The classical teaching methodology was based on passive transmission-based learning. The model has changed toward an orientation based on student-centered learning.
ObjectiveThe objective of the study has been to evaluate the students’ perception when learning about urinary tract infections, and their perspective about the teaching imparted on this pathology in the various subjects that include ITU in their syllabus.
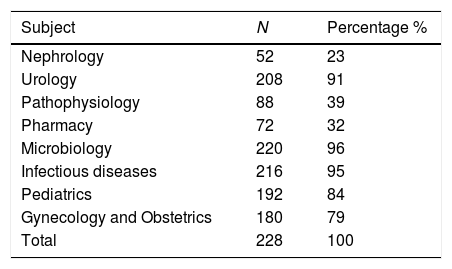
MethodsA cross-sectional analytical study of the responses to an anonymous survey entitled: “Methodology on urine infections. Teaching aspects” issued by 228 students at their fifth year of Medical School, from two promotions. They referred to the following subjects: Pharmacy, Pathophisiology, Gynecology and Obstetrics, Infectious diseases, Microbiology, Nephrology, Pediatrics and Urology.
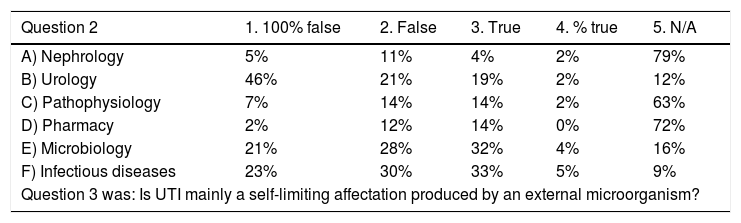
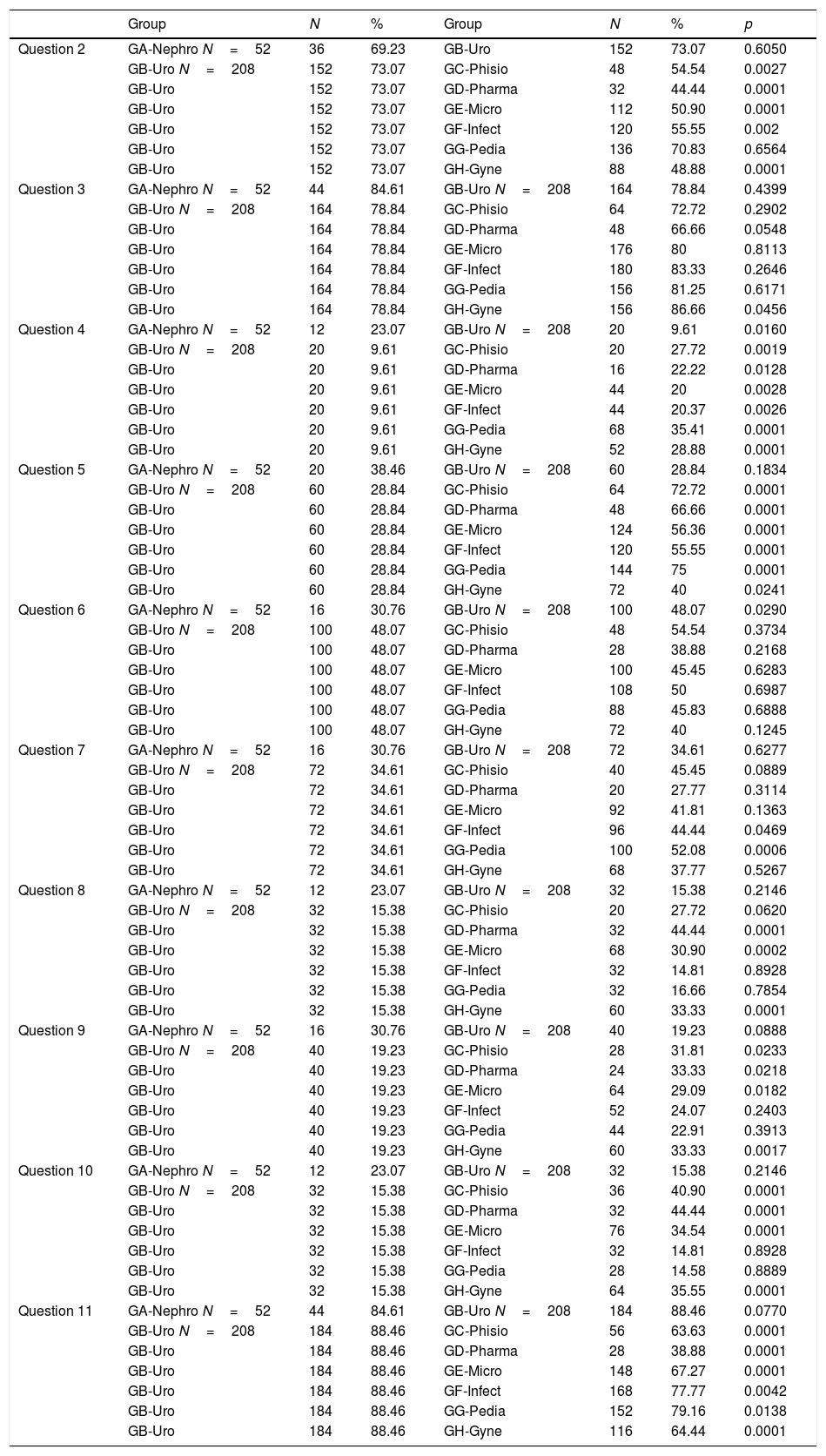
ResultsThe following variables have been analyzed: teaching content, teaching basic aspects of the disease, consideration of teaching methodology and improvement suggestions. Descriptive and inferential statistics were used.
ConclusionThe study has concluded that teaching urinary tract infection is perceived in specific subjects related to microorganism (Microbiology), the target organ (Infectious diseases, Urology), affected patients (Pediatrics, Gynecology and Obstetrics) rather than transversal subjects such as Pathophysiology or Pharmacy. The teaching methodology has been considered appropriate by more than 50% of the students in five from the 8 subjects that teach the concept of urinary tract infection. The students suggest convenient changes in current teaching methodology in several subjects that impart the urinary tract infection concept.
La metodología docente clásica se basaba en la transmisión pasiva de contenidos. El modelo ha cambiado hacia una orientación basada en que el eje del sistema enseñanza-aprendizaje es el alumno.
ObjetivoEl objetivo del estudio es evaluar la percepción del aprendizaje relacionado con las infecciones del tracto urinario que tienen los propios alumnos, y su perspectiva acerca de la docencia impartida sobre esta patología en las diferentes asignaturas que incluyen en su temario la ITU.
MétodosSe realiza un estudio analítico transversal de las respuestas a una encuesta anónima titulada: «Metodología sobre las infecciones de orina. Aspectos docentes» emitidas por 228 alumnos de quinto curso del Grado de Medicina de dos promociones. Se refirieron a las asignaturas de Farmacia, Fisiopatología, Ginecología y Obstetricia, Infecciosas, Microbiología, Nefrología, Pediatría y Urología.
ResultadosSe analizan variables sobre aspectos del contenido docente, docencia de aspectos básicos del problema, consideración sobre la metodología docente y sugerencias de cambio de la misma. Se utiliza estadística descriptiva e inferencial.
ConclusiónEl estudio concluye que la docencia en la infección del tracto urinario se percibe más en asignaturas concretas relativas al microorganismo (Microbiología), el órgano diana (Infecciosas, Urología), pacientes afectados (Pediatría, Ginecología y Obstetricia) que en asignaturas transversales como la Fisiopatología o Farmacia. La metodología docente se considera la apropiada en más del 50% de los alumnos en cinco de las 8 asignaturas que imparten el concepto de infección del tracto urinario. Los alumnos sugieren la conveniencia de cambios en la metodología docente en varias asignaturas que imparten el concepto de infección del tracto urinario.