We aimed to evaluate how the corona virus disease of 2019 (COVID-19) outbreak influenced emergency department (ED) admissions for urolithiasis, hospitalizations and clinical management of the hospitalized Patients.
Patients and methodsWe conducted a multicentric retrospective analysis of ED admissions in three high volume urology departments (one directly involved in COVID-19 patients management and two not involved) in Rome - Italy between March and April 2020 and in the same period of 2019. Statistical analysis was conducted on the number of admissions for urolithiasis, rate of complications, hospitalization and the type of treatment received.
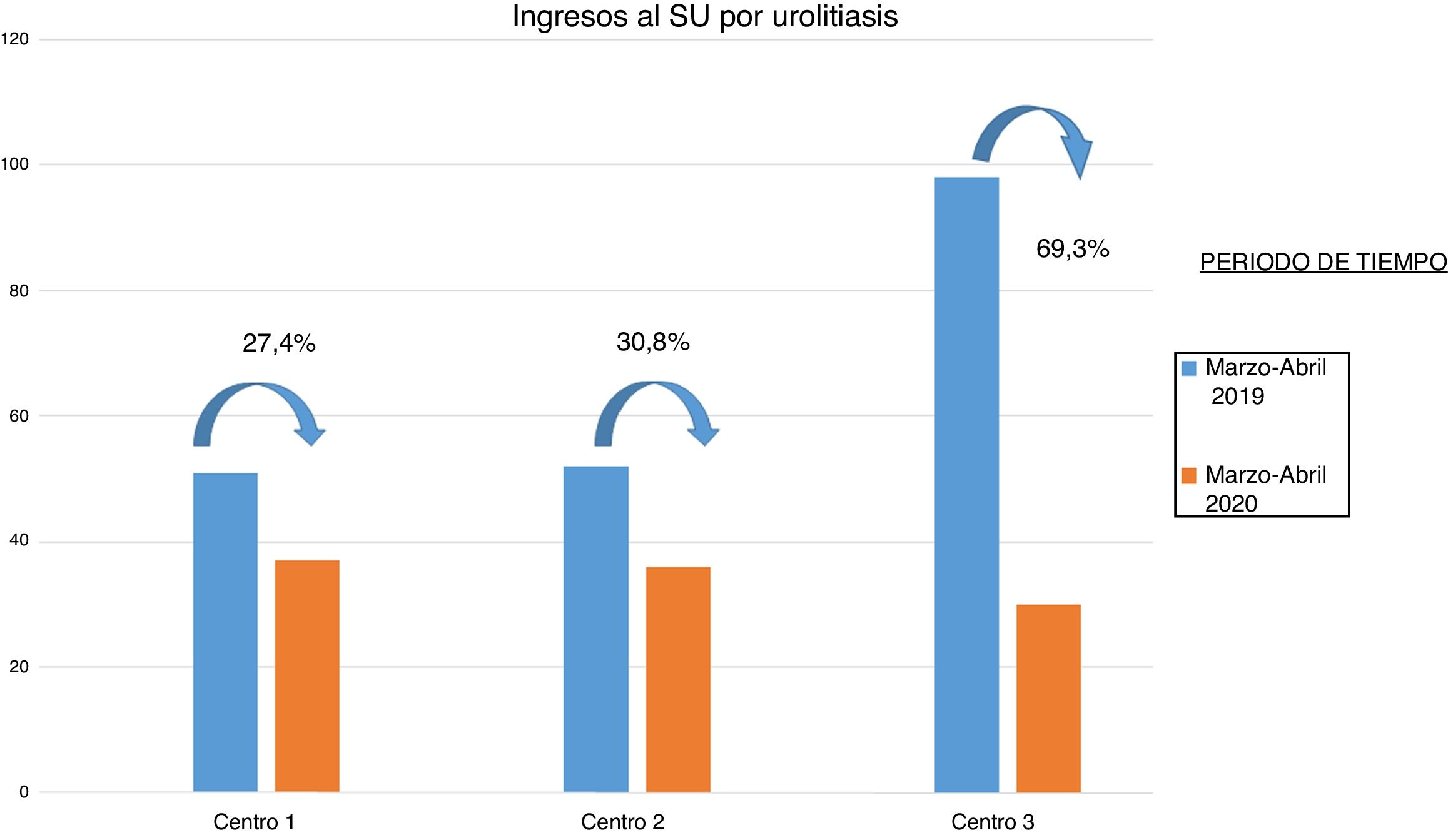
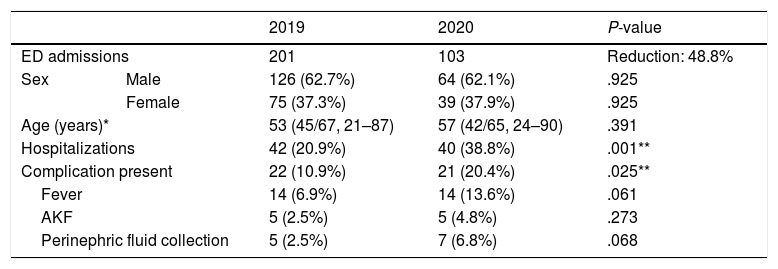
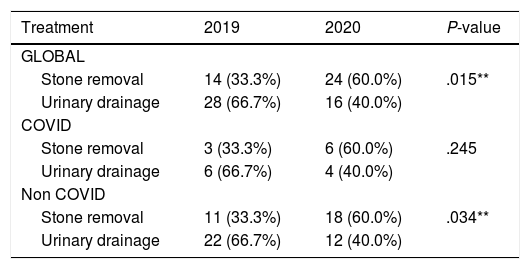
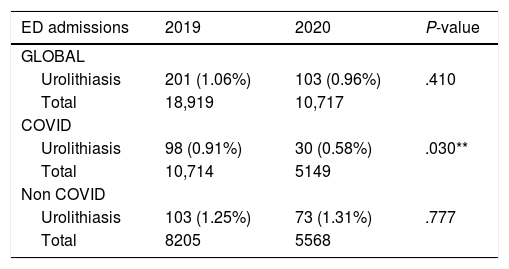
Results304 patients were included in the analysis. A significant reduction in the global number of patients admitted to ED for urolithiasis between 2019 and 2020 (48.8%) was noted. Moreover, regarding the choice of treatment of hospitalized patients, a statistically significant increase of stone removal procedures versus urinary drainage was reported in 2020 (P = .015).
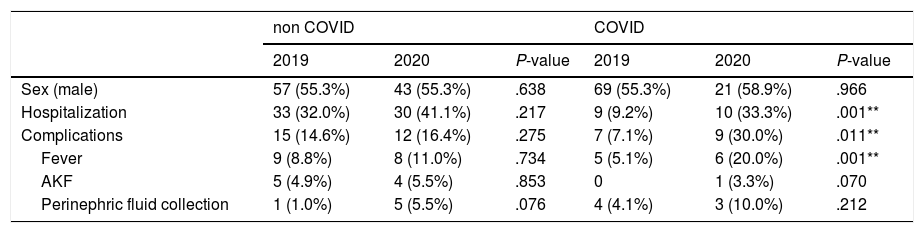
ConclusionsDuring the COVID-19 pandemic in Rome there has been a significant reduction of emergency admissions for urolithiasis. Patients admitted to ED had more complications, more frequently need hospitalization and regarding clinical management early stone removal was preferred over urinary drainage only. All the urologists should be aware that in the next months they could face an increased number of admissions for urolithiasis and manage more complicated cases.
Nuestro objetivo fue evaluar el impacto de la enfermedad del coronavirus de 2019 (COVID-19) en los ingresos en los servicios de urgencias (SU), las hospitalizaciones y el manejo clínico de los pacientes con urolitiasis.
Pacientes y métodosRealizamos un análisis retrospectivo multicéntrico de las admisiones en los servicios de urgencias de tres departamentos de urología de gran volumen (uno directamente implicado en el tratamiento de los pacientes de COVID-19 y dos no implicados) en Roma (Italia) entre marzo y abril de 2020 y en el mismo período de 2019. Se realizó un análisis estadístico del número de admisiones por urolitiasis, la tasa de complicaciones, hospitalización y el tipo de tratamiento recibido.
Resultados304 pacientes fueron incluidos en el análisis. Se observó una reducción significativa en el número global de pacientes ingresados en urgencias por urolitiasis entre 2019 y 2020 (48,8%). Además, con respecto a la elección del tratamiento de los pacientes hospitalizados, se informó un aumento estadísticamente significativo de los procedimientos de extracción de cálculos en comparación con el drenaje urinario en 2020 (P = ,015).
ConclusionesDurante la pandemia de COVID-19 en Roma ha habido una reducción significativa de los ingresos en urgencias por urolitiasis. Los pacientes ingresados en el SU tuvieron más complicaciones, necesitaron hospitalización con mas frecuencia y en cuanto al manejo clínico, se prefirió la extracción temprana de los cálculos en vez del drenaje urinario. Todos los urólogos deben ser conscientes de que en los próximos meses podrían enfrentarse a un mayor número de admisiones por urolitiasis y al manejo de casos más complicados.