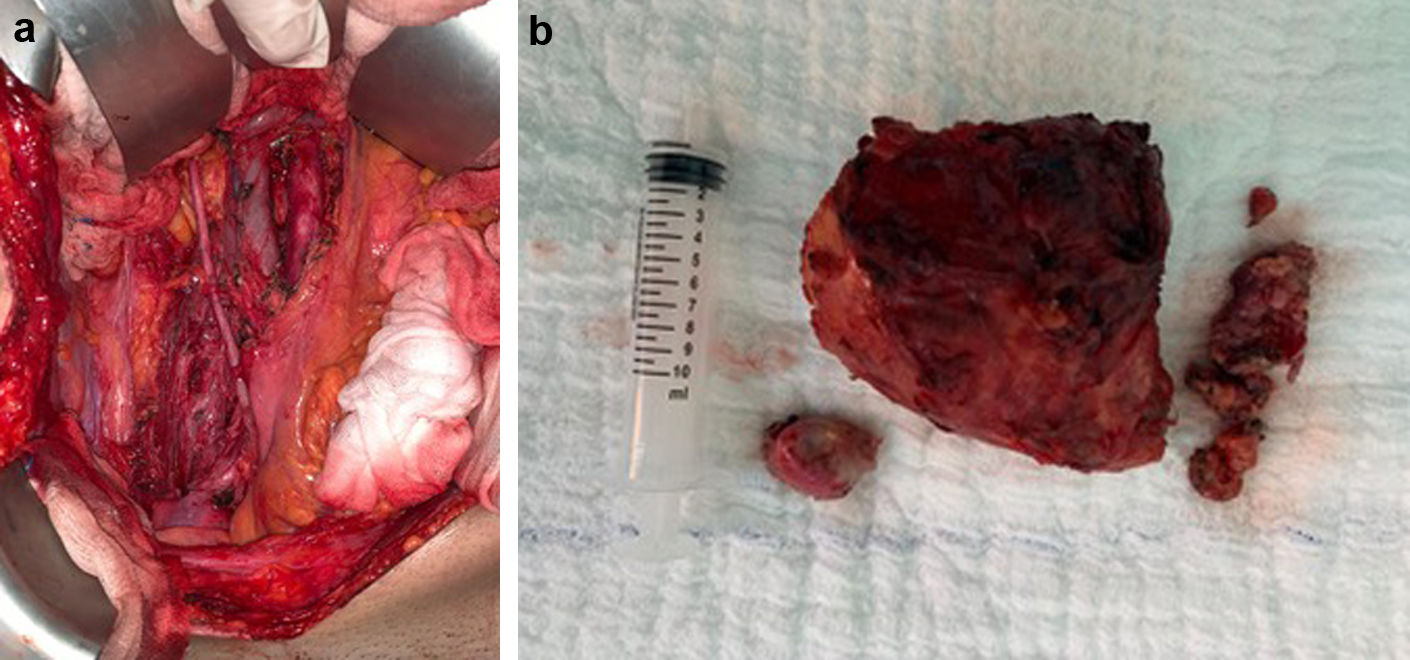
In this retrospective study, we aimed to evaluate lymph node (LN) density in retroperitoneal lymph node dissection (RPLND) to analyze whether residual mass after chemotherapy might behave as predicting factor for recurrence in patients with germ cell testicular cancer (GCTC).
Materials and methodsThe data of 185 patients that were operated between 12/2004 and 02/2017 because of GCTC were reviewed retrospectively. LN density was calculated. The patients were compared statistically in terms of demographic features, tumor characteristics, serum tumor marker levels, treatment strategies, and pathological results according to GCTC subtypes. Correlation analysis was performed to determine the parameters related to recurrent disease.
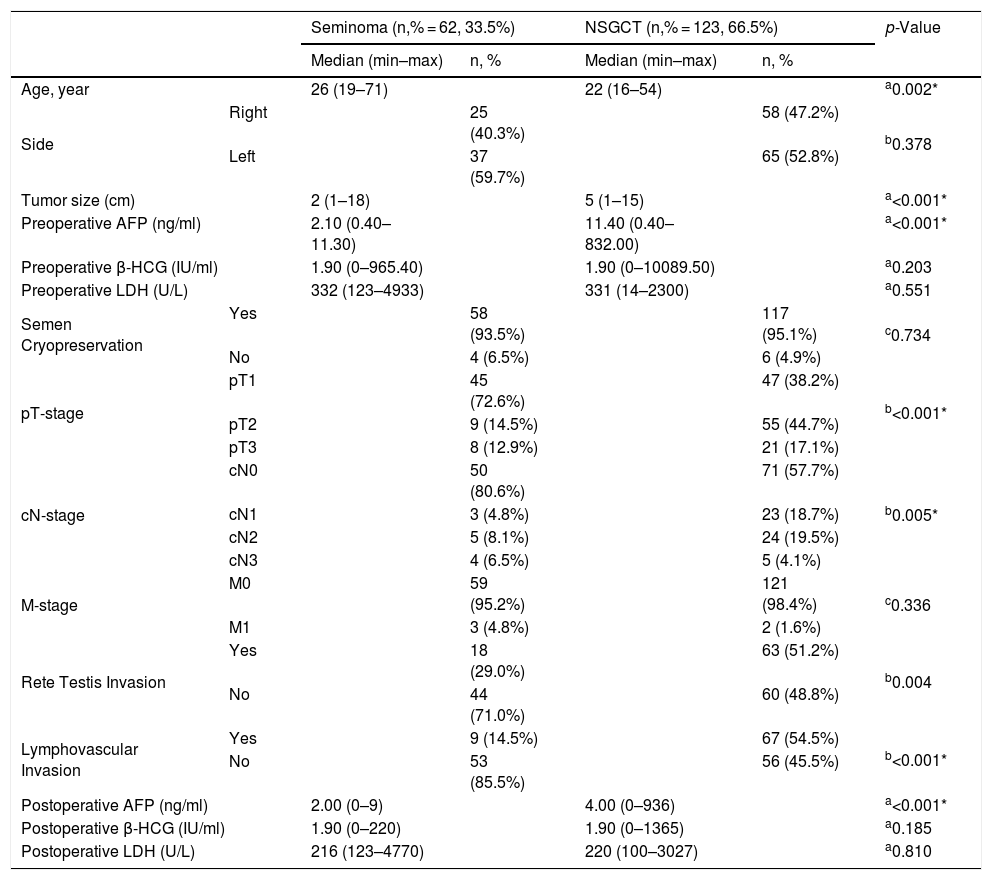
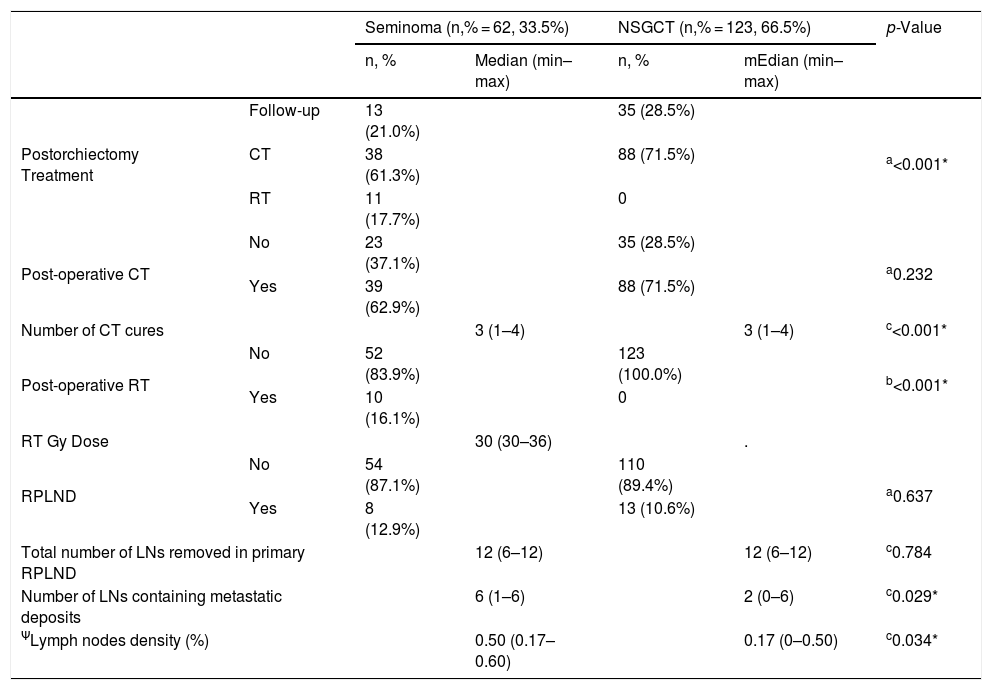
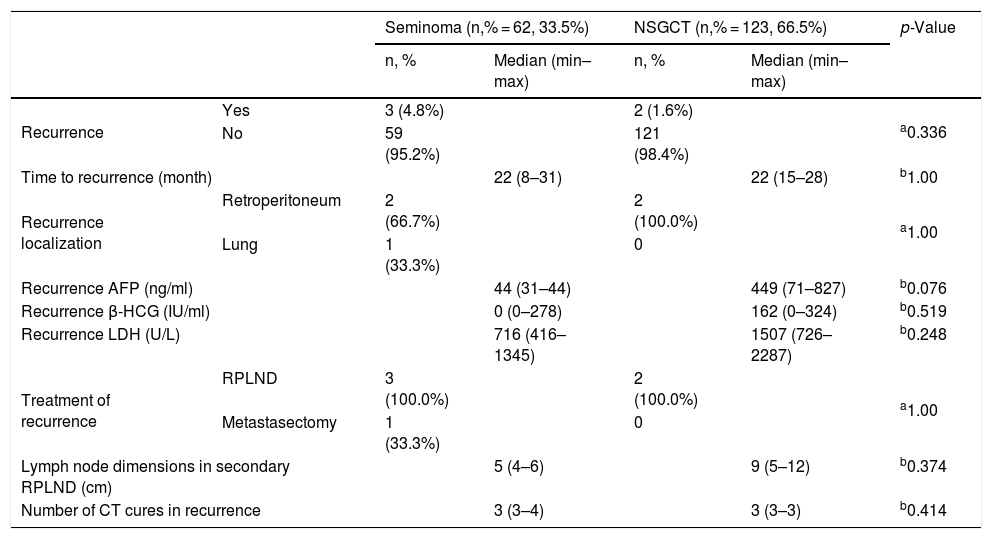
ResultsThe median follow-up was 79 (31–179) months and the median age of the patients was 23 (16–71). The median tumor size was 4 (1–18) cm. Five (2.7%) patients had metastatic disease at initial diagnosis. Seminoma, non-seminomatous-GCT and mix type-GCTC was detected in 62 (33.5%), 60 (32.4%) and 63 (34.1%) patients, respectively. Following inguinal orchiectomy, 48 (25.9%) patients underwent follow-up, 126 (68.1%) patients underwent chemotherapy and 11 (5.9%) patients underwent radiotherapy. A total of 21 (11.4%) patients underwent post-chemotherapy RPLND. Early and late recurrence was seen in 3 (1.6%) and 2 (1.1%) of the patients, respectively. A mild to moderate, negative, but significant correlation was found between the recurrence and the number of LNs containing metastatic deposits and LN density (r = −0.490, p = 0.024 and r = −0.450, p = 00.041, respectively).
ConclusionsThere was a negative correlation between the number of LNs containing metastatic deposits and LN density and recurrent disease.
El objetivo de este estudio retrospectivo fue analizar la densidad de los ganglios linfáticos (GL) en la disección de los ganglios linfáticos retroperitoneales (DGLRP) para evaluar la masa residual tras quimioterapia como factor predictivo de recurrencia en pacientes con cáncer testicular de células germinales (CTCG).
Materiales y métodosSe revisaron retrospectivamente los datos de 185 pacientes operados por CTCG entre dic. 2004 y feb. 2017. Se calculó la densidad de los GL. Los pacientes se compararon estadísticamente en términos de características demográficas, características tumorales, niveles de marcadores tumorales séricos, estrategias de tratamiento y resultados patológicos según los subtipos de CTCG. Se realizó un análisis de correlación para determinar los parámetros relacionados con la enfermedad recurrente.
ResultadosLa mediana de seguimiento fue de 79 (31–179) meses y la mediana de edad de los pacientes fue de 23 (16–71). El tamaño medio del tumor fue de 4 (1–18) cm. Cinco (2,7%) pacientes tenían enfermedad metastásica en el momento del diagnóstico inicial. Se detectó seminoma, TCG no seminomatoso y CTCG de tipo mixto en 62 (33,5%), 60 (32,4%) y 63 (34,1%) pacientes, respectivamente. Tras la orquiectomía inguinal, 48 (25,9%) pacientes recibieron seguimiento, 126 (68,1%) pacientes se sometieron a quimioterapia y 11 (5,9%) pacientes recibieron radioterapia. Un total de 21 (11,4%) pacientes se sometieron a DGLRP postquimioterapia. Se observó recurrencia precoz y tardía en 3 (1,6%) y 2 (1,1%) pacientes, respectivamente. Se encontró una correlación negativa leve/moderada, pero significativa, entre la recurrencia y el número de GL con depósitos metastásicos y la densidad de los GL (r = −0.490, p = 0.024 and r = −0.450, p = 00.041, respectivamente).
ConclusionesHubo una correlación negativa entre el número de GL con depósitos metastásicos y la densidad de GL con la enfermedad recurrente.