The short-term results of endoscopic treatment of vesicoureteral reflux (VUR) are excellent. Over time, however, a number of patients have been identified for whom VUR reappeared after being resolved with this technique. The aim of this study was to analyze the factors related to this event.
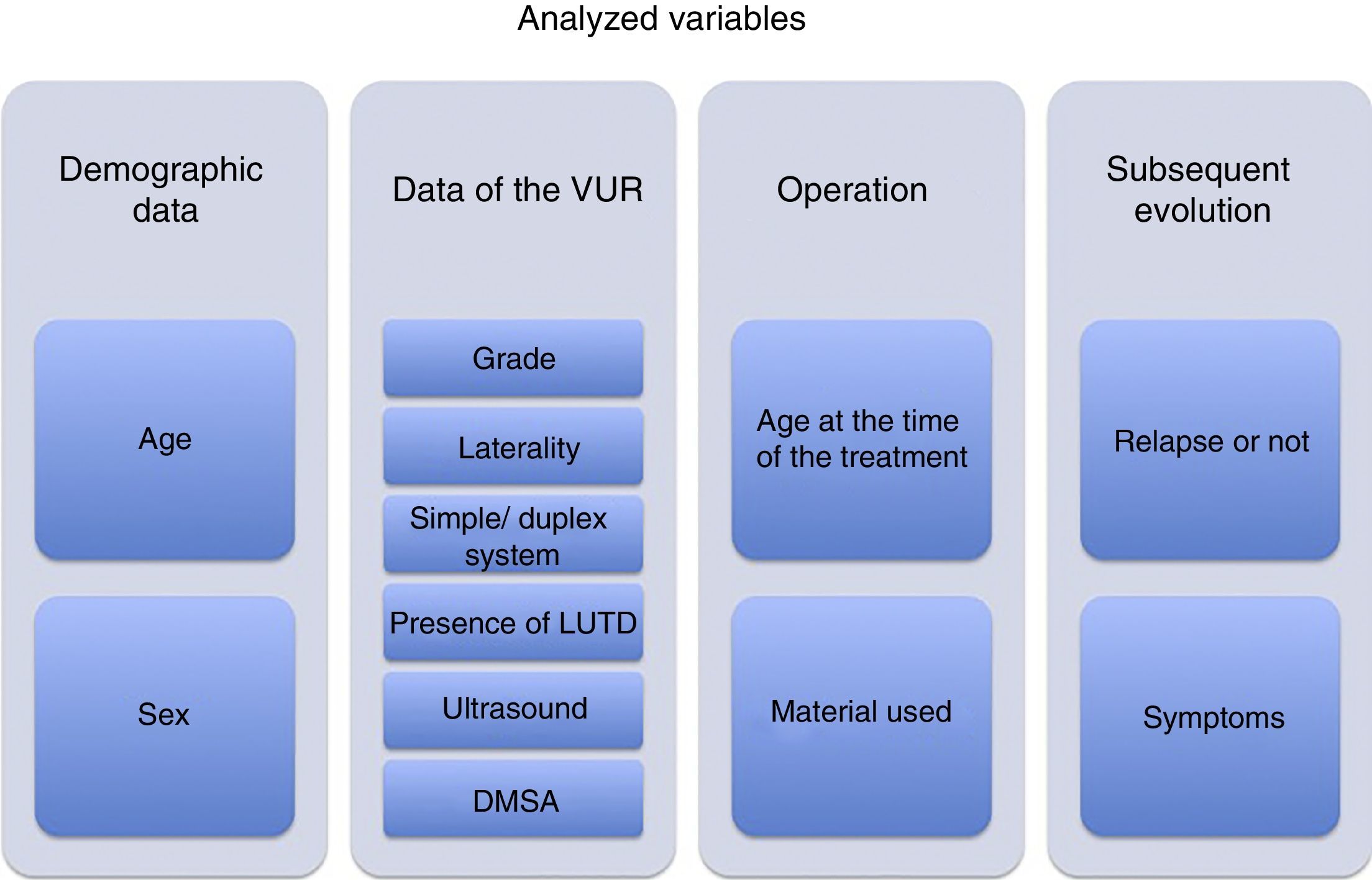
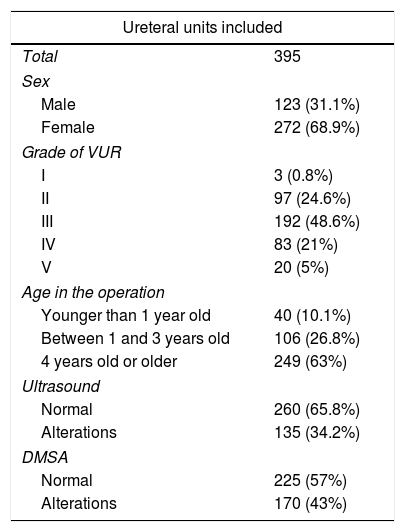
Material and methodsA retrospective, analytical, case–control study included 395 ureteral units with primary VUR treated successfully at our center, with a minimum follow-up of 3 years. We identified cases in which VUR reappeared and analyzed the demographic variables, those related to VUR (grade, laterality, initial study) and those related to the operation (materials used).
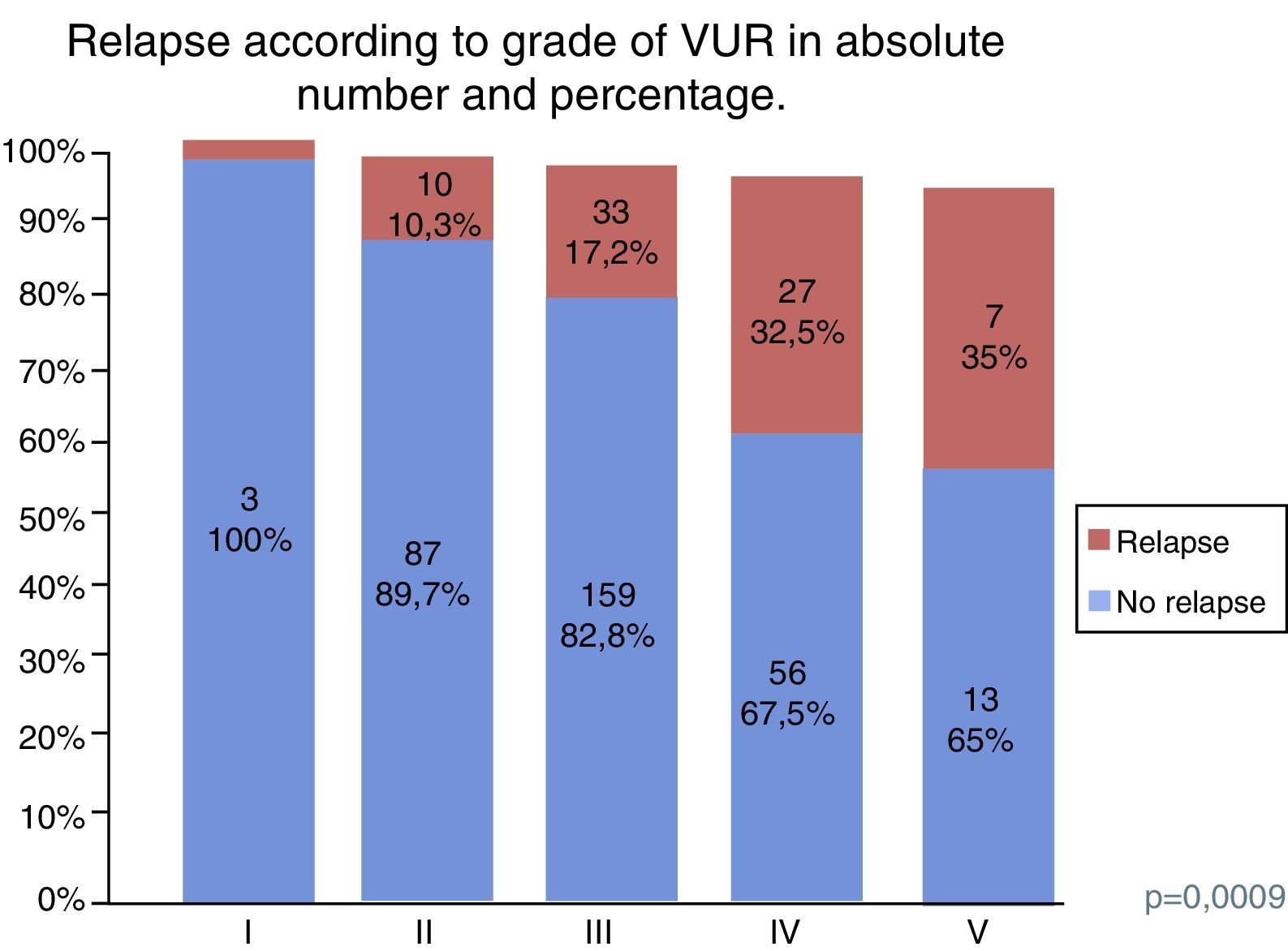
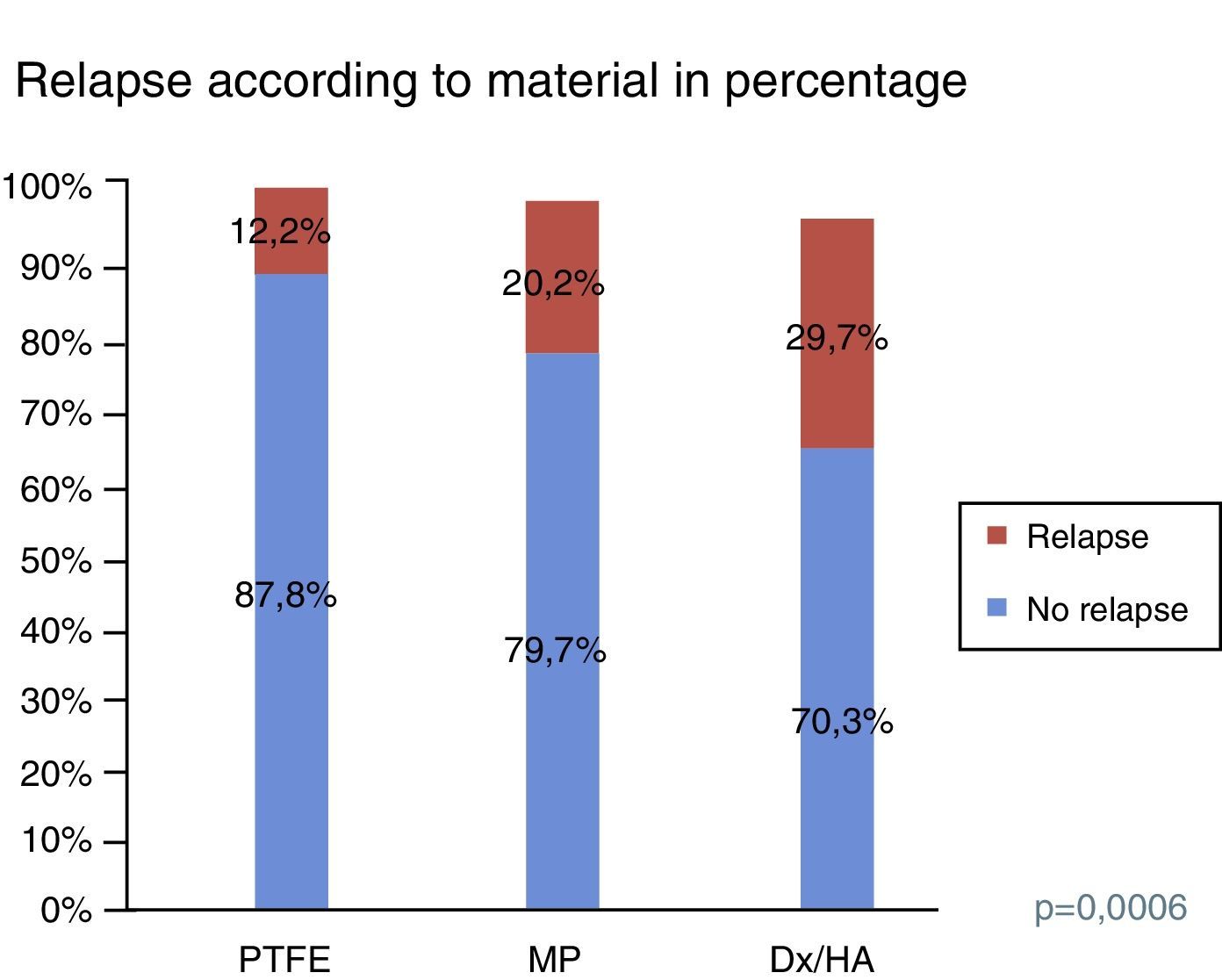
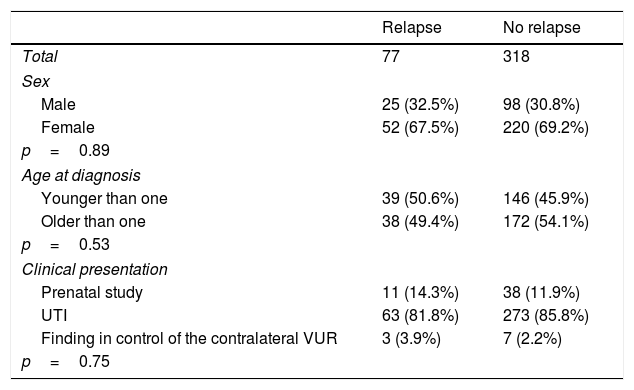
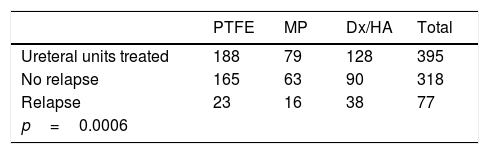
ResultsWe identified 77 ureteral units with recurrence in the 395 included units (19.5%). The recurrence rate was 29.7% for the patients treated with dextranomer/hyaluronic acid (Dx/HA), 20.2% for those treated with polydimethylsiloxane (MP) and 12.2% for polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE). The onset of recurrence rose to 35% for patients treated before 1 year of age and those with grade V VUR. Urinary dysfunction symptoms also increased the recurrence rate to 34.9%.
ConclusionThe use of resorbable dextranomer/hyaluronic acid material was related to recurrence in the endoscopic treatment of VUR. The high-grade reflux and treatment at an early age, as well as the presence of urinary dysfunction, are also factors associated with recurrence.
Los resultados del tratamiento endoscópico del reflujo vesicoureteral (RVU) a corto plazo son excelentes. No obstante, con el paso de los años se ha identificado un número de pacientes en quienes el RVU que fue resuelto mediante esta técnica vuelve a aparecer. El objetivo de este trabajo es analizar los factores relacionados con este evento.
Material y métodosSe ha realizado un estudio analítico retrospectivo tipo caso-control incluyendo 395 unidades ureterales con RVU primario tratadas con éxito en nuestro centro, con seguimiento mínimo de 3 años. Se han identificado los casos en los que el RVU reapareció y se han analizado variables demográficas, variables relativas al RVU (grado, lateralidad, estudio inicial) y a la intervención (material utilizado).
ResultadosSe identificaron 77 unidades ureterales con recidiva de las 395 incluidas (19,5%). La incidencia de recidiva fue del 29,7% en los pacientes tratados con dextranómero/ácido hialurónico (Dx/HA), del 20,2% en los tratados con polidimetilxilosano (MP) y del 12,2% en el caso de politetrafluoroetileno (PTFE). La aparición de recidiva se eleva hasta el 35% en el caso de pacientes tratados antes del año de edad y aquellos con RVU de grado V. La clínica de disfunción miccional también eleva la incidencia de recidiva al 34,9%.
ConclusiónEl uso del material reabsorbible Dx/HA está relacionado con la recidiva del tratamiento endoscópico del RVU. Los reflujos de alto grado, junto con el tratamiento en edades precoces, así como la presencia de disfunción miccional, también son factores asociados a la recurrencia.