Bladder pain syndrome/interstitial cystitis (BPS/IC) and other bladder pathologies share common manifestations, such as the presence of mictional symptoms and a negative impact on the patient's quality of life. To be properly diagnosed and clinically managed, it is important to distinguish between its clinical modalities and diagnostic criteria for adequate exclusion.
ObjectiveThe purpose of this study was to standardize criteria for making decisions in BPS management, for its diagnosis, initial treatment and follow-up.
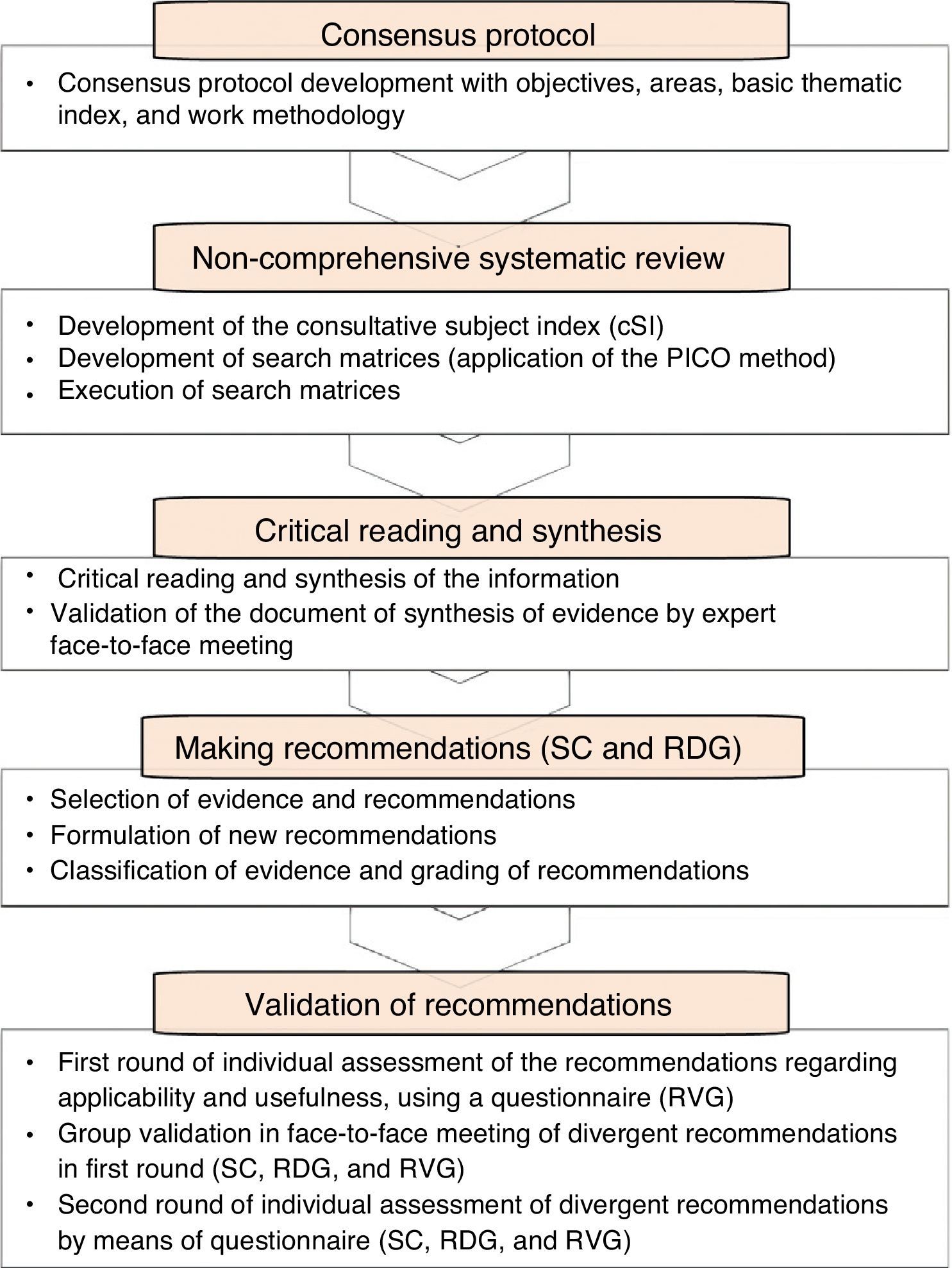
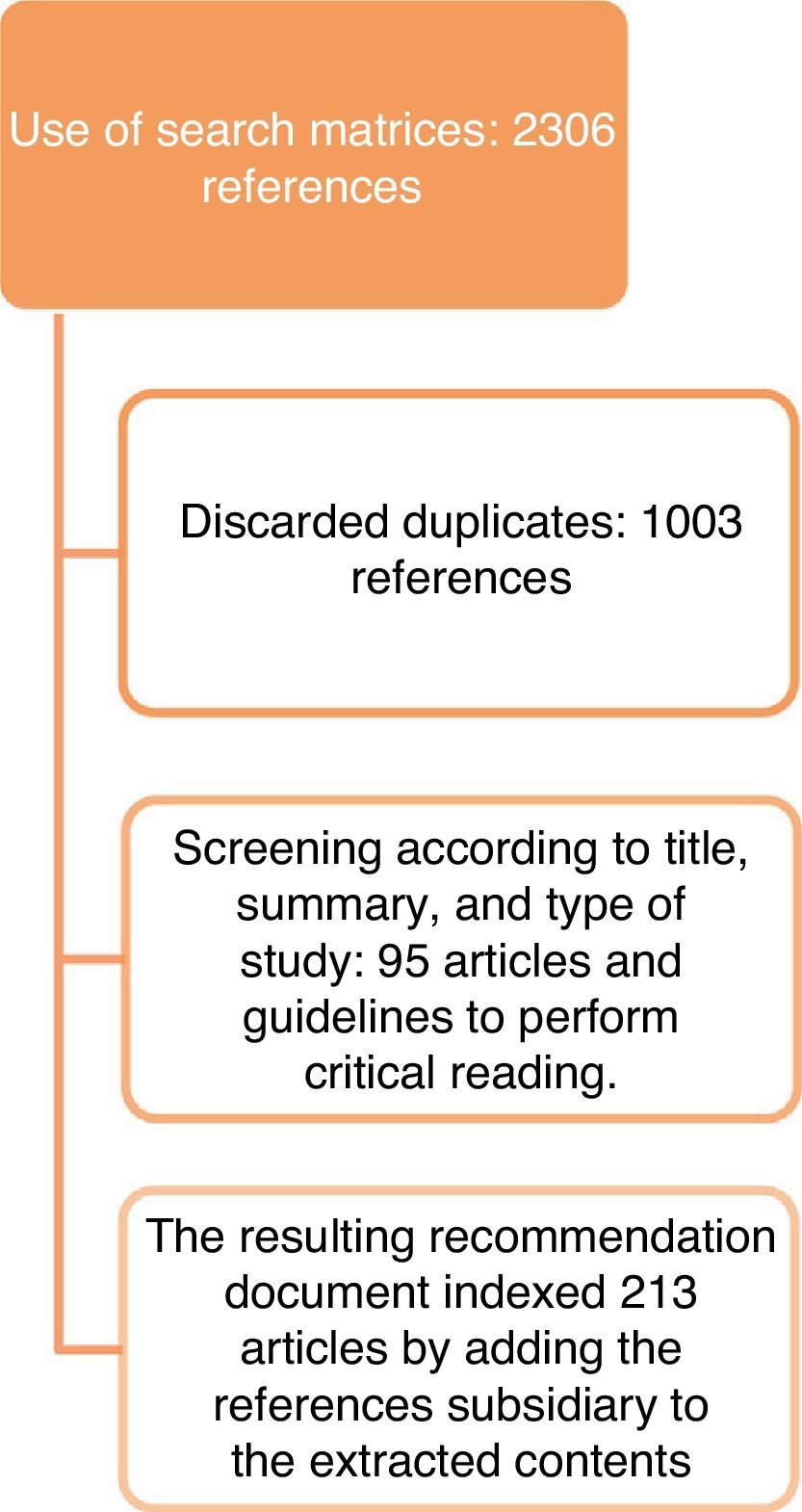
Material and methodA nominal group methodology was employed, using scientific evidence on BPS taken from a systematic (non-exhaustive) literature review for developing recommendations along with specialist expert opinions.
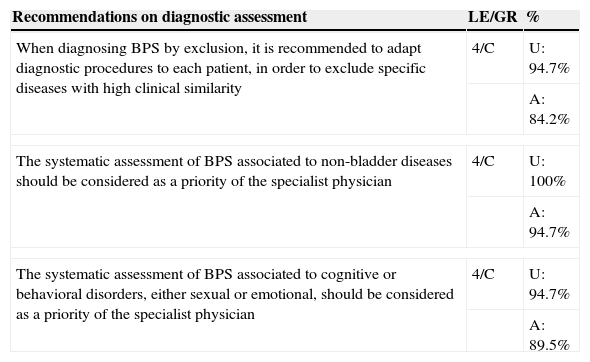
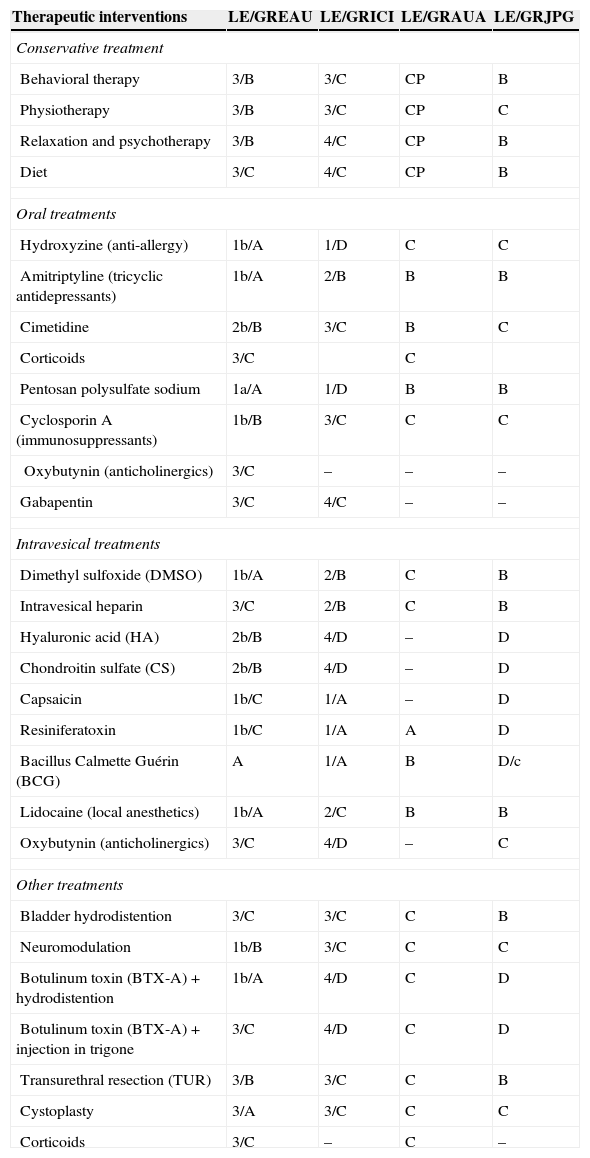
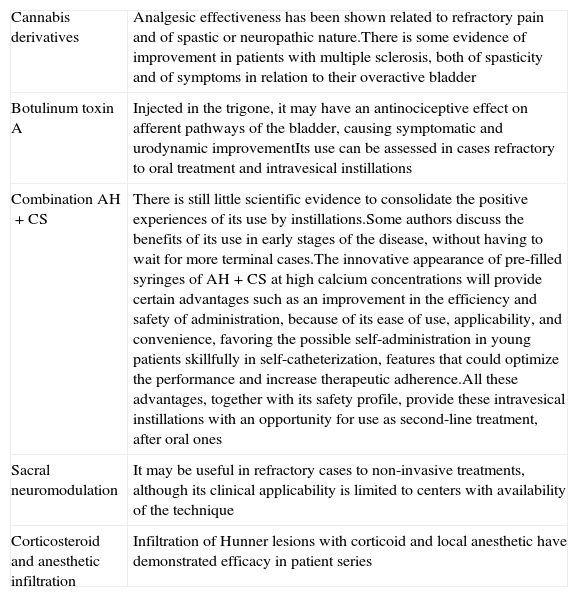
ResultsThe diagnosis of BPS should be made based on the patient's clinical history, with emphasis on pain and mictional symptoms as well as excluding other pathologies with similar symptomatology. BPS treatment should be directed toward restoring normal bladder function, preventing symptom relapse and improving patients’ quality of life. It is therefore advisable to start with conservative treatment and to adopt less conservative treatments as the level of clinical severity increases. It is also recommended to abandon ineffective treatments and reconsider other therapeutic options.
ConclusionsQuickly identifying the pathology is important when trying to positively influence morbidity and care quality for these patients.
El síndrome de dolor vesical/cistitis intersticial (SDV/CI) y otras enfermedades vesicales comparten una sintomatología común, como la presencia de los síntomas miccionales y la repercusión negativa sobre la calidad de vida de los pacientes. Para su correcto diagnóstico y manejo clínico es importante distinguir entre sus diferentes modalidades clínicas y criterios diagnósticos de exclusión adecuados.
ObjetivoEl propósito de este trabajo ha sido homogeneizar los criterios para la toma de decisiones en el manejo del SDV, tanto en su diagnóstico y tratamiento inicial como en su seguimiento.
Material y métodoSe utilizó metodología de grupo nominal, utilizando para la elaboración de las recomendaciones las evidencias científicas sobre el SDV extraídas de una revisión sistemática (no exhaustiva) de la literatura, junto con el juicio experto de especialistas.
ResultadosEl diagnóstico del SDV debe hacerse basándose en la historia clínica del paciente, prestando importancia al dolor y a los síntomas miccionales y a la exclusión de otras enfermedades de sintomatología parecida. El tratamiento del SDV debe dirigirse a la restauración de la función vesical normal, la prevención de recaídas de los síntomas y la mejora de la calidad de vida de los pacientes. Para ello es recomendable empezar con un tratamiento conservador y adoptar tratamientos menos conservadores conforme el nivel de gravedad clínica aumenta. También se recomienda abandonar tratamientos ineficaces y replantearse otras opciones terapéuticas.
ConclusionesLa rápida identificación de la enfermedad resulta importante para intentar influir positivamente en los indicadores de morbilidad y la calidad asistencial de estos pacientes.