For bladder pain syndrome (BPS) refractory to conservative treatment, the European guidelines consider bladder hydrodistention (HD) under anesthesia and the injection of Onabotulinumtoxin A (OnabotA) jointly. The objective of this study was to assess our experience in implementing this technique.
Material and methodsA prospective study of 25 patients with BPS who underwent HD plus a submucosal injection of 100U of OnabotA in trigone. The Hunner lesions were treated endoscopically using resection or electrocoagulation. Thirty-eight procedures were performed (25 first interventions and 13 reoperations). To study the clinical change, we evaluated the subjective improvement (Treatment Benefit Scale [TBS] and Patient Global Impression of Change [PGIC] scales), the visual analog scale (VAS) for pain, the Bladder Pain/Interstitial Cystitis Symptom Score (BPIC-SS) questionnaire and the voiding diary for 3 days. For the data analysis, we employed the Wilcoxon, Kruskal–Wallis, Kaplan–Meier and log-rank tests.
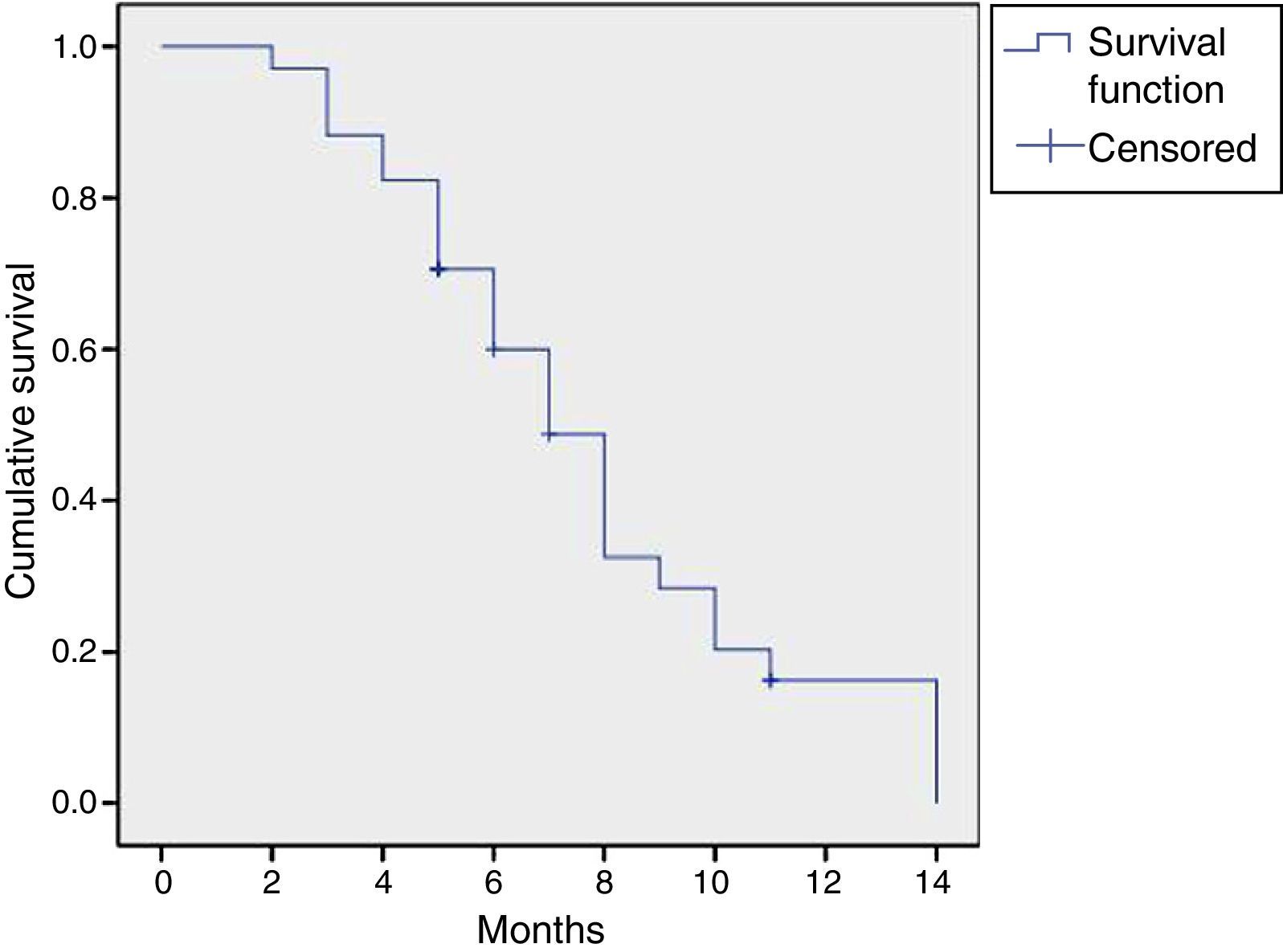
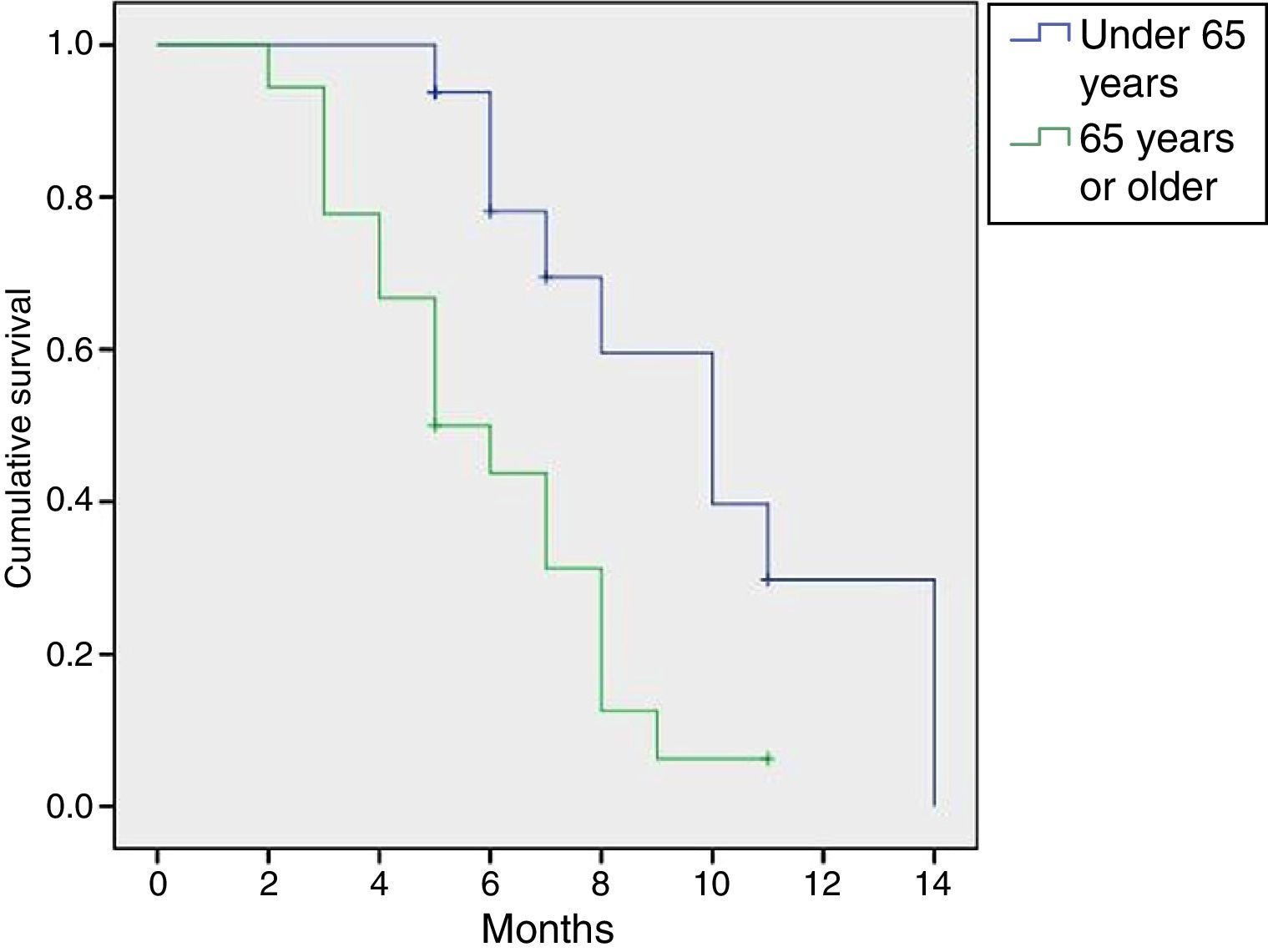
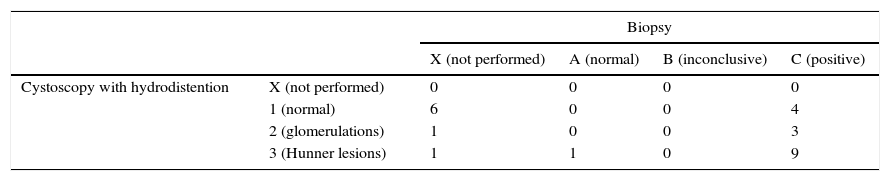
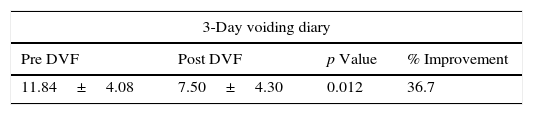
ResultsWe observed subjective improvement in 21 patients (84%), which was significant in 47% of these patients, moderate in 41.2% and slight in 11.8%. Four patients did not improve. A post-treatment reduction in the pain VAS (from 7.1 to 1.8 points; p=.001), in daytime (from 11.8 to 7.5; p=.012) and night-time (from 5.9 to 3.6; p=.003) voiding frequency and in the BPIC-SS (from 27.9 to 11.2 points; p=.042). The degree of improvement was not related to age, the presence of bladder lesions or the treatment of relapses. The median duration of improvement was 7 months (95% CI: 5.69–8.31), although this duration was somewhat longer for the patients younger than 65 years. Mild complications occurred in 23.7% of the cases.
ConclusionsThe joint implementation of HD plus OnabotA is a valid therapeutic option in refractory BPS, which provides good clinical results and maintains its effectiveness in retreatments.
En el síndrome de dolor vesical (SDV) refractario a tratamientos conservadores, la guía europea contempla la hidrodistensión (HD) vesical bajo anestesia y la inyección de Onabotulinumtoxin A (OnabotA) de manera conjunta. El objetivo fue evaluar nuestra experiencia en la aplicación de la técnica.
Material y métodosEstudio prospectivo de 25 pacientes con SDV sometidos a HD más inyección submucosa de 100U de OnabotA en trígono. Las lesiones de Hunner fueron tratadas endoscópicamente mediante resección o electrocoagulación. Se realizaron 38 procedimientos (25 primeras intervenciones y 13 reintervenciones). Para estudiar la modificación clínica se evaluó la mejoría subjetiva (escalas TBS y PGIC), la escala visual analógica (EVA) para dolor, el cuestionario BPIC-SS y el diario miccional de 3 días. Para el análisis de datos se emplearon los test de Wilcoxon, Kruskal–Wallis, Kaplan–Meier y Log-Rank.
ResultadosObservamos mejoría subjetiva en 21 pacientes (84%), en 47% de ellos mejoría importante, en 41,2% moderada y en 11,8% leve. No hubo mejoría en 4 pacientes. Se objetivó una reducción postratamiento en la EVA de dolor (de 7,1 a 1,8 puntos; p=0,001), en la frecuencia miccional diurna (de 11,8 a 7,5; p=0,012) y nocturna (de 5,9 a 3,6; p=0,003) y en el cuestionario BPIC-SS (de 27,9 a 11,2 puntos; p=0,042). El grado de mejoría no tuvo relación con la edad, con la presencia de lesiones vesicales ni con el tratamiento de las recaídas. La mediana en la duración de la mejoría fue de 7 meses (IC 95%: 5,69-8,31) de manera global, aunque en los pacientes menores de 65 años fue algo mayor. Se produjeron complicaciones leves en el 23,7% de los casos.
ConclusionesLa realización conjunta de HD más inyección de OnabotA es una opción terapéutica válida en el SDV refractario, con buenos resultados clínicos y manteniendo la efectividad en los retratamientos.