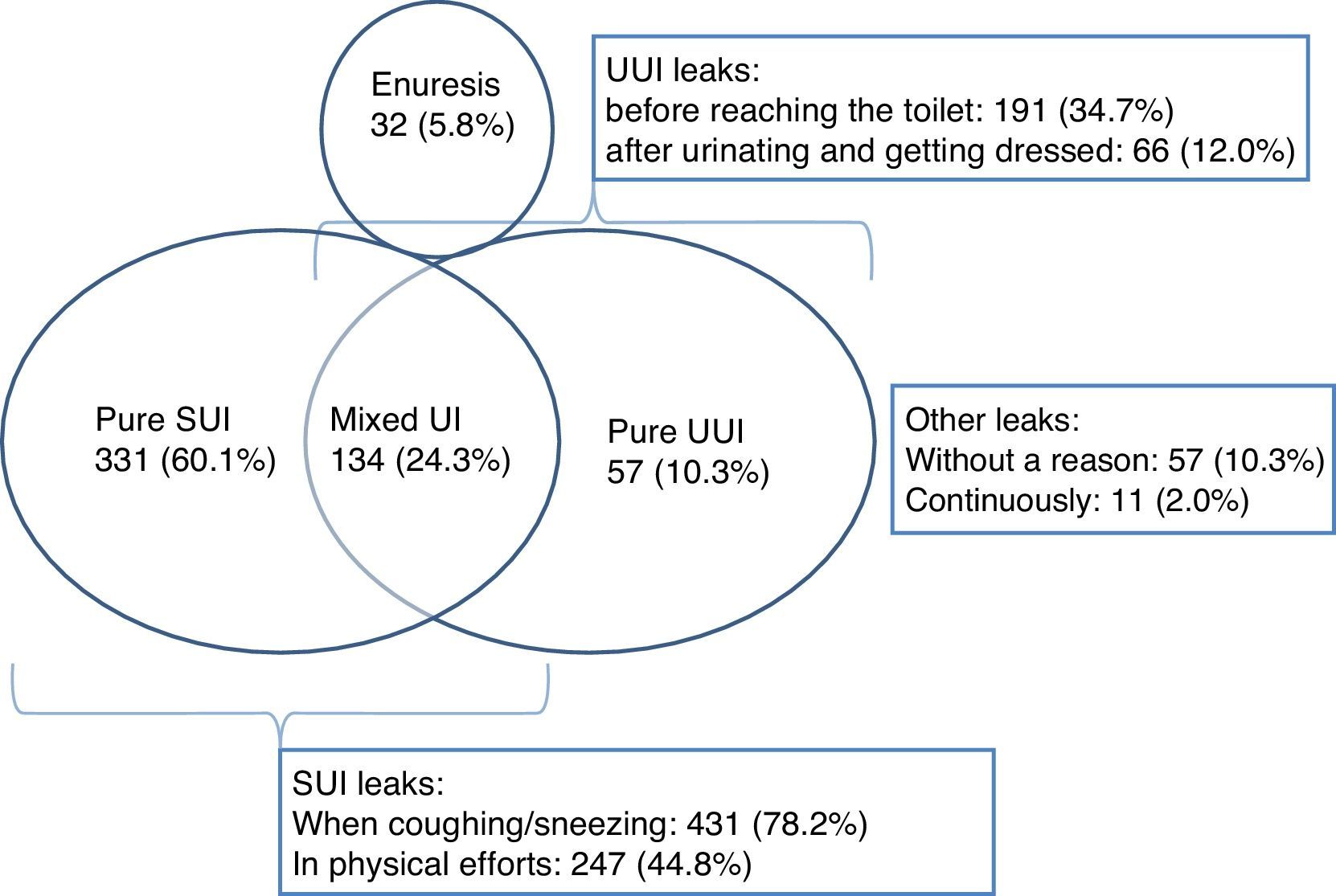
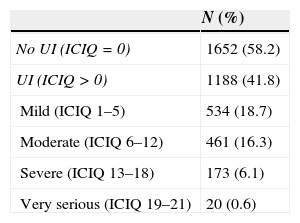
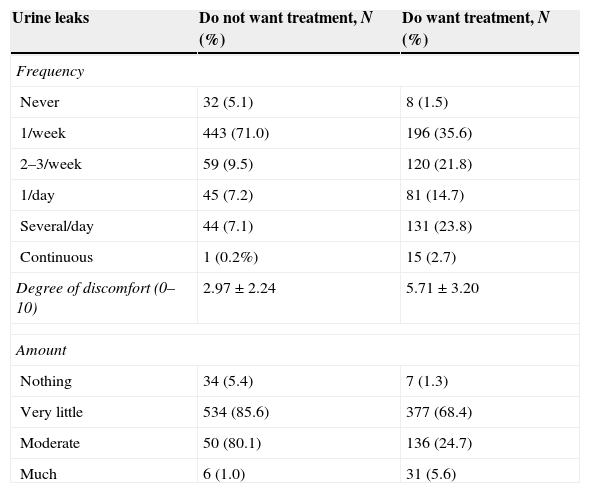
ResultsThe study included 2840 women, 41.8% of whom reported urine losses, especially mild to moderate symptoms. Some 53.62% of the women with UI responded that they did not wish to be treated. Of these, 75% had mild symptoms, 45% had moderate symptoms, and only 16% and 5% had severe or very severe symptoms, respectively. Fifty-three percent of the women did not want treatment because the UI was not a significant problem for them.
ConclusionsAlmost half of the women who attended a specialized consultation for SRH for any reason reported UI symptoms, especially mild and moderate. More than half of the patients with UI symptoms did not want to start a diagnostic and treatment process for their problem. Symptom severity is associated with the willingness to be treated.
Determinar la prevalencia y gravedad de los síntomas de incontinencia urinaria (IU) en mujeres que acuden a consultas de atención primaria de ginecología, así como la proporción con síntomas de IU que desean ser estudiadas y tratadas.
Materiales y métodosEstudio multicéntrico, observacional, descriptivo transversal en mujeres que consultaron por cualquier motivo (excepto IU, embarazo y puerperio), a 8 consultas especializadas en salud sexual y reproductiva de las 4 provincias catalanas. Se utilizó el cuestionario ICQ-UI-SF para la detección de los síntomas de IU. A las mujeres con síntomas de IU (ICI-Q-SF>0) se les preguntó si deseaban recibir atención específica por su problema de IU. A las que contestaron que no se les preguntó por qué.
ResultadosSe incluyeron 2.840 mujeres, de las cuales un 41,8% afirmó tener pérdidas de orina, sobre todo sintomatología leve o moderada. Un 53,62% de las mujeres con IU respondió que no deseaba ser tratadas: un 75% con sintomatología leve, un 45% moderada y solo un 16% y un 5% con sintomatología grave o muy grave, respectivamente. Un 53% de mujeres no deseaba tratamiento porque la IU no era un problema importante para ellas.
ConclusionesCasi la mitad de las mujeres que acuden a una consulta especializada en salud sexual y reproductiva por cualquier motivo refieren síntomas de IU, sobre todo leve y moderada. Más de la mitad de las pacientes con síntomas de IU no desean iniciar un proceso de diagnóstico y tratamiento de su problema. La severidad de los síntomas se asocia a la voluntad de ser tratadas.